 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 What is the Diff algorithm in React? Strategy and implementation of Diff algorithm
What is the Diff algorithm in React? Strategy and implementation of Diff algorithm
What is the Diff algorithm in React? Strategy and implementation of Diff algorithm
The content of this article is about what is the Diff algorithm in React? The strategy and implementation of the Diff algorithm have certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
1. What is Diff algorithm
Traditional Diff: diff algorithm is the difference search algorithm; for Html DOM structure, it is the difference search of tree Algorithm; and the time complexity of calculating the difference between two trees is O(n^3), which is obviously too expensive and it is impossible for React to adopt this traditional algorithm;
React Diff:
As mentioned before, React uses virtual DOM technology to map the real DOM, that is, the difference search of the React Diff algorithm is essentially to compare two JavaScripts Object difference search;
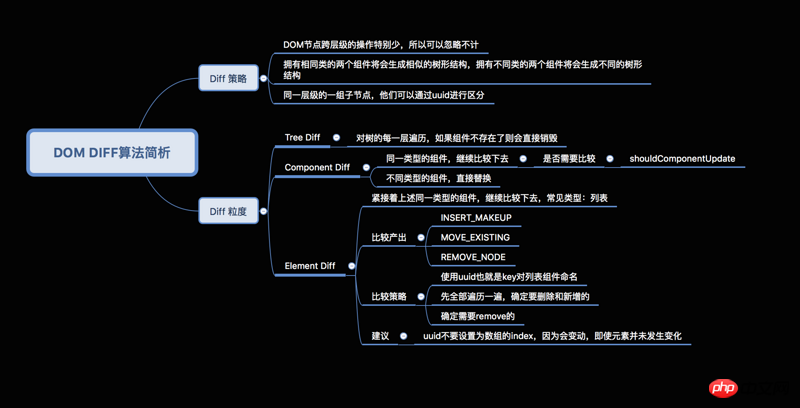
Based on three strategies:
Cross-level movement operation of DOM nodes in Web UI Very small and can be ignored. (tree diff)
Two components with the same class will generate similar tree structures, and two components with different classes will generate different tree structures (component diff )
For a group of child nodes at the same level, they can be distinguished by a unique id. (element diff)
2. Interpretation of React Diff algorithm
First of all, it needs to be clear that Diff will only occur during the React update phase Application of algorithm;
React update mechanism:
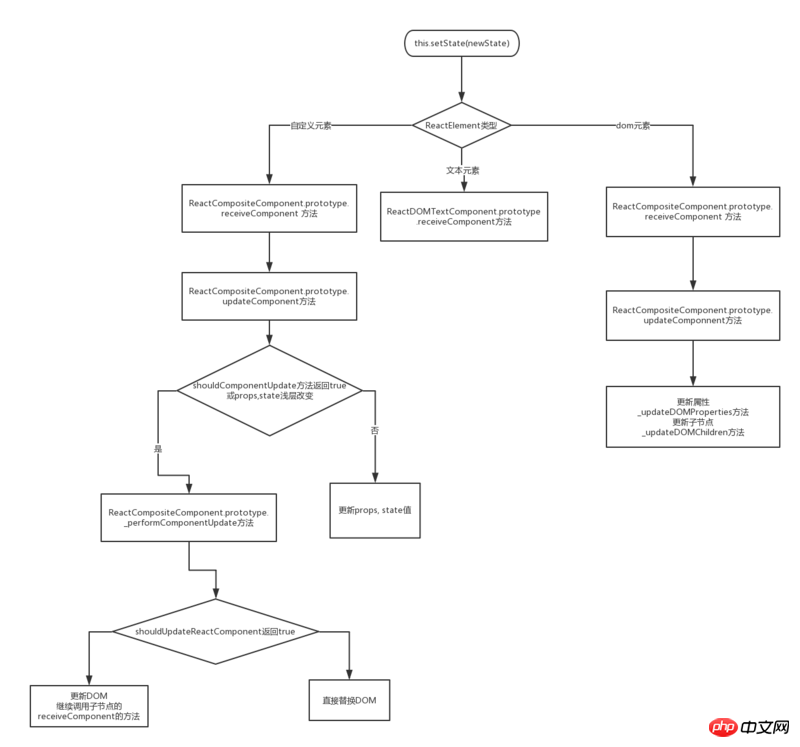
- ##React Diff algorithm optimization strategy chart:
- ##React The update phase will determine the ReactElement type and perform different operations; ReactElement types include three types: text, Dom, and components;
- Element update processing methods of each type:
- Updating the text node is very simple, just update the copy directly.
- The update of basic elements of the browser is divided into two parts:
- The update of custom elements is mainly to update the rendered nodes, and the shopkeeper leaves it to the corresponding component of the rendered nodes to manage the updates.
- Update attributes, compare the before and after attributes Different, partial update. And handle special properties, such as event binding.
- The update of child nodes. The update of child nodes is mainly to find the difference objects. When looking for the difference objects, the above shouldUpdateReactComponent will also be used to judge. If it can be updated directly, it will be recursive. Call the update of the child node, which will also find the difference object recursively. Deleting previous objects or adding new objects cannot be directly updated. Then operate the DOM element (position change, delete, add, etc.) according to the difference object.
- In fact, the Diff algorithm is only called during the DOM element update process in the React update phase;
- Why do you say that?
and the content is different, it will be updated and replaced directly without calling the complex Diff algorithm: ReactDOMTextComponent.prototype.receiveComponent(nextText, transaction) {
//与之前保存的字符串比较
if (nextText !== this._currentElement) {
this._currentElement = nextText;
var nextStringText = '' + nextText;
if (nextStringText !== this._stringText) {
this._stringText = nextStringText;
var commentNodes = this.getHostNode();
// 替换文本元素
DOMChildrenOperations.replaceDelimitedText(
commentNodes[0],
commentNodes[1],
nextStringText
);
}
}
}
class Tab extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
index: 1,
}
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
....
}
render() {
return (
<p>
</p><p>item1</p>
<p>item1</p>
- What needs to be clarified is what a component is. It can be said that a component is just a packaging container of an Html structure. , and has the ability to manage the status of this Html structure;
- For example, the above-mentioned Tab component: its essential content is the Html structure returned by the render function, and what we call the Tab class is The packaging container of this Html structure (can be understood as a packaging box);
- As you can see in the React rendering mechanism diagram, the custom component is finally combined with React Diff optimization strategy 1 ( Two components of different classes have different structures)
ReactDOMComponent.prototype.receiveComponent = function(nextElement, transaction, context) {
var prevElement = this._currentElement;
this._currentElement = nextElement;
this.updateComponent(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context);
}
ReactDOMComponent.prototype.updateComponent = function(transaction, prevElement, nextElement, context) {
//需要单独的更新属性
this._updateDOMProperties(lastProps, nextProps, transaction, isCustomComponentTag);
//再更新子节点
this._updateDOMChildren(
lastProps,
nextProps,
transaction,
context
);
// ......
}
- In this. The diff algorithm is called internally in the _updateDOMChildren method.
- 3. Implementation of Diff algorithm in React
_updateChildren: function(nextNestedChildrenElements, transaction, context) {
var prevChildren = this._renderedChildren;
var removedNodes = {};
var mountImages = [];
// 获取新的子元素数组
var nextChildren = this._reconcilerUpdateChildren(
prevChildren,
nextNestedChildrenElements,
mountImages,
removedNodes,
transaction,
context
);
if (!nextChildren && !prevChildren) {
return;
}
var updates = null;
var name;
var nextIndex = 0;
var lastIndex = 0;
var nextMountIndex = 0;
var lastPlacedNode = null;
for (name in nextChildren) {
if (!nextChildren.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
continue;
}
var prevChild = prevChildren && prevChildren[name];
var nextChild = nextChildren[name];
if (prevChild === nextChild) {
// 同一个引用,说明是使用的同一个component,所以我们需要做移动的操作
// 移动已有的子节点
// NOTICE:这里根据nextIndex, lastIndex决定是否移动
updates = enqueue(
updates,
this.moveChild(prevChild, lastPlacedNode, nextIndex, lastIndex)
);
// 更新lastIndex
lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex);
// 更新component的.mountIndex属性
prevChild._mountIndex = nextIndex;
} else {
if (prevChild) {
// 更新lastIndex
lastIndex = Math.max(prevChild._mountIndex, lastIndex);
}
// 添加新的子节点在指定的位置上
updates = enqueue(
updates,
this._mountChildAtIndex(
nextChild,
mountImages[nextMountIndex],
lastPlacedNode,
nextIndex,
transaction,
context
)
);
nextMountIndex++;
}
// 更新nextIndex
nextIndex++;
lastPlacedNode = ReactReconciler.getHostNode(nextChild);
}
// 移除掉不存在的旧子节点,和旧子节点和新子节点不同的旧子节点
for (name in removedNodes) {
if (removedNodes.hasOwnProperty(name)) {
updates = enqueue(
updates,
this._unmountChild(prevChildren[name], removedNodes[name])
);
}
}
}4. Development suggestions based on Diff
- When developing components based on tree diff:
- , pay attention to keeping the DOM structure stable; that is, dynamically operate the DOM structure as little as possible, especially mobile operations.
- When the number of nodes is too large or the page is updated too many times, the page lag will be more obvious.
- At this time, you can hide or show nodes through CSS instead of actually removing or adding DOM nodes.
:
Pay attention to using shouldComponentUpdate() to reduce unnecessary updates of components.
Similar structures should be encapsulated into components as much as possible, which not only reduces the amount of code, but also reduces the performance consumption of component diff.
Based on element diff:
For list structures, try to reduce the last The operation of moving nodes to the head of the list will affect React's rendering performance to a certain extent when the number of nodes is too large or the update operations are too frequent.
The above is the detailed content of What is the Diff algorithm in React? Strategy and implementation of Diff algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.



