
The content of this article is to introduce the relationship between MySQL tables and tables? Various relationships between tables. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
The relationship between tables
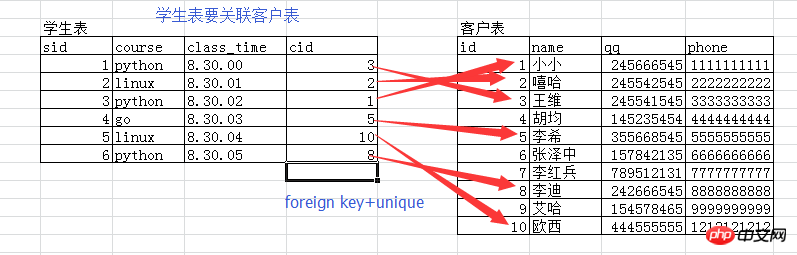
表1 foreign key 表2 则表1的多条记录对应表2的一条记录,即多对一 利用foreign key的原理我们可以制作两张表的多对多,一对一关系多对多: 表1的多条记录可以对应表2的一条记录 表2的多条记录也可以对应表1的一条记录 一对一: 表1的一条记录唯一对应表2的一条记录,反之亦然 分析时,我们先从按照上面的基本原理去套,然后再翻译成真实的意义,就很好理解了
1. First determine the relationship
2. Find the party with more, Write the related fields on the many side
One-to-many
Many-to-one or one-to-many (multiple records in the left table correspond to The only record in the table on the right)
Things to note:
1. Create the related table first to ensure that the fields of the related table must be unique.
2. When creating a related table, the related fields must be duplicated.
Example:
This is an example of a book and a publisher. The book should be associated with the publisher (multiple books can be published by one (a publishing house can also have many books).
Whoever associates with whomever is responsible must follow whose standards.
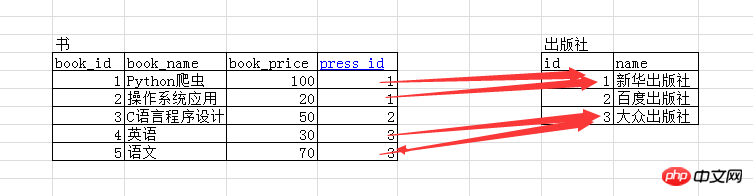
Create table
书要关联出版社 被关联的表 create table press(id int primary key auto_increment, name char(20)); 关联的表 create table book( book_id int primary key auto_increment, book_name varchar(20), book_price int, press_id int, constraint Fk_pressid_id foreign key(press_id) references press(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
Insert data
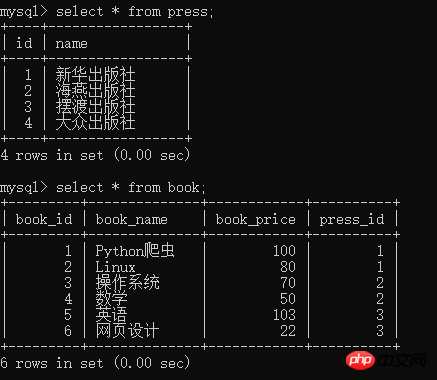
insert into press(name) values('新华出版社'), ('海燕出版社'), ('摆渡出版社'), ('大众出版社'); insert into book(book_name,book_price,press_id) values('Python爬虫',100,1), ('Linux',80,1), ('操作系统',70,2), ('数学',50,2), ('英语',103,3), ('网页设计',22,3);
Running results
One-on-one
Example 1:
Users and administrators (only administrators can log in, one administrator corresponds to one user)
Administrator associated user
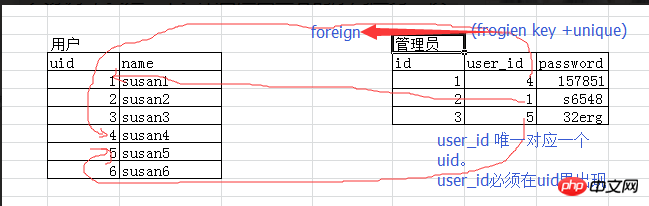
Create table
先建被关联的表 create table user( id int primary key auto_increment, #主键自增name char(10) ); 再建关联表 create table admin( id int primary key auto_increment, user_id int unique, password varchar(16), foreign key(user_id) references user(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
Insert data
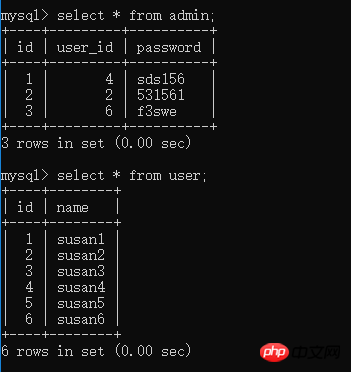
insert into user(name) values('susan1'),('susan2'),('susan3'),('susan4')('susan5'),('susan6'); insert into admin(user_id,password) values(4,'sds156'),(2,'531561'),(6,'f3swe');
Running results
Example 2:
Student table and customer table
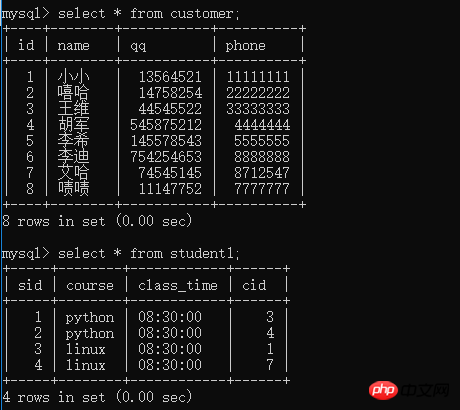
create table customer( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), qq int unique, phone int unique ); create table student1( sid int primary key auto_increment, course char(20), class_time time, cid int unique, foreign key(cid) references customer(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
insert into customer(name,qq,phone) values('小小',13564521,11111111),('嘻哈',14758254,22222222),('王维',44545522,33333333),('胡军',545875212,4444444),('李希',145578543,5555555),('李迪',754254653,8888888),('艾哈',74545145,8712547),('啧啧',11147752,7777777); insert into student1(course,class_time,cid) values('python','08:30:00',3),('python','08:30:00',4),('linux','08:30:00',1),('linux','08:30:00',7);
##Many-to-manyBooks and authors (we can create another table to store the relationship between the book and author tables)
To set the book_id And author_id is set to be jointly unique
Uniquely unique: unique(book_id, author_id)Joint primary key: alter table t1 add primary key(id,avg)
Many-to-many: One author can write multiple books, and one book can also have multiple authors, two-way one-to-many, that is, many pairs
Relationship method: foreign key a new table
Example: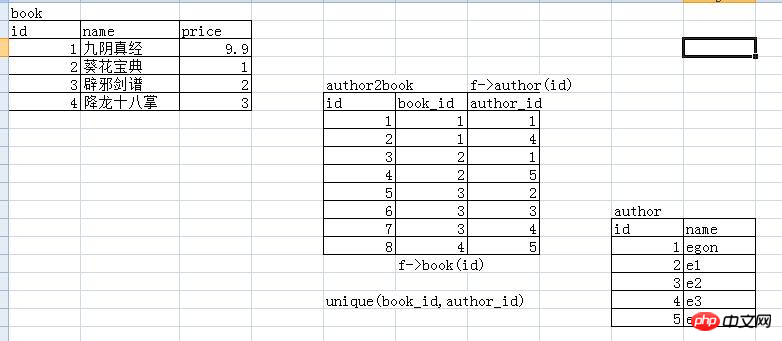

========书和作者,另外在建一张表来存书和作者的关系 #被关联的 create table book1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), price float(3,2) ); #========被关联的 create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(5) ); #========关联的 create table author2book( id int primary key auto_increment, book_id int not null, author_id int not null, unique(book_id,author_id), foreign key(book_id) references book1(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
insert into book1(name,price) values('九阳神功',9.9), ('葵花宝典',9.5), ('辟邪剑谱',5), ('降龙十巴掌',7.3); insert into author(name) values('egon'),('e1'),('e2'),('e3'),('e4'); insert into author2book(book_id,author_id) values(1,1),(1,4),(2,1),(2,5),(3,2),(3,3),(3,4),(4,5);
-- 用户表 create table user (id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(20) not null,password varchar(50) not null); insert into user(username,password) values('egon','123'),('root',147),('alex',123),('haiyan',123),('yan',123); -- 用户组表 create table usergroup(id int primary key auto_increment,groupname varchar(20) not null unique); insert into usergroup(groupname) values('IT'),('Sale'),('Finance'),('boss'); -- 主机表 CREATE TABLE host(id int primary key auto_increment,ip CHAR(15) not NULL UNIQUE DEFAULT '127.0.0.1'); insert into host(ip) values('172.16.45.2'),('172.16.31.10'),('172.16.45.3'),('172.16.31.11'),('172.10.45.3'), ('172.10.45.4'),('172.10.45.5'),('192.168.1.20'),('192.168.1.21'),('192.168.1.22'),('192.168.2.23'),('192.168.2.223'), ('192.168.2.24'),('192.168.3.22'),('192.168.3.23'),('192.168.3.24');
-- 建立user和usergroup的关系表 create table user2usergroup( id int not NULL UNIQUE auto_increment, user_id int not null, group_id int not NULL, PRIMARY KEY(user_id,group_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id) ON DELETE CASCADE on UPDATE CASCADE , foreign key(group_id) references usergroup(id) ON DELETE CASCADE on UPDATE CASCADE ); insert into user2usergroup(user_id,group_id) values(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4),(3,4); -- 建立user和host的关系 create table user2host( id int not null unique auto_increment, user_id int not null, host_id int not null, primary key(user_id,host_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id), foreign key(host_id) references host(id) ); insert into user2host(user_id,host_id) values(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(1,7),(1,8),(1,9),(1,10),(1,11),(1,12),(1,13),(1,14),(1,15),(1,16),(2,2),(2,3),(2,4),(2,5),(3,10),(3,11),(3,12);
The above is the detailed content of What is the relationship between MySQL tables? Various relationships between tables. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!