
The content of this article is about the application of JavaScript anti-shake and throttling and the introduction of implementation methods (code examples). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. help.
First give an example:
Simulates making an ajax query request after inputting in the input box, without adding anti-shake and throttling effects. Here is the complete executable code:
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>没有防抖</title>
<style></style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
//模拟ajax请求
function ajax(content) {
console.log('ajax request ' + content)
}
let inputNormal = document.getElementById('normal');
inputNormal.addEventListener('keyup', function (e) {
ajax(e.target.value)
})
}
</script>
<div>
1.没有防抖的输入:
<input>
</div>
Effect: Entering one in the input box will trigger an "ajax request" (here is the console).
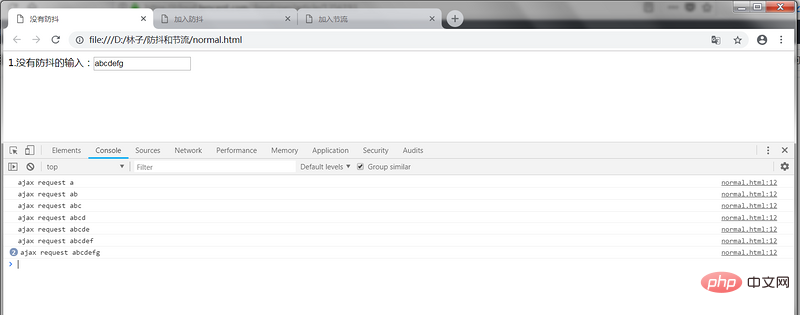
No anti-shake and throttling
Disadvantages: Waste of request resources, you can add anti-shake and throttling to optimize it.
This article will introduce what anti-shake and throttling are, their application scenarios, and implementation methods. Anti-shake and throttling are both intended to solve performance problems caused by triggering a large number of functions in a short period of time. For example, if the trigger frequency is too high, the response speed cannot keep up with the trigger frequency. Delay, freeze or freeze. However, the business needs they deal with are different, so the implementation principles are also different. Let’s take a look at them in detail below.
1. Debounce
1.1 What is debounceExecute the callback function n seconds after the event is triggered. If If it is triggered again within these n seconds, the time will be restarted. 1.2 Application Scenario(1) After the user continuously inputs a string of characters in the input box, the last query ajax request will only be executed after the input is completed, which can effectively reduce the number of requests. times, saving request resources; (2) The resize and scroll events of the window will trigger the corresponding events when constantly adjusting the browser window size or scrolling, and the anti-shake will only trigger it once;1.3 Implementation is still the same as above. Here, anti-shake is added to optimize it. The complete code is as follows:
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>加入防抖</title>
<style></style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
//模拟ajax请求
function ajax(content) {
console.log('ajax request ' + content)
}
function debounce(fun, delay) {
return function (args) {
//获取函数的作用域和变量
let that = this
let _args = args
//每次事件被触发,都会清除当前的timeer,然后重写设置超时调用
clearTimeout(fun.id)
fun.id = setTimeout(function () {
fun.call(that, _args)
}, delay)
}
}
let inputDebounce = document.getElementById('debounce')
let debounceAjax = debounce(ajax, 500)
inputDebounce.addEventListener('keyup', function (e) {
debounceAjax(e.target.value)
})
}
</script>
<div>
2.加入防抖后的输入:
<input>
</div>
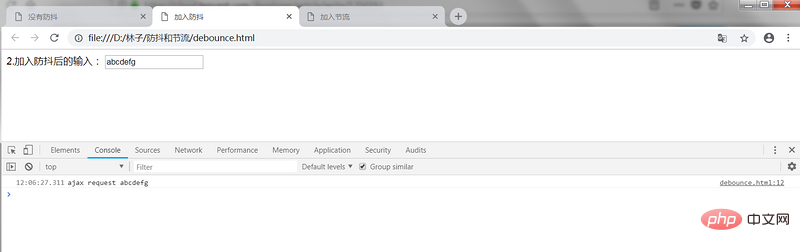
2.Throttle
2.1 What is throttling Specifies a unit time. Within this unit time, the callback function that triggers the event can only be executed once. If an event is triggered multiple times in the same unit time, only one time can take effect. 2.2 Application Scenario(1) The mouse continuously triggers an event (such as click), and only triggers it once per unit time; (2) On the page In the infinite loading scenario, the user needs to send an ajax request every once in a while while scrolling the page, instead of requesting data only when the user stops scrolling the page; (3) Monitor the scrolling event, For example, whether to slide to the bottom to automatically load more, use throttle to judge; 2.3 Implementation It is still the above example, add throttling here to optimize it, the complete code is as follows:nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>加入节流</title>
<style></style>
<script>
window.onload = function () {
//模拟ajax请求
function ajax(content) {
console.log('ajax request ' + content)
}
function throttle(fun, delay) {
let last, deferTimer
return function (args) {
let that = this;
let _args = arguments;
let now = +new Date();
if (last && now < last + delay) {
clearTimeout(deferTimer);
deferTimer = setTimeout(function () {
last = now;
fun.apply(that, _args);
}, delay)
} else {
last = now;
fun.apply(that, _args);
}
}
}
let throttleAjax = throttle(ajax, 1000)
let inputThrottle = document.getElementById('throttle')
inputThrottle.addEventListener('keyup', function (e) {
throttleAjax(e.target.value)
})
}
</script>
<div>
3.加入节流后的输入:
<input>
</div>
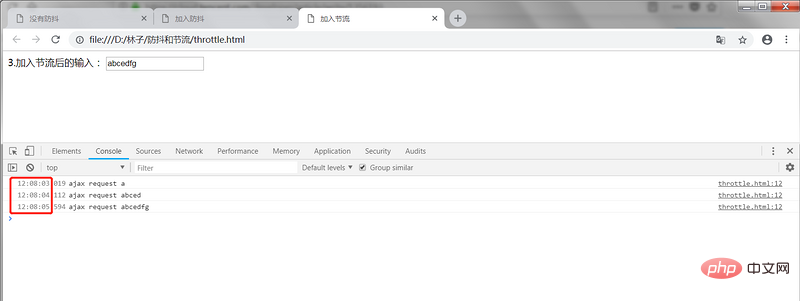
3. Summary
Summarize the difference between anti-shake and throttling: -- Effect: Function anti-shake is within a certain period of time It is only executed once; function throttling is executed at intervals. No matter how frequently the event is triggered, it is guaranteed that the real event processing function will be executed once within the specified time. -- Principle: Anti-shake maintains a timer, which stipulates that the function is triggered after the delay time. However, if it is triggered again within the delay time, the current timer will be cleared and the timeout will be reset. Called, that is, retiming. In this way, only the last operation can be triggered. Throttling is a function that is triggered by judging whether a certain time is reached. If the specified time is not reached, a timer is used to delay, and the next event will reset the timer.The above is the detailed content of Application of JavaScript anti-shake and throttling and introduction to implementation methods (code examples). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!



