Detailed introduction to functions in typescript
This article brings you a detailed introduction to the functions in typescript. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Needless to say the role of functions, let’s take a look at the true appearance of functions in the typescript world!
The basic appearance of the function is as follows:
function fnanme(arg1: Type1, arg2: Type2, ...):Type {
// 函数体
}Function name parameters function body return value
The function name is of course a legal identifier, there is nothing to say, the important thing is the parameters and return value determine the shape of this function.
As for the function body, it is the code that implements the function, which varies depending on the function.
Parameter declaration
The parameter is the input of the function and needs to conform to a specific type of format
The parameters in the function declaration are called formal parameters, and when called What the function passes is called the actual parameter
The format of each parameter is name: Type, the front represents the parameter name, and the back represents the parameter type; multiple parameters need to be separated by commas, which is also very common. The following is an example
function fa(name: string, age: number) {}Optional parameters
Parameters do not have to be passed, you can pass them if you want to, if you don’t want to not pass them, add one after the parameter name ?, this function can be achieved
For example,
function fa(name: string, age?: number) {}means that age can be passed or not.
Default parameters
By giving the parameter A default value can actually achieve the effect of optional parameters, but the effect achieved at this time is that when this parameter is not passed, the default parameter will be used instead
It is worth noting that optional parameters must be required. After selecting the parameters, otherwise the compiler will be confused. In fact, think about it, if you don't do this, you will be confused too.
Function return
The function return must have a return type. The return type is usually written in front of the function body, that is, in front of the curly braces.
function fa(name: string): string {}The return type of the above function is the string type. Of course, you can use any type you want.
When you do not declare a return type, the compiler will automatically infer your return type based on the return in your function body. If there is no return, the return type will be void
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to functions in typescript. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 5 common JavaScript memory errors
Aug 25, 2022 am 10:27 AM
5 common JavaScript memory errors
Aug 25, 2022 am 10:27 AM
JavaScript does not provide any memory management operations. Instead, memory is managed by the JavaScript VM through a memory reclamation process called garbage collection.
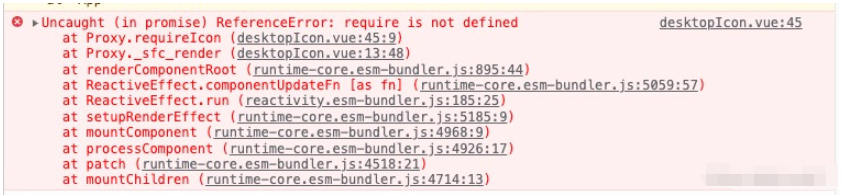 How does Vue3+TypeScript+Vite use require to dynamically introduce static resources such as images?
May 16, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
How does Vue3+TypeScript+Vite use require to dynamically introduce static resources such as images?
May 16, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
Question: How to use require to dynamically introduce static resources such as images in a Vue3+TypeScript+Vite project! Description: When developing a project today (the project framework is Vue3+TypeScript+Vite), it is necessary to dynamically introduce static resources, that is, the src attribute value of the img tag is dynamically obtained. According to the past practice, it can be directly introduced by require. The following code: Write After uploading the code, a wavy line error is reported, and the error message is: the name "require" cannot be found. Need to install type definitions for node? Try npmi --save-dev@types/node. ts(2580) after running npmi--save-d
 How to implement data type conversion function in TypeScript using MySQL
Jul 29, 2023 pm 02:17 PM
How to implement data type conversion function in TypeScript using MySQL
Jul 29, 2023 pm 02:17 PM
How to implement data type conversion function in TypeScript using MySQL Introduction: Data type conversion is a very common requirement when developing web applications. When processing data stored in a database, especially when using MySQL as the back-end database, we often need to convert the data in the query results to the type we require. This article will introduce how to use MySQL to implement data type conversion in TypeScript and provide code examples. 1. Preparation: Starting
 How to use TypeScript in Vue3
May 13, 2023 pm 11:46 PM
How to use TypeScript in Vue3
May 13, 2023 pm 11:46 PM
How to declare a type with field name enum? By design, the type field should be an enumeration value and should not be set arbitrarily by the caller. The following is the enumeration declaration of Type, with a total of 6 fields. enumType{primary="primary",success="success",warning="warning",warn="warn",//warningaliasdanger="danger",info="info",}TypeSc
 How to develop high-performance computing functions using Redis and TypeScript
Sep 20, 2023 am 11:21 AM
How to develop high-performance computing functions using Redis and TypeScript
Sep 20, 2023 am 11:21 AM
Overview of how to use Redis and TypeScript to develop high-performance computing functions: Redis is an open source in-memory data structure storage system with high performance and scalability. TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that provides a type system and better development tool support. Combining Redis and TypeScript, we can develop efficient computing functions to process large data sets and make full use of Redis's memory storage and computing capabilities. This article will show you how to
 Develop scalable front-end applications using Redis and TypeScript
Aug 01, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
Develop scalable front-end applications using Redis and TypeScript
Aug 01, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
Title: Developing Scalable Front-End Applications Using Redis and TypeScript Introduction: In today’s Internet age, scalability is one of the key elements of any application. Front-end applications are no exception. In order to meet the growing needs of users, we need to use efficient and reliable technology to build scalable front-end applications. In this article, we will introduce how to use Redis and TypeScript to develop scalable front-end applications and demonstrate its application through code examples. Introduction to Redis
 Write better code with TypeScript in PHP
Jun 19, 2023 pm 06:31 PM
Write better code with TypeScript in PHP
Jun 19, 2023 pm 06:31 PM
With the continuous development of JavaScript, front-end engineers have gradually become aware of some problems in JavaScript itself, such as the lack of type checking and modularity, which often cause confusion and errors in large projects. In order to solve these problems, TypeScript came into being and became an increasingly popular language in front-end development. In the field of back-end development, PHP has always been an extremely popular scripting language. Therefore, combine TypeScript to develop PHP applications
 Changes in Vue3 compared to Vue2: Better TypeScript type inference
Jul 07, 2023 pm 01:05 PM
Changes in Vue3 compared to Vue2: Better TypeScript type inference
Jul 07, 2023 pm 01:05 PM
Changes in Vue3 compared to Vue2: Better TypeScript type inference Vue is a popular JavaScript framework for building user interfaces. Vue3 is the latest version of the Vue framework, with a lot of improvements and optimizations based on Vue2. One of them is improvements in TypeScript type inference. This article will introduce the improvements in type inference in Vue3 and illustrate them through code examples. In Vue2, we need to manually configure the Vue component




