The use of ThreadLocal in Java multi-threading
The content of this article is about the use of ThreadLocal in Java multi-threading. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
In a multi-threaded environment, thread synchronization must be performed when accessing non-thread-safe variables, such as using the synchronized method to access a HashMap instance. However, synchronous access will reduce concurrency and affect system performance. At this time, you can trade space for time. If we allocate an independent variable to each thread, you can use non-thread-safe variables in an asynchronous manner. We call such variables thread-local variables.
As the name suggests, thread local variables mean that each thread has its own independent copy of the variable, which cannot be accessed by other threads like ordinary local variables. Java does not provide language-level thread local variables, but provides the function of thread local variables in the class library, which is the protagonist this time ThreadLocal class.
Usage of ThreadLocal
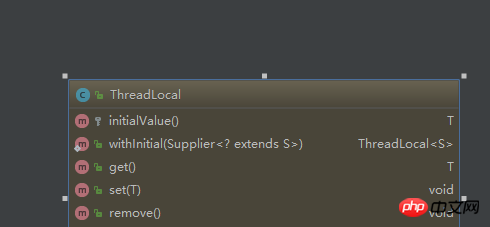
ThreadLocal<integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<integer>() {
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return 0;
}
};</integer></integer>ThreadLocal<integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> 0); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); threadLocal.set(16); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); threadLocal.remove(); System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); // 同一个线程的输出 0 16 0 Process finished with exit code 0</integer>
The principle of ThreadLocal
Then ThreadLocal is How to implement the function of thread local variables? In fact, the basic principle of ThreadLocal is not very complicated. ThreadLocal internally defines a static class ThreadLocalMap. The key of ThreadLocalMap is the ThreadLocal object. The value of ThreadLocalMap is the value stored by ThreadLocal. However, this ThreadLocalMap is maintained in the Thread class. Let’s take a look at some of the source code of ThreadLocal: // ThreadLocal的set方法
public void set(T value) {
// 获取当前线程对象
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取Map
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
// 设置值
map.set(this, value);
else
// 初始化Map
createMap(t, value);
}
// ThreadLocal的createMap方法
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
// Thread类定义的实例域
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;static class Entry extends WeakReference<threadlocal>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}</threadlocal> // ThreadLocalMap的set方法
private void set(ThreadLocal> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 计算在Entry[]中的索引,每个ThreadLocal对象都有一个hash值threadLocalHashCode,每初始化一个ThreadLocal对象,hash值就增加一个固定的大小0x61c88647
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal> k = e.get();
// 如果键已存在就更新值
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
// 代替无效的键
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 You can see that ThreadLocalMap treats the Entry[] array as a ring. Starting from the calculated index position, if the index already has data, it will be judged whether the Key is the same, and if it is the same, the value will be updated. Otherwise, just wait until you find an empty position and put the value in it. The same is true when obtaining values. Starting from the calculated index position, one by one is checked to see if the keys are the same. If there are many hash collisions, the performance may not be very good. <p></p><p>The application of ThreadLocal<strong></strong><code><br></code></p><p>##The application of ThreadLocal is very wide, for example, Java engineers are very familiar with it ThreadLocal is used in the Spring framework to encapsulate non-thread-safe stateful objects, so we can declare most beans as singleton scope. When writing multi-threaded code, we can also think about whether it is better to access non-thread-safe stateful objects in a synchronous manner, or whether it is better to use ThreadLocal to encapsulate non-thread-safe stateful objects. <code><span style="font-family: 微软雅黑, Microsoft YaHei;"></span><br></code></p><p class="comments-box-content"></p>The above is the detailed content of The use of ThreadLocal in Java multi-threading. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




