What is VPS
VPS refers to virtual private server, which is a service that divides one server into multiple virtual private servers. Each VPS can be assigned an independent public IP address and independent operating system to achieve isolation of disk space, memory, CPU resources, processes and system configurations between different VPS, simulating the experience of "exclusive" use of computing resources for users and applications. .

#The operating environment of this article: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
VPS, or Virtual Private Server, is a service that divides a server into multiple virtual private servers. The technologies used to implement VPS are divided into container technology and virtual machine technology. In a container or virtual machine, each VPS can be assigned an independent public IP address and independent operating system to achieve isolation of disk space, memory, CPU resources, processes and system configurations between different VPS, simulating " Exclusive” experience using computing resources. VPS can reinstall the operating system, install programs, and restart the server independently just like a standalone server. VPS provides users with the freedom to manage configurations and can be used for enterprise virtualization and IDC resource rental.
A single physical host server can be configured to run multiple virtual private servers, each running its own operating system and applications and with dedicated resources such as RAM, memory, and storage.
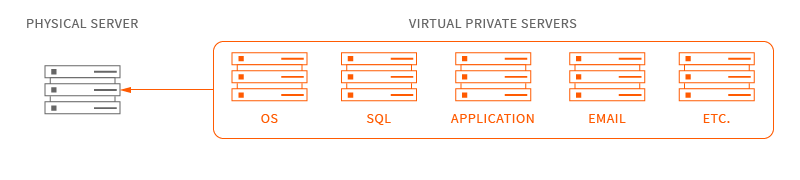
How VPS Works
The two common forms of virtualization technology used in VPS are hardware virtualization ization and container virtualization, both technologies are available in commercial and open source options.
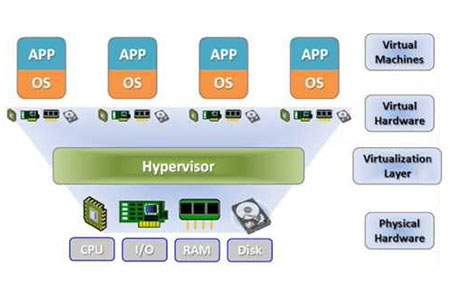
Hardware virtualization
Hardware virtualization refers to the emulation of all hardware components in a computer. This includes keyboard, mouse, video card, hard drive, network card, processor and memory. This virtualization provides optimal performance and is sometimes called a Virtual Private Server (VDS).
In addition to running different operating systems such as Windows and Linux on the same server, it allows the installation of almost any Intel-compatible operating system. Examples include VirtualBox, Hyper-V, VMware, Xen and KVM.
Container Virtualization
Containers run on the same operating system as the host machine and use special software to create the illusion that it is a standalone server. It can also shield one VPS from another.
What to consider when choosing a VPS
1. Hardware specifications of the host server (CPU, storage, RAM, bandwidth, etc.)
2. Maximum number of VPS instances on the host server
3. Virtualization technology, host server operating system and version
4. Procedures and costs for additional resources
5. Company type, support provided, company experience, reputation, customer retention rate, annual downtime, backup and/or redundancy measures
Benefits of Virtual Private Servers
1. Highly customizable, feature-rich, with dedicated server capabilities
2. Affordable, flexible and easy to expand
3. Enterprises can Full control over the server, including full root access, self-service reboot, IP allocation and re-imaging
5, Wide range of operating systems and seamless switching between different operating systems
6, Dynamic VPS allows real-time upgrade of server resources, while adding memory, bandwidth, storage or processor while the server is still running
Summary: The above is the entire content of this article, I hope it will be helpful to everyone's learning .
The above is the detailed content of What is VPS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to solve the problem that eMule search cannot connect to the server
Jan 25, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
How to solve the problem that eMule search cannot connect to the server
Jan 25, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
Solution: 1. Check the eMule settings to make sure you have entered the correct server address and port number; 2. Check the network connection, make sure the computer is connected to the Internet, and reset the router; 3. Check whether the server is online. If your settings are If there is no problem with the network connection, you need to check whether the server is online; 4. Update the eMule version, visit the eMule official website, and download the latest version of the eMule software; 5. Seek help.
 Solution to the inability to connect to the RPC server and the inability to enter the desktop
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:34 AM
Solution to the inability to connect to the RPC server and the inability to enter the desktop
Feb 18, 2024 am 10:34 AM
What should I do if the RPC server is unavailable and cannot be accessed on the desktop? In recent years, computers and the Internet have penetrated into every corner of our lives. As a technology for centralized computing and resource sharing, Remote Procedure Call (RPC) plays a vital role in network communication. However, sometimes we may encounter a situation where the RPC server is unavailable, resulting in the inability to enter the desktop. This article will describe some of the possible causes of this problem and provide solutions. First, we need to understand why the RPC server is unavailable. RPC server is a
 Detailed explanation of CentOS installation fuse and CentOS installation server
Feb 13, 2024 pm 08:40 PM
Detailed explanation of CentOS installation fuse and CentOS installation server
Feb 13, 2024 pm 08:40 PM
As a LINUX user, we often need to install various software and servers on CentOS. This article will introduce in detail how to install fuse and set up a server on CentOS to help you complete the related operations smoothly. CentOS installation fuseFuse is a user space file system framework that allows unprivileged users to access and operate the file system through a customized file system. Installing fuse on CentOS is very simple, just follow the following steps: 1. Open the terminal and Log in as root user. 2. Use the following command to install the fuse package: ```yuminstallfuse3. Confirm the prompts during the installation process and enter `y` to continue. 4. Installation completed
 How to configure Dnsmasq as a DHCP relay server
Mar 21, 2024 am 08:50 AM
How to configure Dnsmasq as a DHCP relay server
Mar 21, 2024 am 08:50 AM
The role of a DHCP relay is to forward received DHCP packets to another DHCP server on the network, even if the two servers are on different subnets. By using a DHCP relay, you can deploy a centralized DHCP server in the network center and use it to dynamically assign IP addresses to all network subnets/VLANs. Dnsmasq is a commonly used DNS and DHCP protocol server that can be configured as a DHCP relay server to help manage dynamic host configurations in the network. In this article, we will show you how to configure dnsmasq as a DHCP relay server. Content Topics: Network Topology Configuring Static IP Addresses on a DHCP Relay D on a Centralized DHCP Server
 Best Practice Guide for Building IP Proxy Servers with PHP
Mar 11, 2024 am 08:36 AM
Best Practice Guide for Building IP Proxy Servers with PHP
Mar 11, 2024 am 08:36 AM
In network data transmission, IP proxy servers play an important role, helping users hide their real IP addresses, protect privacy, and improve access speeds. In this article, we will introduce the best practice guide on how to build an IP proxy server with PHP and provide specific code examples. What is an IP proxy server? An IP proxy server is an intermediate server located between the user and the target server. It acts as a transfer station between the user and the target server, forwarding the user's requests and responses. By using an IP proxy server
 How to enable TFTP server
Oct 18, 2023 am 10:18 AM
How to enable TFTP server
Oct 18, 2023 am 10:18 AM
The steps to start the TFTP server include selecting the TFTP server software, downloading and installing the software, configuring the TFTP server, and starting and testing the server. Detailed introduction: 1. When choosing TFTP server software, you first need to choose the TFTP server software that suits your needs. Currently, there are many TFTP server software to choose from, such as Tftpd32, PumpKIN, tftp-hpa, etc., which all provide simple and easy-to-use functions. interface and configuration options; 2. Download and install TFTP server software, etc.
 What should I do if I can't enter the game when the epic server is offline? Solution to why Epic cannot enter the game offline
Mar 13, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
What should I do if I can't enter the game when the epic server is offline? Solution to why Epic cannot enter the game offline
Mar 13, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
What should I do if I can’t enter the game when the epic server is offline? This problem must have been encountered by many friends. When this prompt appears, the genuine game cannot be started. This problem is usually caused by interference from the network and security software. So how should it be solved? The editor of this issue will explain I would like to share the solution with you, I hope today’s software tutorial can help you solve the problem. What to do if the epic server cannot enter the game when it is offline: 1. It may be interfered by security software. Close the game platform and security software and then restart. 2. The second is that the network fluctuates too much. Try restarting the router to see if it works. If the conditions are OK, you can try to use the 5g mobile network to operate. 3. Then there may be more
 How to install PHP FFmpeg extension on server?
Mar 28, 2024 pm 02:39 PM
How to install PHP FFmpeg extension on server?
Mar 28, 2024 pm 02:39 PM
How to install PHPFFmpeg extension on server? Installing the PHPFFmpeg extension on the server can help us process audio and video files in PHP projects and implement functions such as encoding, decoding, editing, and processing of audio and video files. This article will introduce how to install the PHPFFmpeg extension on the server, as well as specific code examples. First, we need to ensure that PHP and FFmpeg are installed on the server. If FFmpeg is not installed, you can follow the steps below to install FFmpe




