 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 HTML Tutorial
HTML Tutorial
 Do you know what a native HTML component is? Introduction to native HTML components
Do you know what a native HTML component is? Introduction to native HTML components
Do you know what a native HTML component is? Introduction to native HTML components
The content of this article is about do you know what a native HTML component is? The introduction of native HTML components has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Hey! Look at the past few years, the development of Web front-end is so fast!
Think about a few years ago, HTML was a basic skill for front-end developers. A usable website could be built through various tags, and basic interaction was not a problem. If you have some more CSS, well, it's golden, crispy, and delicious. Adding a few more JavaScripts to the mix at this time is simply addictive.
With the growth of demand, the structure of HTML is becoming more and more complex, and a large number of repeated codes make it extremely difficult to modify the page. This has also hatched a batch of template tools to extract the common parts into Public components. Later, with Performance improvements for JavaScript, JavaScript Its status is getting higher and higher, and it is no longer just a side dish. The emergence of front-end rendering has reduced the pressure on the server to parse templates. The server only needs to provide static files and APIs. Just the interface will do. Then, the front-end rendering tools were moved back to the server, and back-end rendering appeared (black question mark???)
In short, componentization makes the complex front-end structure clear and makes each part independent. High cohesion and low coupling greatly reduce maintenance costs.
So, have you heard of native HTML components?

Four Web Component Standards
Before talking about native HTML components, let’s briefly introduce them The four major Web component standards are: HTML Template, Shadow DOM, Custom Elements and HTML Imports. In fact, one of them has been abandoned, so it became the "big three".
HTML Template I believe many people have heard of it. Simply put, it is the tag in HTML5. Under normal circumstances, it is colorless and odorless, and its existence cannot be perceived, even the img below it. Neither will be downloaded, nor the script will be executed. Just like its name, it is just a template, and it will only become meaningful when you use it.
Shadow DOM is the basic tool for native component encapsulation, which can achieve independence between components.
Custom Elements is a container used to package native components. Through it, you only need to write a tag to get a complete component.
HTML Imports is something similar to ES6 Module in HTML. You can directly import another html file and then use it. DOM node. However, since HTML Imports and ES6 Module are so similar, except Chrome No other browser is willing to implement it, so it has been deprecated and is not recommended. In the future, ES6 Module will be used to replace it, but it seems that there is no replacement plan yet. In the new version This feature has been removed in Chrome, and a warning will be given in the Console when used. The warning says to use ES Modules instead, but when I tested The ES Module in Chrome 71 will force the MIME type of the detected file to be a JavaScript type, which may not be supported yet.

##Shadow DOM
To talk about native HTML components, we must first talk about what Shadow DOM is. what. Everyone is familiar with DOM. It exists as the most basic skeleton in HTML. It is a tree structure, and every node in the tree is part of HTML. As a tree, DOM has a hierarchical relationship between superiors and subordinates. We usually use "parent node", "child node", "sibling node", etc. to describe it (of course some people think that these terms emphasize gender, so they also create some gender-neutral titles). The child node will inherit some things from the parent node to a certain extent, and will also have a certain impact from the sibling nodes. The most obvious thing is that when applying CSS Style, the child node will inherit some styles from the parent node. And Shadow DOM is also a type of DOM, so it is also a tree, except that it is a special purple sweet potato growing on the DOM tree, ah no, a sub-tree. What? Isn't the DOM itself composed of subtrees one by one? Is there anything special about this Shadow DOM? The special thing about Shadow DOM is that it is committed to creating a relatively independent space. Although it also grows on the DOM tree, its environment is isolated from the outside world. Of course, this isolation is relative Yes, in this isolated space, you can selectively inherit some properties from the parent node on the DOM tree, or even inherit a DOM tree. Using the isolation of Shadow DOM, we can create native HTML components.In fact, the browser has already implemented some components through Shadow DOM, but we have used it without realizing it. This is also the charm of the components encapsulated by Shadow DOM: you just write an HTML tag and leave the rest to me. . (Isn’t it a bit like React’s JSX?)
Let’s take a look at an example implemented by the browser using Shadow DOM, that is the video tag:
<video></video>
Let’s take a look at browsing The result of the renderer:
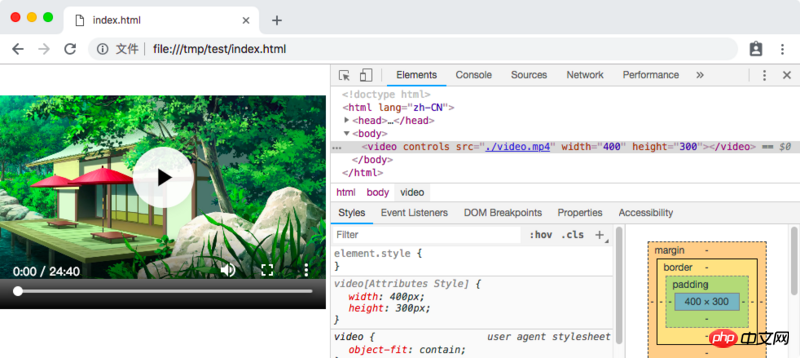
#Wait a minute! Don't you mean Shadow DOM? How is this different from a normal DOM? ? ?
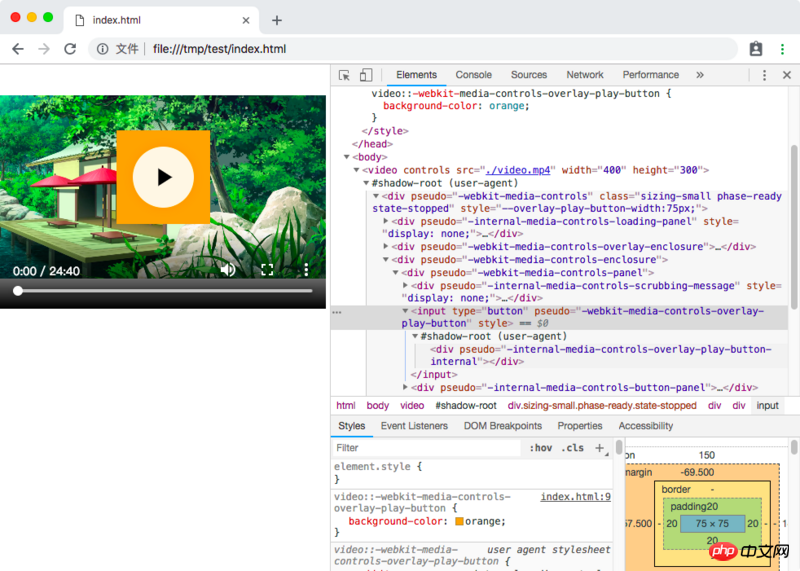
In Chrome, Elements does not display the internally implemented Shadow DOM node by default. It needs to be enabled in the settings:
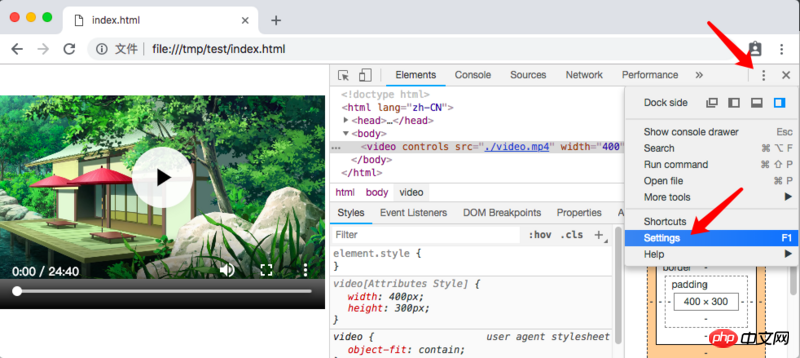
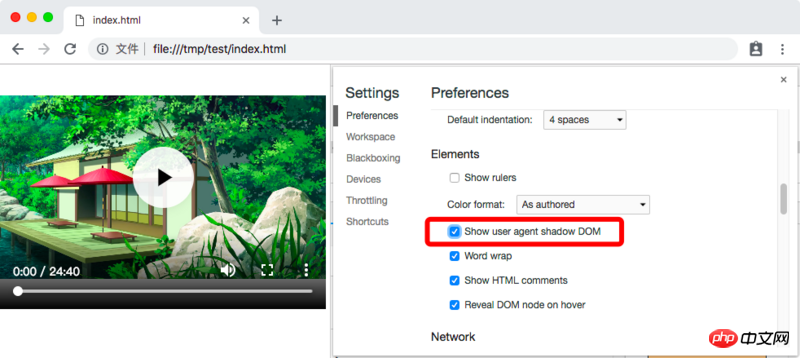
Then, we can see the true face of the video tag:
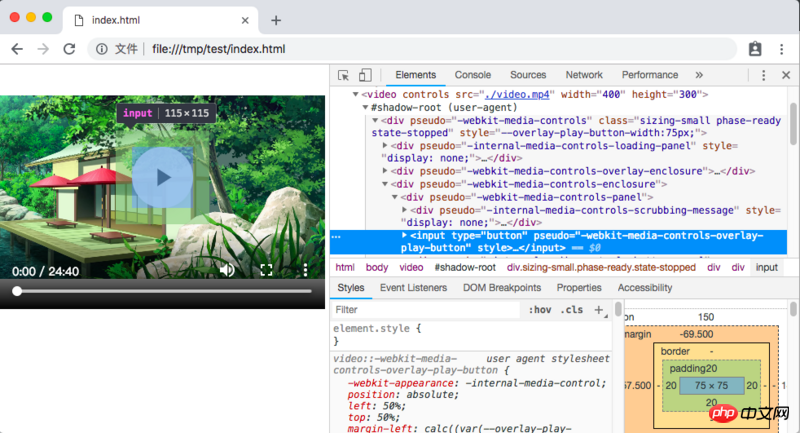
Here, you can adjust it at will just like debugging a normal DOM The content in the Shadow DOM (anyway, it is the same as the ordinary DOM and will be restored after refreshing).
We can see that most of the nodes in the shadow DOM above have pseudo attributes. According to this attribute, you can write CSS styles outside to control the corresponding node styles. For example, change the background color of the input button above pseudo="-webkit-media-controls-overlay-play-button" to orange:
video::-webkit-media-controls-overlay-play-button {
background-color: orange;
}
Since Shadow DOM is actually a type of DOM, you can continue to nest Shadow DOM in Shadow DOM, just like above.
There are many Elements in the browser that are encapsulated in the form of Shadow DOM, such as ,
Due to the isolation of Shadow DOM, even if you write a style outside: div { background-color: red !important; }, the div inside Shadow DOM will not be affected in any way
In other words, when writing styles, use id when you should use id, and use class when you should use class. If the class of a button should be written as .button, then it should be written as .button. There is no need to consider that the id and class in the current component may conflict with other components. You only need to ensure that there is no conflict within a component - this is easy to do.
This solves the problem faced by most component-based frameworks today: How to write the class(className) of Element? Using a prefixed namespace will result in a class name that is too long, like this: .header-nav-list-sublist-button-icon; using some CSS-in-JS tools, you can create some unique class names, like this: .Nav__welcomeWrapper___lKXTg, this name is still a bit long and contains redundant information.
ShadowRoot
ShadowRoot is the root under Shadow DOM. You can treat it like
in DOM, but it is not . So you can't use some properties on even though it's not a node.You can operate the entire Shadow DOM tree through attributes or methods such as appendChild and querySelectorAll under ShadowRoot.
For an ordinary Element, such as
, you can create a ShadowRoot by calling the attachShadow method on it (there is also a createShadowRoot method, which is outdated and not recommended). attachShadow accepts an object. Initialization: { mode: 'open' }, this object has a mode attribute, which has two values: 'open' and 'closed'. This attribute needs to be initialized when creating ShadowRoot, and after creating ShadowRoot Become a read-only property.
mode: 'open' 和 mode: 'closed' 有什么区别呢?在调用 attachShadow 创建 ShadowRoot 之后,attachShdow 方法会返回 ShadowRoot 对象实例,你可以通过这个返回值去构造整个 Shadow DOM。当 mode 为 'open' 时,在用于创建 ShadowRoot 的外部普通节点(比如
)上,会有一个 shadowRoot 属性,这个属性也就是创造出来的那个 ShadowRoot,也就是说,在创建 ShadowRoot 之后,还是可以在任何地方通过这个属性再得到 ShadowRoot,继续对其进行改造;而当 mode 为 'closed' 时,你将不能再得到这个属性,这个属性会被设置为 null,也就是说,你只能在 attachShadow 之后得到 ShadowRoot 对象,用于构造整个 Shadow DOM,一旦你失去对这个对象的引用,你就无法再对 Shadow DOM 进行改造了。
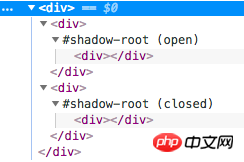
可以从上面 Shadow DOM 的截图中看到 #shadow-root (user-agent) 的字样,这就是 ShadowRoot 对象了,而括号中的 user-agent 表示这是浏览器内部实现的 Shadow DOM,如果使用通过脚本自己创建的 ShadowRoot,括号中会显示为 open 或 closed 表示 Shadow DOM 的 mode。
HTML Template
有了 ShadowRoot 对象,我们可以通过代码来创建内部结构了,对于简单的结构,也许我们可以直接通过 document.createElement 来创建,但是稍微复杂一些的结构,如果全部都这样来创建不仅麻烦,而且代码可读性也很差。当然也可以通过 ES6 提供的反引号字符串(const template = `......`;)配合 innerHTML 来构造结构,利用反引号字符串中可以任意换行,并且 HTML 对缩进并不敏感的特性来实现模版,但是这样也是不够优雅,毕竟代码里大段大段的 HTML 字符串并不美观,即便是单独抽出一个常量文件也是一样。
这个时候就可以请 HTML Template 出场了。我们可以在 html 文档中编写 DOM 结构,然后在 ShadowRoot 中加载过来即可。
HTML Template 实际上就是在 html 中的一个 标签,正常情况下,这个标签下的内容是不会被渲染的,包括标签下的 img、style、script 等都是不会被加载或执行的。你可以在脚本中使用 getElementById 之类的方法得到 标签对应的节点,但是却无法直接访问到其内部的节点,因为默认他们只是模版,在浏览器中表现为 #document-fragment,字面意思就是“文档片段”,可以通过节点对象的 content 属性来访问到这个 document-fragment 对象。
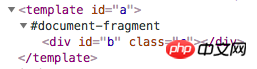
通过 document-fragment 对象,就可以访问到 template 内部的节点了,通过 document.importNode 方法,可以将 document-fragment 对象创建一份副本,然后可以使用一切 DOM 属性方法替换副本中的模版内容,最终将其插入到 DOM 或是 Shadow DOM 中。
<div></div> <template> <div></div> </template>
const template = document.getElementById('temp');
const copy = document.importNode(template.content, true);
copy.getElementById('title').innerHTML = 'Hello World!';
const div = document.getElementById('div');
const shadowRoot = div.attachShadow({ mode: 'closed' });
shadowRoot.appendChild(copy);HTML Imports
有了 HTML Template,我们已经可以方便地创造封闭的 Web 组件了,但是目前还有一些不完美的地方:我们必须要在 html 中定义一大批的 ,每个组件都要定义一个 。
此时,我们就可以用到已经被废弃的 HTML Imports 了。虽然它已经被废弃了,但是未来会通过 ES6 Modules 的形式再进行支持,所以理论上也只是换个加载形式而已。
通过 HTML Imports,我们可以将 定义在其他的 html 文档中,然后再在需要的 html 文档中进行导入(当然也可以通过脚本按需导入),导入后,我们就可以直接使用其中定义的模版节点了。
已经废弃的 HTML Imports 通过 标签实现,只要指定 rel="import" 就可以了,就像这样:,它可以接受 onload 和 onerror 事件以指示它已经加载完成。当然也可以通过脚本来创建 link 节点,然后指定 rel 和 href 来按需加载。Import 成功后,在 link 节点上有一个 import 属性,这个属性中存储的就是 import 进来的 DOM 树啦,可以 querySelector 之类的,并通过 cloneNode 或 document.importNode 方法创建副本后使用。
未来新的 HTML Imports 将会以 ES6 Module 的形式提供,可以在 JavaScript 中直接 import * as template from './template.html';,也可以按需 import,像这样:const template = await import('./template.html');。不过目前虽然浏览器都已经支持 ES6 Modules,但是在 import 其他模块时会检查服务端返回文件的 MIME 类型必须为 JavaScript 的 MIME 类型,否则不允许加载。
Custom Elements
有了上面的三个组件标准,我们实际上只是对 HTML 进行拆分而已,将一个大的 DOM 树拆成一个个相互隔离的小 DOM 树,这还不是真正的组件。
要实现一个真正的组件,我们就需要用到 Custom Elements 了,就如它的名字一样,它是用来定义原生组件的。
Custom Elements 的核心,实际上就是利用 JavaScript 中的对象继承,去继承 HTML 原生的 HTMLElement 类(或是具体的某个原生 Element 类,比如 HTMLButtonElement),然后自己编写相关的生命周期函数,处理成员属性以及用户交互的事件。
看起来这和现在的 React 很像,在 React 中,你可以这样创造一个组件:class MyElement extends React.Component { ... },而使用原生 Custom Elements,你需要这样写:class MyElement extends HTMLElement { ... }。
Custom Elements 的生命周期函数并不多,但是足够使用。这里我将 Custom Elements 的生命周期函数与 React 进行一个简单的对比:
constructor(): 构造函数,用于初始化 state、创建 Shadow DOM、监听事件之类。
对应 React 中 Mounting 阶段的大半部分,包括:constructor(props)、static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) 和 render()。
在 Custom Elements 中,constructor() 构造函数就是其原本的含义:初始化,和 React 的初始化类似,但它没有像 React 中那样将其拆分为多个部分。在这个阶段,组件仅仅是被创建出来(比如通过 document.createElement()),但是还没有插入到 DOM 树中。
connectedCallback(): 组件实例已被插入到 DOM 树中,用于进行一些展示相关的初始化操作。
对应 React 中 Mounting 阶段的最后一个生命周期:componentDidMount()。
在这个阶段,组件已经被插入到 DOM 树中了,或是其本身就在 html 文件中写好在 DOM 树上了,这个阶段一般是进行一些展示相关的初始化,比如加载数据、图片、音频或视频之类并进行展示。
attributeChangedCallback(attrName, oldVal, newVal): 组件属性发生变化,用于更新组件的状态。
对应 React 中的 Updating 阶段:static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state)、shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)、render()、getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) 和 componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)。
当组件的属性(React 中的 props)发生变化时触发这个生命周期,但是并不是所有属性变化都会触发,比如组件的 class、style 之类的属性发生变化一般是不会产生特殊交互的,如果所有属性发生变化都触发这个生命周期的话,会使得性能造成较大的影响。所以 Custom Elements 要求开发者提供一个属性列表,只有当属性列表中的属性发生变化时才会触发这个生命周期函数。
这个属性列表通过组件类上的一个静态只读属性来声明,在 ES6 Class 中使用一个 getter 函数来实现,只实现 getter 而不实现 setter,getter 返回一个常量,这样就是只读的了。像这样:
class AwesomeElement extends HTMLElement {
static get observedAttributes() {
return ['awesome'];
}
}disconnectedCallback(): 组件被从 DOM 树中移除,用于进行一些清理操作。
对应 React 中的 Unmounting 阶段:componentWillUnmount()。
adoptedCallback(): 组件实例从一个文档被移动到另一个文档。
这个生命周期是原生组件独有的,React 中没有类似的生命周期。这个生命周期函数也并不常用到,一般在操作多个 document 的时候会遇到,调用 document.adoptNode() 函数转移节点所属 document 时会触发这个生命周期。
在定义了自定义组件后,我们需要将它注册到 HTML 标签列表中,通过 window.customElements.define() 函数即可实现,这个函数接受两个必须参数和一个可选参数。第一个参数是注册的标签名,为了避免和 HTML 自身的标签冲突,Custom Elements 要求用户自定义的组件名必须至少包含一个短杠 -,并且不能以短杠开头,比如 my-element、awesome-button 之类都是可以的。第二个参数是注册的组件的 class,直接将继承的子类类名传入即可,当然也可以直接写一个匿名类:
window.customElements.define('my-element', class extends HTMLElement {
...
});注册之后,我们就可以使用了,可以直接在 html 文档中写对应的标签,比如:
或是
),但是只有规定的少数几个标签允许自关闭,所以,在 html 中写 Custom Elements 的节点时必须带上关闭标签。
由于 Custom Elements 是通过 JavaScript 来定义的,而一般 js 文件都是通过

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Table Border in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to Table Border in HTML. Here we discuss multiple ways for defining table-border with examples of the Table Border in HTML.
 HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
HTML margin-left
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:48 PM
Guide to HTML margin-left. Here we discuss a brief overview on HTML margin-left and its Examples along with its Code Implementation.
 Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Nested Table in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
This is a guide to Nested Table in HTML. Here we discuss how to create a table within the table along with the respective examples.
 HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Table Layout
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Table Layout. Here we discuss the Values of HTML Table Layout along with the examples and outputs n detail.
 HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
HTML Input Placeholder
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:54 PM
Guide to HTML Input Placeholder. Here we discuss the Examples of HTML Input Placeholder along with the codes and outputs.
 HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
HTML Ordered List
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Guide to the HTML Ordered List. Here we also discuss introduction of HTML Ordered list and types along with their example respectively
 Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Moving Text in HTML
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:45 PM
Guide to Moving Text in HTML. Here we discuss an introduction, how marquee tag work with syntax and examples to implement.
 HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
HTML onclick Button
Sep 04, 2024 pm 04:49 PM
Guide to HTML onclick Button. Here we discuss their introduction, working, examples and onclick Event in various events respectively.



