What is a java virtual machine? A brief introduction to JVM
This article brings you what is JVM in Java? A brief introduction to the Java virtual machine to let everyone understand what the JVM can do and the role of the JVM. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.

What is JVM?
The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a virtual machine that runs Java bytecode, which is the core of the Java programming language. When we run a program, the JVM is responsible for converting the byte code into machine-specific code. JVM is also platform dependent and provides core Java functions such as memory management, garbage collection, security, etc.
JVM is called virtual because the interface it provides does not depend on the underlying operating system and machine hardware. This independence from hardware and operating system allows Java programs to be written once anywhere.
In the real world, JVM is a specification that provides a runtime environment that can execute Java bytecode.
What can the JVM do?
JVM performs the following operations:
1. Loading code
2. Verification code
3. Execute code
3. Provide runtime environment
JVM provides the following definitions:
1.Memory area
2. Class file format
3. Registration set
4. Garbage collection heap
5. Fatal error report, etc.
JVM Architecture
Let us take a look at the internal architecture of the JVM. It contains class loaders, memory areas, execution engines, etc.
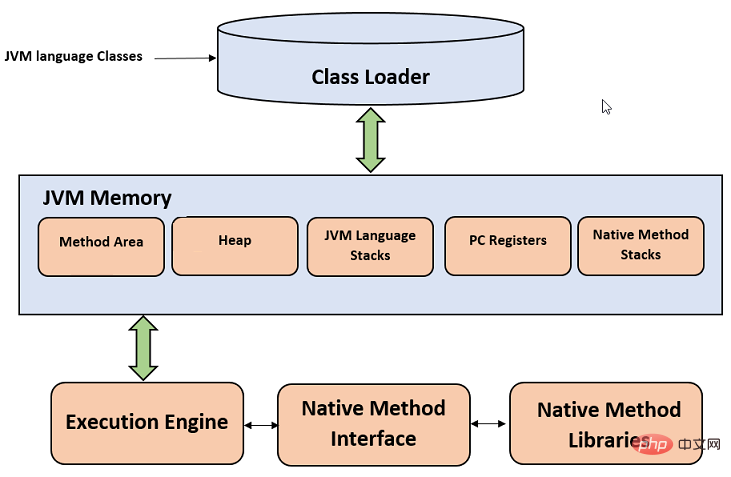
1. Class loader
Classloader is a subsystem of the JVM, used to load class files. Whenever we run a java program, it is first loaded by the class loader. There are three built-in class loaders in Java.
1), Bootstrap ClassLoader: This is the first class extension, which is the super class of the Extension class loader. It loads the rt.jar file, which contains all the class files of Java Standard Edition, such as java.lang package class, java.net package class, java.util package class, java.io package class, java.sql package class, etc.
2), Extension ClassLoader: This is the subclass loader of Bootstrap and the parent class loader of the System class loader. It goes through the jar files located in the $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext directory.
3), System/Application ClassLoader: This is a subclass loader of the Extension class loader. It loads class files from the classpath. By default, classpath is set to the current directory. You can change the classpath using the "-cp" or "-classpath" switch. It is also known as Application class loader.
2. Class (method) area
Method area stores each type of structure, such as runtime constant pool, field and method data, and method code.
3. Heap
Heap is the runtime data area where objects are allocated.
4. Stacking
Java stacks storage frames. Stack contains local variables and partial results, and plays a role in method calls and returns.
Each thread has a private JVM stack, which is created at the same time as the thread.
A new frame is created each time the method is called. When the method call completes, the frame will be destroyed.
5. Program Counter Register
PC (Program Counter) register contains the address of the Java virtual machine instruction currently being executed.6. Native Method Stack(Native Method Stack)
It contains all native methods used in the application.7. Execution Engine(Execution Engine)
It includes:1), virtual processor2), Interpreter: reads the bytecode stream and executes the instructions. 3), just-in-time (JIT) compiler: used to improve performance. JIT simultaneously compiles parts of the byte code with similar functionality, thus reducing the time required for compilation. Here, the term "compiler" refers to the converter from the instruction set of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to the instruction set of a specific CPU.8. Java Native Interface(Java Native Interface)
Java Native Interface (JNI) is a framework that provides an interface for communicating with another Communicate with another application written in a language like C, C++, Assembly, etc. Java uses the JNI framework to send output to the console or interact with OS libraries.Summary: The above is the entire content of this article, I hope it will be helpful to everyone's study. For more related video tutorials, please visit: JavaTutorial!
The above is the detailed content of What is a java virtual machine? A brief introduction to JVM. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






