
This article brings you an introduction to the necessity and classification of locks in MySQL. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
When the number of user visits increases, the database is often the performance bottleneck of a system, but not only the performance bottleneck, data security will also emerge. At this time, the lock mechanism is very necessary.
Data security issues caused by concurrency are mainly divided into three aspects: dirty reading, phantom reading, and non-repeatable reading
1. Dirty reading
Dirty reading is a transactional reading Uncommitted data from another transaction was obtained.
时间线 事务1 事务2 1 begin; 2 select * from lock where id = 1; 3 begin; 4 update lock set name='dirty'; 6 select * from lock where id = 1; 7 commit; commit;
2. Phantom reading
Phantom reading is when one transaction reads the data inserted by another transaction
时间线 事务1 事务2 1 begin; 2 select * from lock where id > 1; 3 begin; 4 insert lock select 2; 5 commit; 6 select * from lock where id > 1; 7 commit;
3. Non-repeatable reading
Non-repeatable reading means that the results returned by reading unified data multiple times are inconsistent. Different from dirty reading, this is reading already submitted data; different from phantom reading, this is updating data, while phantom reading is inserting data.
时间线 事务1 事务2 begin; select * from lock where id = 1; begin; update lock set name='non-rr'; commit; select * from lock where id = 1; commit;
MySQL solves the above three problems by isolating transactions
There are 4 isolation levels
隔离级别 脏读 幻读 不可重复读 未提交读(RUC) 是 是 是 已提交读(RC) 否 是 是 可重复读(RR) 否 是 否 可串行化 否 否 否
MySQL implements transaction isolation through the lock mechanism
The classification of locks is as follows
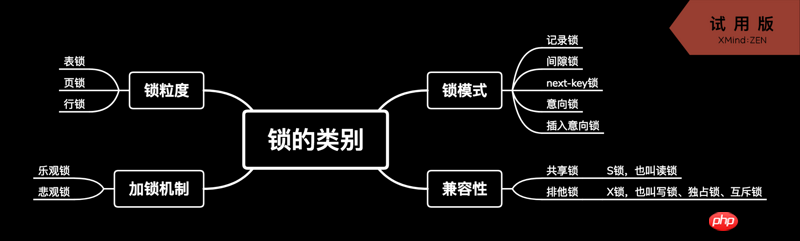
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the necessity and classification of locks in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!