Relevant introduction to Spring transaction management (with code)
This article brings you an introduction to Spring transaction management (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Transaction
A logical group of operations. Each part of the operation either succeeds or fails.
Characteristics of transactions
Consistency: The data integrity before and after the transaction remains consistent
Atomicity: The transaction cannot be divided, either all succeed or all fail
-
Isolation: The execution of a transaction is not affected by other transactions and is isolated from each other
Persistence: Once the transaction is completed, it will be saved to the database and is not affected by the system Impact of crash
Problems caused if the characteristics are not met
Problems caused by isolation:
Read the question
Dirty read: A transaction reads data that has not been committed by other transactions
Non-repeatable read: A transaction reads data submitted by other transactionsUpdate Data, resulting in inconsistent query results for multiple times
-
Phantom reading: One transaction reads insert data from another transaction, resulting in inconsistent query results for multiple times
Write problem
Lost operation
Solving the read problem
Set transaction isolation Level
int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1;
int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;
int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;
int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;
int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;ISOLATION_DEFAULT: Represents the spring default value, indicating that the default isolation level of the underlying database is used. For example, mysql uses ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ and uses ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED: Uncommitted read, cannot solve the read problem
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED: Committed read, can solve the dirty problem Read, cannot solve phantom reads and non-repeatable reads
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ: Repeated reads, can solve dirty reads and non-repeatable reads
- ##ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE: Can Solve all reading problems, the efficiency is not high
PlatformTransactionManager is an interface, used by the bottom layer of Spring Object to manage transactions. 
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}spring things official website addressThe more common implementation classes are:
- DataSourceTransactionManager: The bottom layer uses JDBC Transaction management
- HibernateTransactionManager: The bottom layer uses Hibernate transaction management
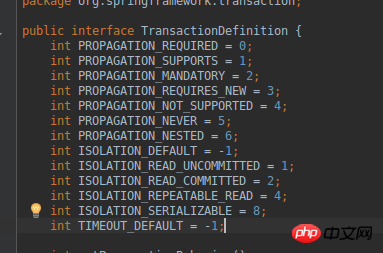
- TransactionDefinition:
Transaction definition: transactions can be defined Related information, transaction propagation behavior, isolation level, timeout information, whether read-only
package org.springframework.transaction;
//可以看到事物的定义也是一个接口
public interface TransactionDefinition {
//事物的传播行为,7种
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0;
int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1;
int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2;
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3;
int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4;
int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5;
int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6;
//事物的隔离级别五种
int ISOLATION_DEFAULT = -1;
int ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;
int ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;
int ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;
int ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;
//事物的超时时间,-1代表没有超时时间
int TIMEOUT_DEFAULT = -1;
int getPropagationBehavior();
int getIsolationLevel();
int getTimeout();
boolean isReadOnly();
String getName();
}- TransactionStatus: Transaction status
Transaction status: Record management transaction process Objects in transaction status
Official website portalPrecondition:
Call method A() in method B()
- PROPAGATION_NESTED: There is a transaction in A, and transaction A is executed normally. After the execution of transaction A is completed, set a save point and perform operation B. If B throws an exception, it can be rolled back to the initial position or rolled back to the save point.
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED in the transaction: If method B calls method A and method A has a transaction, method B will use the transaction in A. If there is no transaction in A, B will create a transaction
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS: B calls A. If there is a transaction in A, the transaction in A will be used. If there is no transaction in A, B will not use the transaction
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY: If A has a transaction, use the transaction in A. If there is no transaction in A, an exception will be thrown.
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW in the transaction: There is a transaction in A, suspend the A transaction, and the opened transaction of B only includes its own operations. There is no transaction in A, and the transaction created by B only contains its own operation
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED: There is a transaction in A, A is suspended, and B does not use the transaction
*PROPAGATION_NEVER: There is a transaction in A and B is thrown Exception
- Declarative transaction management: Process transactions declaratively in the Spring configuration file To replace code-based transaction processing (used more often)
- Programming transaction management: code-based transaction processing requires writing code in the programDeclarative transactions ManagementBased on xml
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="trancationManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!--配置事务-->
<tx:advice id="myAdvice" transaction-manager="trancationManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--配置事务传播和事务隔离-->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--事务是利用aop实现的-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="ponitcut" expression="execution(* com.amber.xml.service.AccountServiceImpl.transferMoney(..))"></aop:pointcut>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="myAdvice" pointcut-ref="ponitcut" />
</aop:config>基于注解
<!--配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="trancationManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" >
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" ></property>
</bean>
<!--开启注解事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="trancationManager" />使用tx:annotation-driven 开启事务的注解后,在使用的时候只需要在类或者方法上加入@Transactional就可以开启注解
基于xml的事务和基于注解的事务对比
文件配置对比
事务基于注解简化了xml中的使用比较
使用注解必须在类或者方法上添加@Trasactional,如果有多个业务类,则需要在每个业务类上添加
使用xml只需要在配置文件中配置包名即可
The above is the detailed content of Relevant introduction to Spring transaction management (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
In 2023, AI technology has become a hot topic and has a huge impact on various industries, especially in the programming field. People are increasingly aware of the importance of AI technology, and the Spring community is no exception. With the continuous advancement of GenAI (General Artificial Intelligence) technology, it has become crucial and urgent to simplify the creation of applications with AI functions. Against this background, "SpringAI" emerged, aiming to simplify the process of developing AI functional applications, making it simple and intuitive and avoiding unnecessary complexity. Through "SpringAI", developers can more easily build applications with AI functions, making them easier to use and operate.
 Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
As an industry leader, Spring+AI provides leading solutions for various industries through its powerful, flexible API and advanced functions. In this topic, we will delve into the application examples of Spring+AI in various fields. Each case will show how Spring+AI meets specific needs, achieves goals, and extends these LESSONSLEARNED to a wider range of applications. I hope this topic can inspire you to understand and utilize the infinite possibilities of Spring+AI more deeply. The Spring framework has a history of more than 20 years in the field of software development, and it has been 10 years since the Spring Boot 1.0 version was released. Now, no one can dispute that Spring
 What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
How to implement spring programmatic transactions: 1. Use TransactionTemplate; 2. Use TransactionCallback and TransactionCallbackWithoutResult; 3. Use Transactional annotations; 4. Use TransactionTemplate in combination with @Transactional; 5. Customize the transaction manager.
 How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
May 24, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
May 24, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
Java implements scheduled tasks In the library that comes with Jdk, there are two ways to implement scheduled tasks, one is Timer, and the other is ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor. When Timer+TimerTask creates a Timer, it creates a thread, which can be used to schedule TimerTask tasks. Timer has four construction methods, and you can specify the name of the Timer thread and whether to set it as a daemon thread. The default name is Timer-number, and the default is not a daemon thread. There are three main methods: cancel(): terminate task scheduling, cancel all currently scheduled tasks, running tasks will not be affected purge(): remove tasks from the task queue
 The differences and connections between Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Jun 22, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
The differences and connections between Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Jun 22, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
SpringBoot and SpringCloud are both extensions of Spring Framework that help developers build and deploy microservice applications faster, but they each have different purposes and functions. SpringBoot is a framework for quickly building Java applications, allowing developers to create and deploy Spring-based applications faster. It provides a simple, easy-to-understand way to build stand-alone, executable Spring applications
 The 7 most commonly used annotations in Spring, the most powerful organization in history!
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
The 7 most commonly used annotations in Spring, the most powerful organization in history!
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
With the update and iteration of technology, Java5.0 began to support annotations. As the leading framework in Java, spring has slowly begun to abandon xml configuration since it was updated to version 2.5, and more annotations are used to control the spring framework.
 How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set the transaction isolation level in Spring: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation; 2. Set it in the Spring configuration file; 3. Use PlatformTransactionManager; 4. Set it in the Java configuration class. Detailed introduction: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation, add the @Transactional annotation to the class or method that requires transaction management, and set the isolation level in the attribute; 2. In the Spring configuration file, etc.
 Learn Spring Cloud from scratch
Jun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
Learn Spring Cloud from scratch
Jun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
As a Java developer, learning and using the Spring framework is an essential skill. With the popularity of cloud computing and microservices, learning and using Spring Cloud has become another skill that must be mastered. SpringCloud is a development toolset based on SpringBoot for quickly building distributed systems. It provides developers with a series of components, including service registration and discovery, configuration center, load balancing and circuit breakers, etc., allowing developers to build micro




