 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
This article brings you an example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in Python. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
flask_sqlalchemy
Uses the Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) framework, which abstracts low-level database operation instructions into high-level object-oriented operations. In other words, if we use the database engine directly, we have to write SQL operation statements, but if we use the ORM framework, we can simplify the operation of database entities such as tables and documents into Python object operations
SQLAlchemy has become the standard for ORM in the Python world. Flask is a lightweight web framework that can be freely used with ORM. Flask-sqlalchemy is a plug-in specifically designed for Flask.
In Flask-SQLAlchemy, the database is specified using a URL.
MySQL --> mysql://username:password@hostname/database
Installation
pip install flask-sqlalchemy
Database operation
##1. How to create a database operation connection
from flask import Flask from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy app = Flask(__name__) db = SQLAlchemy(app) app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql+pymysql://root:sheen@localhost/zaj_sql' app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True class User(db.Model): id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) username = db.Column(db.String(80), unique=True) email = db.Column(db.String(120), unique=True)
db.create_all()
admin = User('admin', 'admin@example.com')
guest = User('guest', 'guest@example.com')db.session.add(admin) db.session.add(guest) db.session.commit()
2. Create relationships Type database table
SQLAlchemy is connected to a relational database. The best thing about relational data is relationships. Therefore, we will create an application that uses two related tables as an example.The most common relationship is the one-to-many relationship. Because relationships are declared before they are created, you can use strings to refer to classes that have not yet been created
Relationships are represented using the relationship() function. However, foreign keys must be declared separately using the class sqlalchemy.schema.ForeignKey.
from datetime import datetime
from flask_bootstrap import Bootstrap
from flask_wtf import FlaskForm
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from flask import Flask
import pymysql
from sqlalchemy import desc
app = Flask(__name__)
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql+pymysql://root:sheen@localhost/zaj_sql'
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True
bootstrap = Bootstrap(app)
class User(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer,autoincrement=True,primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True)
passwd = db.Column(db.String(100))
add_time = db.Column(db.DATETIME,default=datetime.now())
gender = db.Column(db.BOOLEAN,default=True)
role_id = db.Column(db.INTEGER,db.ForeignKey('role.id'))
def __repr__(self):
return '<user:>' %(self.name)
class Role(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.INTEGER,autoincrement=True,primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True)
users = db.relationship('User',backref='role')
# 给Role模型添加users属性
# backref 是定义反向引用
def __repr__(self):
return '<role:>' % (self.name)
if __name__ =='__main__':
# 1. 创建数据库表
# db.drop_all()
# db.create_all()
# # 2. 创建role数据库表数据
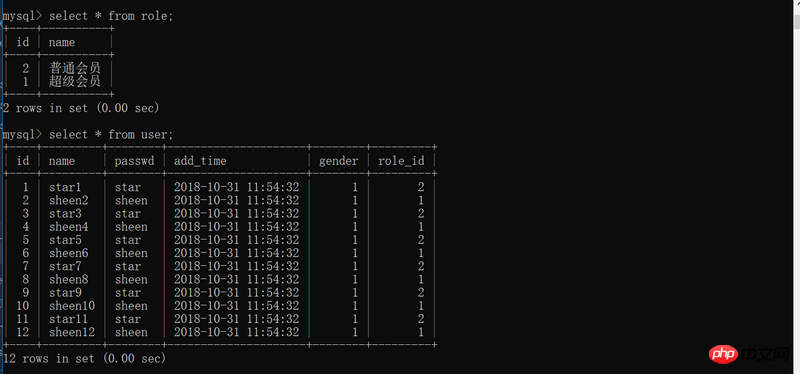
role_1 = Role(name='超级会员')
role_2 = Role(name='普通会员')
db.session.add(role_1)
db.session.add(role_2)
db.session.commit()
# # # 3. 添加user表内数据,100个用户,50个为超级会员,50个为普通会员
for i in range(1,13):
if i%2 == 0:
u = User(name='sheen'+str(i),passwd='sheen',role_id=1)
db.session.add(u)
else:
u = User(name='star'+str(i),passwd='star',role_id=2)
db.session.add(u)
db.session.commit()</role:></user:>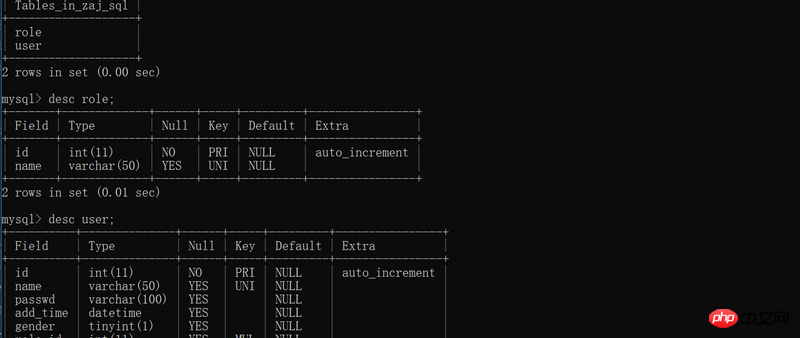
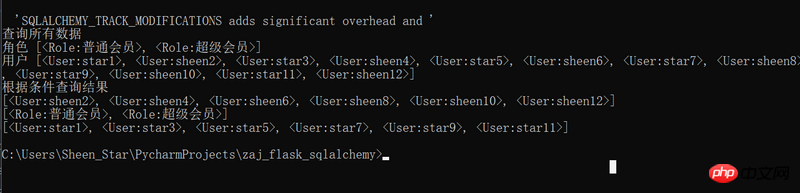
print('角色',Role.query.all())
print('用户',User.query.all())# select * from tablename where xxx=xxxxx print(User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).all()) print(Role.query.filter_by().all()) print(User.query.filter_by(role_id=2).all())
print('进行数据更新',end='\n')
u =User.query.filter_by(name='sheen2').first()
print(u)
u.passwd = '123'
db.session.add(u)
db.session.commit()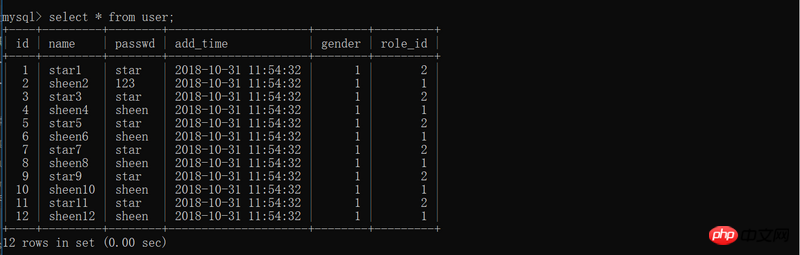
print('数据筛选', end='\n')
user = User.query.filter(User.role_id==1)
print(user) 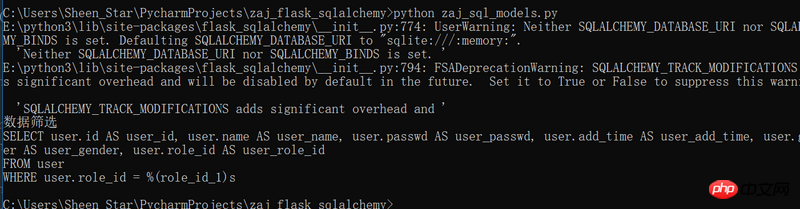
print('限制查询数据的显示', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).limit(3).all()
print(users) print('数据再处理', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).all()
print(users)print('多个过滤函数', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).limit(3).offset(1).all()
print(users)
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).slice(1,4).all()
print(users)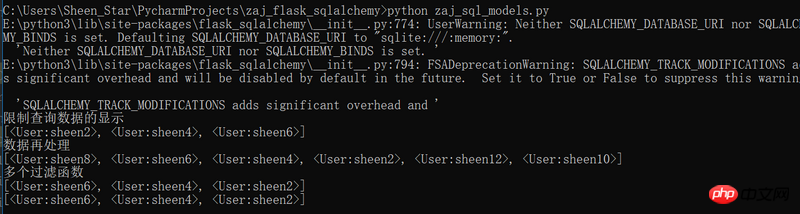
print('分页显示', end='\n')
users = User.query.paginate(1,5)
print(users.items)
users = User.query.paginate(2, 5)
print(users.items)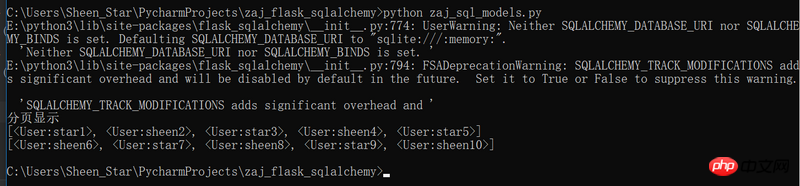
The above is the detailed content of Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 How to call docker lnmp
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:15 AM
How to call docker lnmp
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Docker LNMP container call steps: Run the container: docker run -d --name lnmp-container -p 80:80 -p 443:443 lnmp-stack to get the container IP: docker inspect lnmp-container | grep IPAddress access website: http://<Container IP>/index.phpSSH access: docker exec -it lnmp-container bash access MySQL: mysql -u roo
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 What language is vscode used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
What language is vscode used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is developed by Microsoft, built using the Electron framework, and is mainly written in JavaScript. It supports a wide range of programming languages, including JavaScript, Python, C, Java, HTML, CSS, etc., and can add support for other languages through extensions.
 What's going on with vscode not running python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
What's going on with vscode not running python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
The most common "cannot run Python" problem stems from the misconfiguration of the Python interpreter path. Solutions include: confirming Python installation, configuring VS Code, and using a virtual environment. In addition, there are efficient debugging techniques and best practices such as breakpoint debugging, variable monitoring, log output, and code formatting, such as isolating dependencies using virtual environments, tracking code execution using breakpoints, and tracking variable changes in real time using monitoring expressions, etc., which can greatly improve development efficiency.



