 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 An explanation of the practical application of :before and :after in css
An explanation of the practical application of :before and :after in css
An explanation of the practical application of :before and :after in css
By definition: before and :after are CSS pseudo-elements. We can use them to insert content before or after the element content. There are many articles that give their basic knowledge, so I want to write one about: before and :after are used in practical articles, indicating that we are using them.
Syntax
Suppose we have the following simple html tag:
<p>paragraph text</p>
We can use a pseudo-element like this:
p:before {
content: "this is ";
font-weight: bold;
font-style: italic;
}The result is:
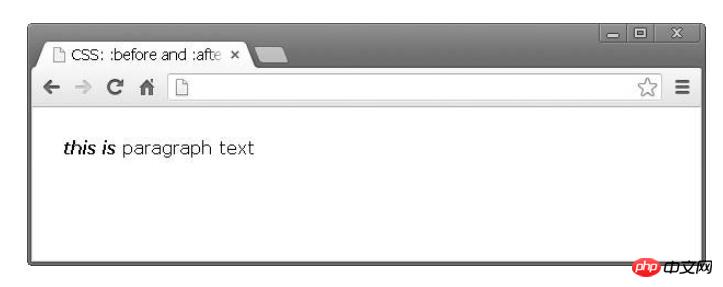
Note that you are actually adding elements before or after the content. It's not something that appears next to the selected element, but rather is related to its content. (Recommended course: css video tutorial)
Icon
Using :before and :after to implement a small icon is very easy to use, because You can add every CSS style attribute, so you can set the newly created element to a block element and attach a background image.
Again, we have the same markup
Paragraph text
Look at the CSS code below:
p:before {
content: "";
display: block;
background: url("icon.jpg") no-repeat;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
float: left;
margin: 0 6px 0 0;
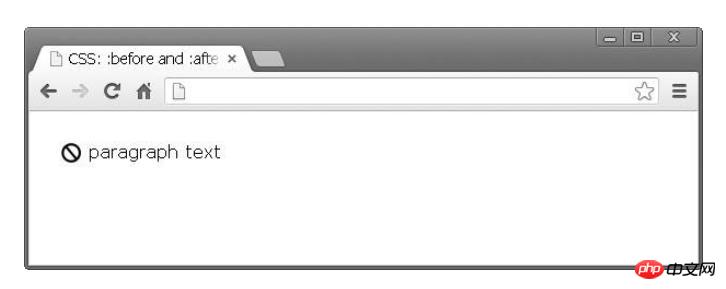
}icon.jpg is a 20x20 image exported from Photoshop . Here's what it looks like in the browser:
Style External Links
I see this in a lot of products. It's a good practice to set up links to external resources in different ways. This can be easily done using the techniques mentioned above. Suppose we have the following paragraph of text:
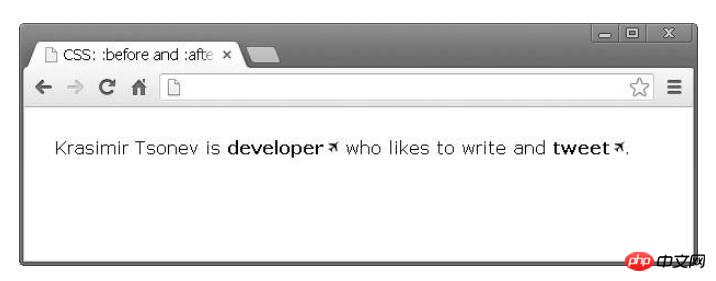
<p>Krasimir Tsonev is <a href="http://krasimirtsonev.com">developer</a>who likes to write and <a href="https://twitter.com/KrasimirTsonev">tweet</a>.</p>
We can add a small icon after the link to indicate that it points to a page outside the current domain.
a {
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: #000;
}
a:after {
content: "";
display: inline-block;
background: url("icon-external.jpg") no-repeat top right;
width: 14px;
height: 12px;
}
Breadcrumbs (Navigation)
Usually when you do breadcrumbs, there are links and separators between them. Instead of adding elements in the DOM, you can achieve the same effect using pure css.
HTML:
<p>
<a href="#">Home</a>
<a href="#">Team</a>
<a href="#">Developers</a>
</p>Just a few lines of CSS:
a {
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: #000;
}
a:after {
content: " /";}
a:first-child:before {
content: " » ";
}
a:last-child:after {
content: "";
}The results are as follows:
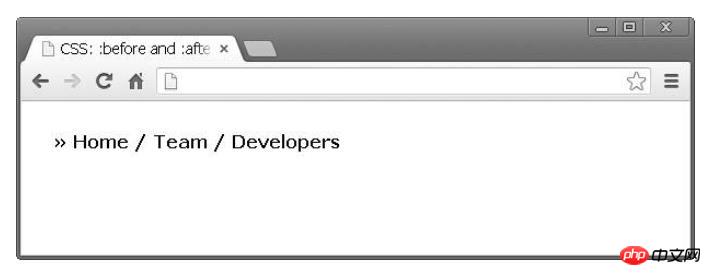
The above results are produced The effect. First, there is a symbol before all links. I combined two pseudo-elements the first child element and the before expression: "Joined » before the first link". Finally, I did the same thing, removing the separator from the last link in the list.
I found this very helpful. Mainly because I don't have to worry about this in the code that generates the navigation. I mean if I have to build the same thing in PHP I should write some extra code. For example:
$links = array('Home', 'Team', 'Developers');
$str = '» ';for($i=0; $i<count($links); $i++) {
$str .= '<a href="#">'.$links[$i].'</a>';
if($i < count($links)-1)
{
$str .= ' / ';
}
}
echo $str;That is, in the above code, I added the symbol before the link and added some logic for the separator in PHP. There's something wrong with this, because PHP code shouldn't be responsible for how things look.
Clear floats
Using the float attribute is still fine. After all, it helps a lot with layout organization. However, once an element is floated, you need another element to clear the float. Otherwise the results are not very good. For example, the following code:
* html
<a href="#">Home</a>
<a href="#">Products</a>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec at purus ac lacus ultrices vehicula.</p>
* css
a {
float: left;
display: block;
width: 100px;
... other styling
} will produce the following layout:
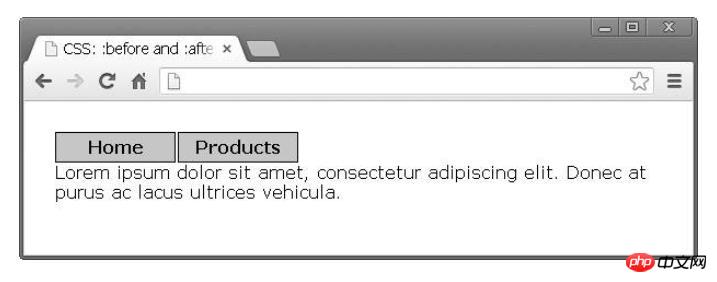
The text should be below the link, and instead of adding a new DOM node, you can Use the pseudo-element :before to clear floats:
p:before {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
Quote
:before and :after are great for quoting text. Let's say we have an idea and we want to format it.
<p>
Martin Fowler said
<span class="quoted">Any fool can write code that a computer can understand.
Good programmers write code that humans can understand.
</span>
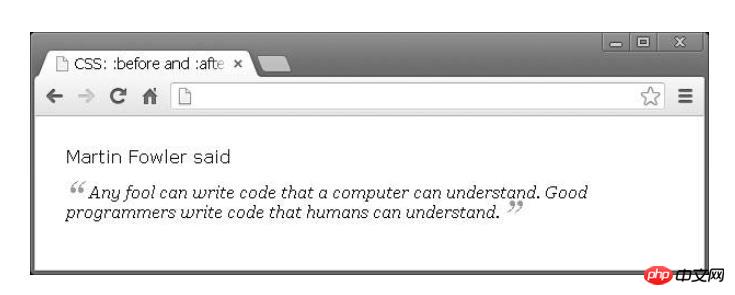
</p>Only by using CSS can the following effects be achieved:
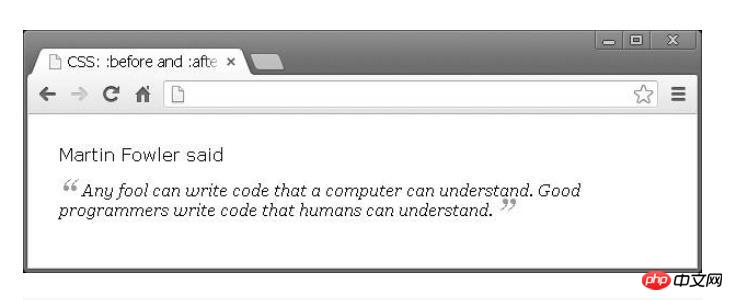
span.quoted {
font-family: Georgia;
font-size: 16px;
display: block;
margin: 14px 0 0 0;
font-style: italic;
}
span.quoted:before {
content: "“";
font-size: 40px;
color: #999;
line-height: 0;
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 6px 0 0;
}
span.quoted:after {
content: " ”";
font-size: 40px;
color: #999;
line-height: 0;
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 0 0 4px;
}Arrow
In web design, there are Sometimes some nice decorations will be added to pop-ups or tooltips. It's a bit difficult to encode them directly. Fortunately, we can solve this problem using CSS files without additional images or JavaScript. Let’s take a closer look below.
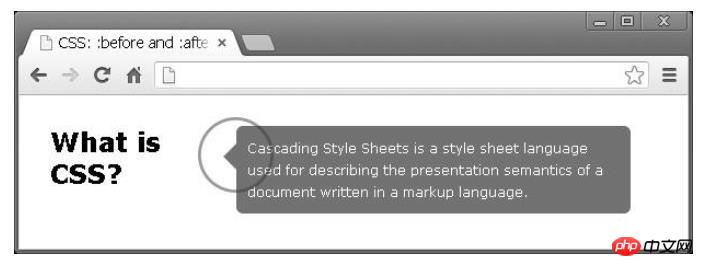
To start, our markup will look like this
<h2 id="What-nbsp-is-nbsp-CSS">What is CSS?</h2>
<div class="popup">
Cascading Style Sheets is a style sheet language used for describing
the presentation semantics of a document written in a markup language.
</div>我们左边有一个标题,右边有弹出窗口。我们需要在描述文本的左侧添加这个小箭头指向标题;怎么解决这个问题呢?我们可以使用简单的边框样式制作箭头并将这样的元素附加到弹出窗口中。
h2 {
float: left;
width: 170px;
}
.popup {
float: left;
width: 340px;
background: #727272;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 6px;
color: #FFF;
position: relative;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 20px;
}
.popup:before {
content: "";
display: block;
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-top: 12px solid transparent;
border-bottom: 12px solid transparent;
border-right: 12px solid #727272;
position: absolute;
top: 16px;
left: -12px;
}设计不同的标题类型
目前有一个单页网站的项目,项目中有不同部分的标题。每个标题都包含两行。以下是最终设计的样子:
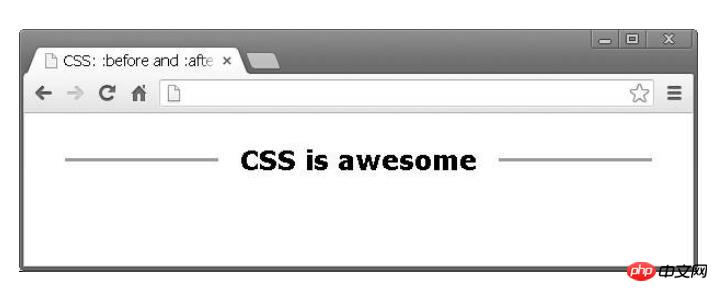
这个就是我们利用:before和:after设计出来的:
h2 {
width: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-align: center;
}
h2:after {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 0 8px 20px;
height: 3px;
content: " ";
text-shadow: none;
background-color: #999;
width: 140px;
}
h2:before {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 20px 8px 0;
height: 3px;
content: " ";
text-shadow: none;
background-color: #999;
width: 140px;
}最后
伪元素:after和:before元素是你可以设置HTML样式而不添加新的DOM节点最好用的方法。
The above is the detailed content of An explanation of the practical application of :before and :after in css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Working With GraphQL Caching
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:36 AM
Working With GraphQL Caching
Mar 19, 2025 am 09:36 AM
If you’ve recently started working with GraphQL, or reviewed its pros and cons, you’ve no doubt heard things like “GraphQL doesn’t support caching” or
 Building an Ethereum app using Redwood.js and Fauna
Mar 28, 2025 am 09:18 AM
Building an Ethereum app using Redwood.js and Fauna
Mar 28, 2025 am 09:18 AM
With the recent climb of Bitcoin’s price over 20k $USD, and to it recently breaking 30k, I thought it’s worth taking a deep dive back into creating Ethereum
 Vue 3
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:32 PM
Vue 3
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:32 PM
It's out! Congrats to the Vue team for getting it done, I know it was a massive effort and a long time coming. All new docs, as well.
 Can you get valid CSS property values from the browser?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:17 PM
Can you get valid CSS property values from the browser?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:17 PM
I had someone write in with this very legit question. Lea just blogged about how you can get valid CSS properties themselves from the browser. That's like this.
 A bit on ci/cd
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
A bit on ci/cd
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
I'd say "website" fits better than "mobile app" but I like this framing from Max Lynch:
 Comparing Browsers for Responsive Design
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:25 PM
Comparing Browsers for Responsive Design
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:25 PM
There are a number of these desktop apps where the goal is showing your site at different dimensions all at the same time. So you can, for example, be writing
 Stacked Cards with Sticky Positioning and a Dash of Sass
Apr 03, 2025 am 10:30 AM
Stacked Cards with Sticky Positioning and a Dash of Sass
Apr 03, 2025 am 10:30 AM
The other day, I spotted this particularly lovely bit from Corey Ginnivan’s website where a collection of cards stack on top of one another as you scroll.
 Using Markdown and Localization in the WordPress Block Editor
Apr 02, 2025 am 04:27 AM
Using Markdown and Localization in the WordPress Block Editor
Apr 02, 2025 am 04:27 AM
If we need to show documentation to the user directly in the WordPress editor, what is the best way to do it?



