Explanation of CSS style classes (with examples)
This article brings you an explanation of CSS style classes (with examples). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
CSS Overview
CSS refers to Cascading Style Sheets
Styles define how to display HTML elements
Styles are usually stored in styles In the table
, styles are added to HTML 4.0 to solve the problem of separation of content and presentation
External style sheets can greatly improve work efficiency
External style sheets are usually stored in CSS files
Multiple Style definitions can be cascaded into a
HTML tag was originally designed to define document content. By using tags like
, , , the original intention of HTML was to express information such as "This is a title", "This is a paragraph", "This is a table". At the same time, the document layout is completed by the browser without using any formatting tags. All major browsers support cascading style sheets
Understanding of div and span
div is an html tag , a block-level element (displaying a line alone), it has no meaning when used alone, and must be used in conjunction with CSS. It is mainly used for page layout;
span is an html tag, an inner Linked element (displays a row), it has no meaning when used alone, must be used in combination with css, mainly to modify the style of the enclosed content;
Class selector
Before using the class selector, you must mark the century document so that the class selector can play its role.
.name{text-align:center}Copy after login
Explicitly select the specific case for this tag later in the document by including the 'class' attribute associated with the style and specifying one of the predefined styles as the 'name' value What style to use
<p></p>
Copy after login
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>类选择器</title>
<style>
.sheen{font-size: large;color: salmon}
</style>
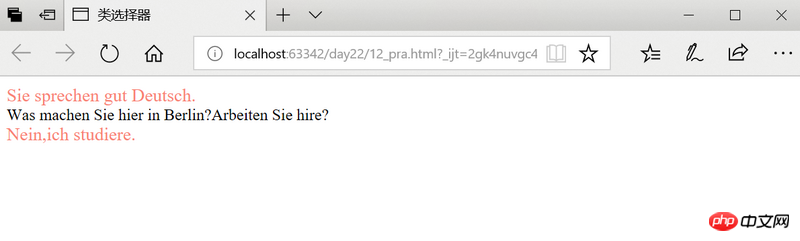
<div>
Sie sprechen gut Deutsch.
</div>
<div>
Was machen Sie hier in Berlin?Arbeiten Sie hire?
</div>
<div>
Nein,ich studiere.
</div>
Copy after login

##ID selector
ID selector is similar to class Selector, ID Selectors are preceded by a # sign - also known as a checkerboard number or pound sign. As with class selectors, wildcard selectors can be ignored in ID selectors. ID is a unique identifier and can only be used once
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>ID选择器</title>
<style>
#sheen{font-size: x-large;color: rosybrown}
#star{font-size: large;color: #c0ffff}
#clotho{font-size: xx-large;color: darkgreen}
</style>
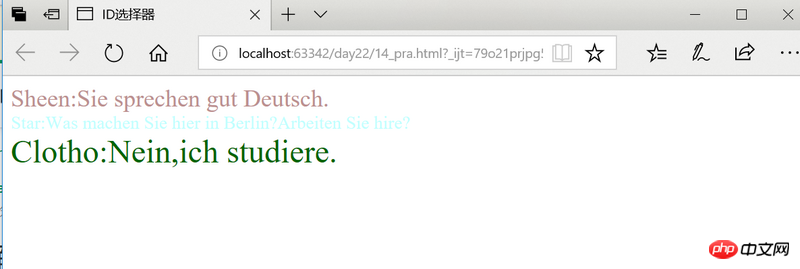
<div>
Sheen:Sie sprechen gut Deutsch.
</div>
<div>
Star:Was machen Sie hier in Berlin?Arbeiten Sie hire?
</div>
<div>
Clotho:Nein,ich studiere.
</div>
Copy after login

##Tag selectornbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>标签选择器</title>
<style>
div{margin: 0 auto;border: 1px;color: darkgreen;font-size: larger;text-align: center}
</style>
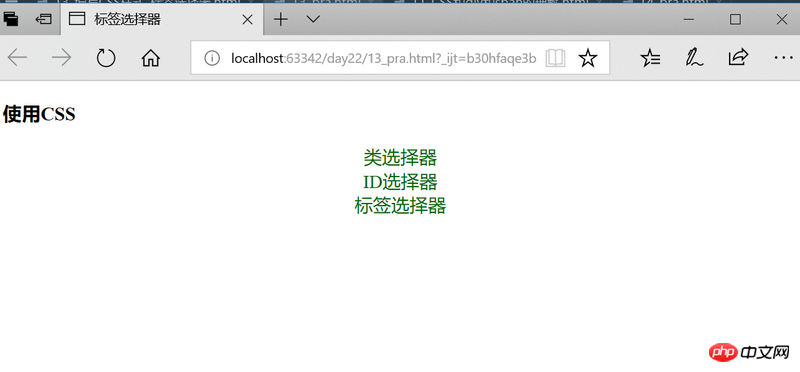
<h3 id="使用CSS">使用CSS</h3>
<div>
类选择器
</div>
<div>ID选择器</div>
<div>标签选择器</div>
Copy after login

Set the link styleThere are many CSS properties that can set the link style (such as color, font-family, background, etc.).
The special thing about links is the ability to style them based on the state they are in. Four states of links:
a:link - ordinary, unvisited link
a:visited - link that the user has visited
a:hover - the mouse pointer is above the link
a:active - The moment when the link is clicked
Introduction of CSS styleIntroduction method:
1). Inline introduction:
2). Internal introduction: the style written in the style tag inside the head tag;3). External introduction: separate the css style into a file, through Linked with the current html file.
Priority of the three introduction methods: Proximity principle
//CSS文件
div {
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
list-style-type: none
}
li {
display: inline-block;
width: 20%;
background: snow;
color: #333333;
padding-top: 10px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-size: large;
text-transform: capitalize;
}
li:hover {
background: green;
color: snow;
}
a:hover {
color: snow;
}Copy after login<!--HTML文件-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
li {
background: red;
}
</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/main.css">
</head>
<body>
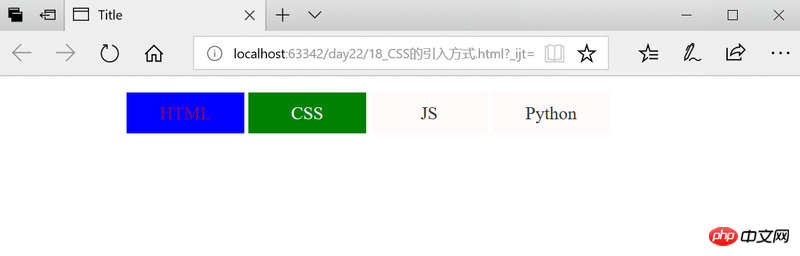
<div>
<ul>
<li style="background: blue">
<a href="http://www.w3school.com.cn/h.asp" style="text-decoration: none">HTML</a>
</li>
<li>CSS</li>
<li>JS</li>
<li>python</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>Copy after login

The above is the detailed content of Explanation of CSS style classes (with examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-
 React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React's Role in HTML: Enhancing User Experience
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
React combines JSX and HTML to improve user experience. 1) JSX embeds HTML to make development more intuitive. 2) The virtual DOM mechanism optimizes performance and reduces DOM operations. 3) Component-based management UI to improve maintainability. 4) State management and event processing enhance interactivity.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.