
The content of this article is a brief introduction (code example) about positioning in CSS. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
1. Relative positioning
position: relative
Position relative to the default layout position, that is, position relative to where you should be.
.avatar {
top: 3px; //从上到下偏移3px
left: 7px; //从左到右偏移7px
position: relative;
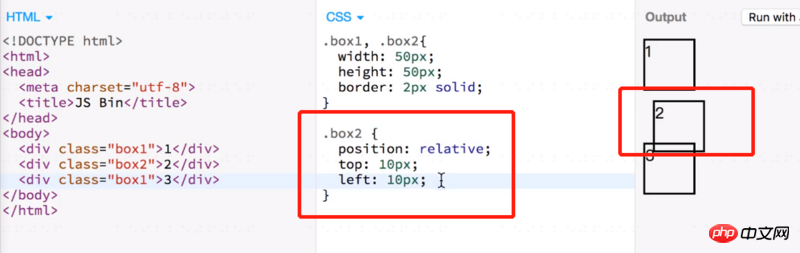
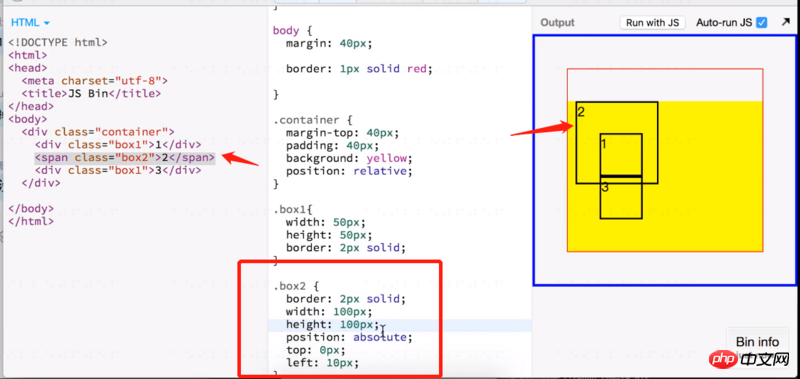
}Relative positioning does not break away from the ordinary document flow. For other elements on the page, box2 still stays in place.
2. Absolute positioning
position: absolute
.box {
position:absolute;
top:10px;//相对定位点,从上到下偏移10px
left:10px; //相对定位点,从左到右偏移10px
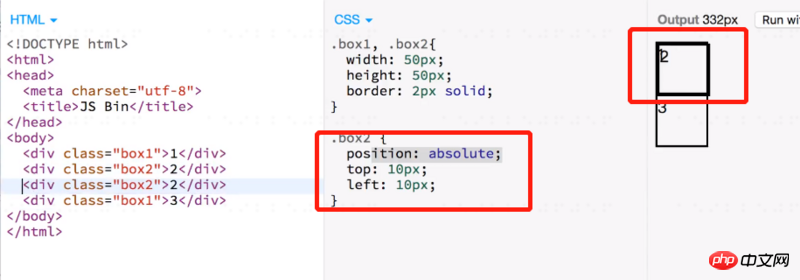
}Absolutely positioned elements Detached from the normal document flow, it is invisible to other elements. Absolutely positioned elements are also invisible. So the two box2s in the picture below overlap
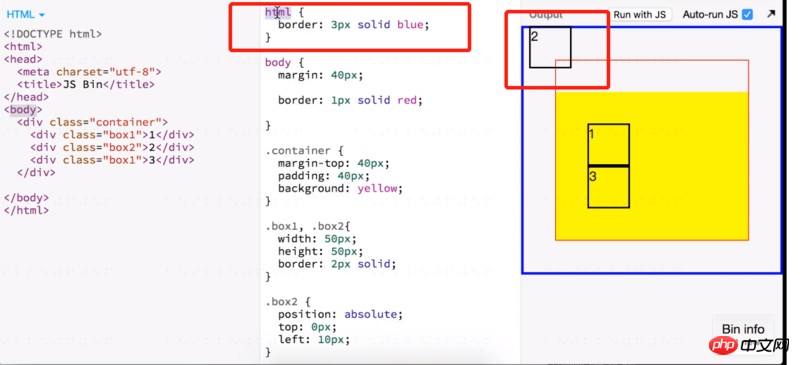
The absolutely positioned positioning object is to find out whether there is one from its parent element relative/fix/absolute. If the parent element is set with relative/fix/absolute, then the parent element is the anchor point of the absolutely positioned element. If the parent element is not set with relative/fix/absolute, continue to look up until the body and html. If it cannot be found, the html root node is used as the anchor point.
So when using absolute positioning, it is best to set relative positioning relative on the parent element.
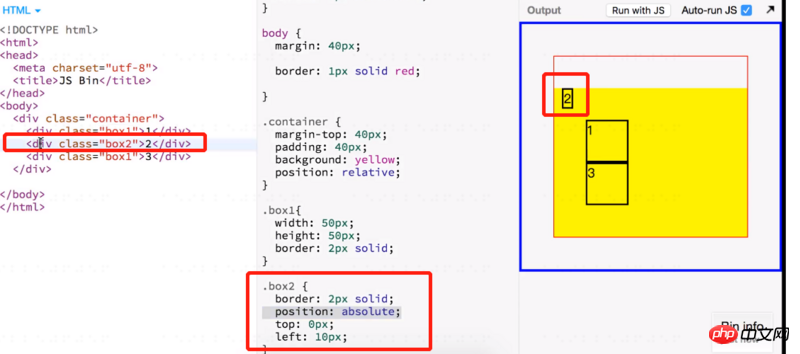
After setting absolute positioning, the width of the block-level element will shrink, and the width is determined by the content. Inline elements can set width, height, and internal and external margins.
##3. z-index
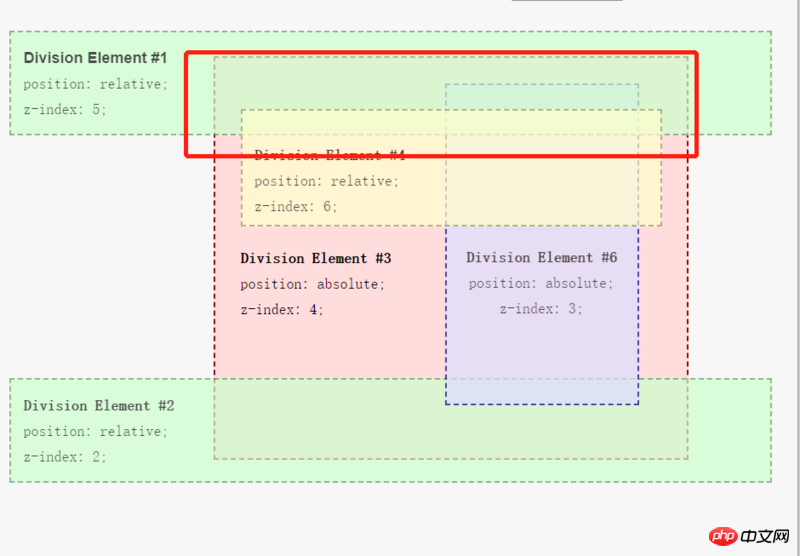
z-index Detailed introduction1. z-index definition: The attribute sets the stacking order of elements. This attribute sets the position of a positioning element along the z-axis. The z-axis is defined as extending vertically to the display area. axis. If it is a positive number, it is closer to the user, and if it is a negative number, it is further away from the user. This means that elements with a higher stacking order will always be in front of elements with a lower stacking order.Note: Elements can have negative z-index attribute values.
Note: Z-index only works on positioned elements (such as position:absolute;)!
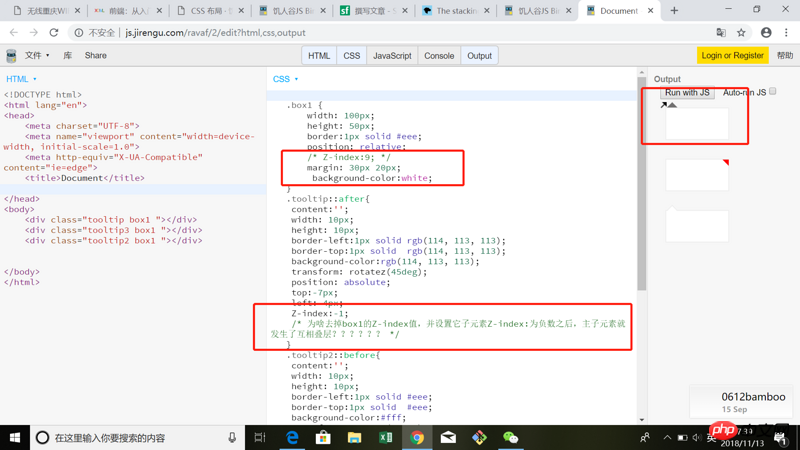
As shown below, box1 does not have z-index set, and the z-index of the tooltip is set to negative, so box1 covers the tooltip
demo link link description, which is not satisfactory at the moment, and will be fixed later
4. Fixed positioning
position: fixedPosition relative to the browser window. Therefore, when scrolling occurs, the fixed positioning element is still at a fixed position in the window.
For example, the back to top button on the right side of the browser uses fixed positioning.
.feedback {
right: 30px;
bottom: 30px;
position: fixed;
}The above is the detailed content of A brief introduction to positioning in css (code example). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!