
This article mainly introduces relevant information about examples of deformation, transition and animation of CSS summary notes. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
1. Transition transition
Transition property usage: transition :ransition-property transition-duration transition -timing-function transition-delay
can be specified together or separately
transition-property: is to be transitioned Properties (such as width, height), all are changed.
Transition-duration: the time spent, the unit is s or ms
transition-timing-function: specifies the animation type (motion area curve), the motion curve has the following types
ease=>Gradually slow down (default value) linear=>Constant speed ease-in=>Accelerate ease-out=>Decelerate ease-in-out=>Accelerate first and then decelerate
transition-delay delay time, unit is s or ms
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
transition: width 2s ease-in-out 0.5s;
}
p:hover {
width: 500px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>The results are as follows. When the mouse goes up, the change is no longer completed instantaneously, but the transition is completed.

2. Transformationtransform
(1), 2D deformation
(a) Move translate(x,y)
Movement can specify the pixel value or the percentage. Note: The specified percentage is the percentage of its own size, so it can be used Center alignment when setting the box positioning (set left: 50% and then move it by -50%).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
transition: all 2s;
}
p:active {
transform: translate(200px, 200px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
The box moved after clicking. The code used to center the positioned box is as follows
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.fa {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
transition: all 0.5s;
position: relative;
}
.son {
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
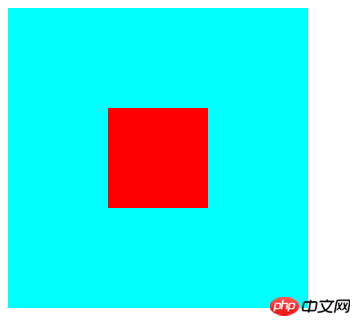
<p class="fa">
<p class="son"></p>
</p>
</body>
</html>The result is
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
margin: 200px auto;
transition: all 2s;
}
p:hover {
transform: scale(0.5, 2);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
</p>
</body>
</html>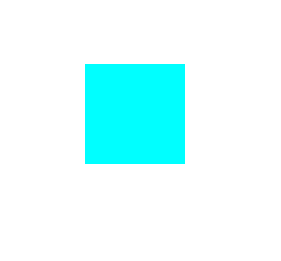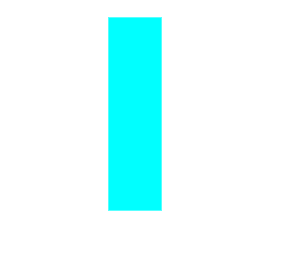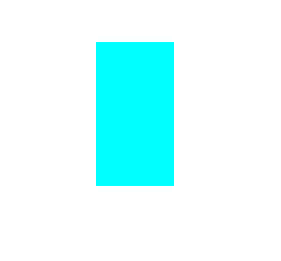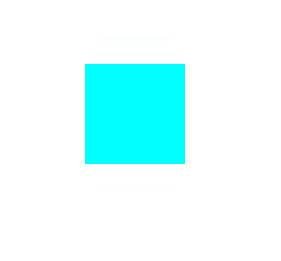
transform-origin to specify the rotation center point. Transform-origin can also specify specific pixel values for left top right bottom.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
margin: 200px auto;
transition: all 2s;
transform-origin: bottom left;
}
p:hover {
transform: rotate(120deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
border: 1px solid red;
transition: all 1s;
margin: 200px auto;
}
p:hover {
transform: skew(30deg, 20deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>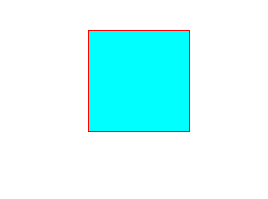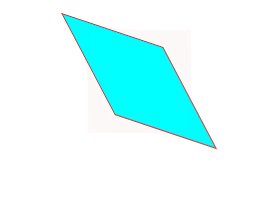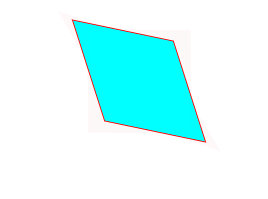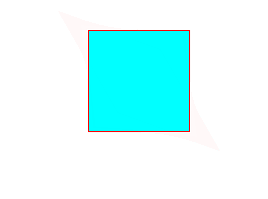
(2) 3D deformation
(a) Rotate (rotateX,rotateY,rotateZ) 3D rotation is similar to 2D, except that one is based on two-dimensional coordinates and the other is based on three-dimensional coordinates. The three values can be specified simultaneously or individually.<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
margin: 200px auto;
transition: all 2s;
transform-origin: bottom left;
}
p:hover {
transform: rotateX(120deg);
/* transform: rotateY(120deg); */
/* transform: rotateZ(120deg); */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
perspective: 1000px;
/* 数值越小说明眼睛离的越近 */
}
p {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
transition: all 0.5s;
margin: 200px auto;
}
p:hover {
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 200px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
</p>
</body>
</html>
##3. Animation animation (1),
animation:animation- name || animation- duration|| animation- timing-function || animation- delay || animation- iteration-count|| animation- direction|| animation- fill-mode; animation-name: animation name (animation defined by yourself using @keyframes)
animation-duration: duration
animation-timing-function: motion curve, similar to the motion curve of transition.
animation-delay: delay time
animation-iteration-count: number of loops (infinite is an infinite loop)
animation-direction: whether to reverse (whether the animation is by The ending is placed upside down)
animation-fill-mode:设置在动画播放之外的状态(结束时的状态)none | forwards(设为结束时的状态)| backwards(设为开始时的状态)|both(设为开始或结束时的状态)
animation-play-state:设置动画状态 running 开始|paused 暂停
(2)、@keyframes 自定义动画
格式如下
@keyframes 动画名称 {
from{ 开始} 0%
to{ 结束 } 100%
}可以用 from...to 来指定动画过程,也可以用0%~100%指定动画过程。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
/* animation: 动画名称 动画时间 运动曲线 何时开始 播放次数 是否反方向 */
animation: move 5s linear 3;
}
@keyframes move {
0% {
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0);
}
25% {
transform: translate3d(400px, 0, 0);
}
50% {
transform: translate3d(400px, 300px, 0);
}
75% {
transform: translate3d(0, 300px, 0);
}
100% {
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0);
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
</body>
</html>
总结:以上就是本篇文的全部内容,希望能对大家的学习有所帮助。更多相关教程请访问 CSS视频教程,CSS3视频教程!
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of CSS Summary Notes: Examples of Transformations, Transitions, and Animations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!