Super detailed summary of javascript array methods_javascript skills
1. Common methods of arrays
1: join();
Convert array to string for display. If no parameters are entered, they will be connected by commas by default; if parameters are entered, they will be connected by parameters.
var arr=[1,2,3];
console.log(arr.join()); // 1,2,3;
console.log(arr.join("_")); // 1_2_3;
console.log(arr); // [1,2,3];
The original array remains unchanged.
2: reverse();
Arrange the array in reverse order and the original array is modified.
var arr=[1,2,3]; var arr2=arr.reverse(); console.log(arr2); // [3,2,1]; console.log(arr); // [3,2,1];
3: sort();
By default, the array items are arranged in ascending order, call the toString() method of each array item, and then compare the resulting strings, starting from the beginning of the string.
var arr=[2,12,14,21,5]; console.log(arr.sort()); //[12, 14, 2, 21, 5];
You can also pass in a comparison function as a parameter. If the first parameter should come first, the comparison function returns a value less than 0; otherwise, the first parameter comes last, and the comparison function returns a value greater than 0; if the order does not matter, the comparison function returns 0;
var arr=[2,12,14,21,5];
console.log(arr.sort(function(a,b){return a-b})); // [2,5,12,14,21];
var arr1=[2,12,14,21,5];
console.log(arr1.sort(function(a,b){return b-a})); // [21,14,12,5,2];
4: concat();
Arrays are merged, and the original arrays remain unchanged.
var arr=[1,2,3]; console.log(arr.concat(4,5)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; console.log(arr.concat([4,5],6)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; console.log(arr.concat([[4,5],6])); // [1, 2, 3, [4, 5],6]; console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3];
5: slice();
Returns a partial array, including the array item corresponding to the first parameter, but not the array item corresponding to the second parameter. If the parameter passed in is less than 0, it will be counted from back to front, and the last item will be -1. If only one parameter is passed in, the returned array contains all elements from the starting position to the end of the array. The original array remains unchanged.
var arr=[1,2,3,4,5]; console.log(arr.slice(1,3)); // [2,3]; console.log(arr.slice(1)); // [2,3,4,5]; console.log(arr.slice(1,-1)); // [2,3,4]; console.log(arr); // [1,2,3,4,5];
6: splice();
Array concatenation:
1). Delete - used to delete elements, two parameters, the first parameter (the position of the first item to be deleted), the second parameter (the number of items to be deleted);
2). Insertion-Insert any element into the specified position in the array. Three parameters, the first parameter (actual position), the second parameter (0), the third parameter (the inserted item);
3). Replacement - Insert any item element into the specified position of the array, and delete any number of items at the same time, three parameters. First parameter (starting position), second parameter (number of items to delete), third parameter (insert any number of items);
splice() returns an array consisting of deleted elements, or an empty array if no elements were deleted. The original array is modified.
var arr=[1,2,3,4,5,6]; console.log(arr.splice(2)); // [3,4,5,6]; console.log(arr); // [1,2]; console.log(arr.splice(2,0,3,4,5,6)); // []; console.log(arr); // [1,2,3,4,5,6]; console.log(arr.splice(2,2)); // [3,4]; console.log(arr); // [1,2,5,6];
7: push() and pop() methods, unshift() and shift() methods;
push() and pop() stack methods, last in first out. The original array is changed.
The push() method adds one or more elements to the end of the array and returns the new length of the array.
The pop() method removes the last element of the array, reduces the length of the array and returns the deleted value.
unshift() and shift() queue methods, first in first out. The original array is changed.
The unshift() method adds one or more elements to the head of the array, changes the index of the existing elements, and then returns the new length of the array.
The shift() method deletes the first element of the array and returns it, changing the index of the existing element.
var arr=[1,2,3]; console.log(arr.push(4)); //4; console.log(arr); //[1,2,3,4]; console.log(arr.pop()); //4; console.log(arr); //[1,2,3]; console.log(arr.unshift(0)); //4; console.log(arr); //[0,1,2,3]; console.log(arr.shift()); //0; console.log(arr); //[1,2,3];
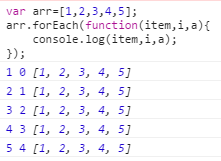
8:forEach();
forEach()里第一个参数为该集合里的元素,第二个参数为集合里的索引,第三个参数为集合本身。
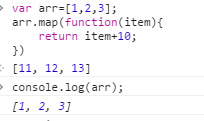
9:map();
map()对数组中的每一项运行给定函数,返回每次函数调用的结果组成的数组,原数组未被修改。
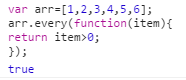
10:every()
对数组的每一项运行给定函数,如果该函数对每一项都返回true,则返回true。
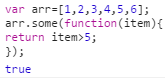
11:some()
对数组的每一项运行给定函数,如果该函数对任一项返回true,则返回true。
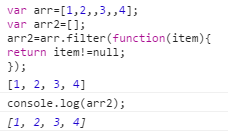
12:filter()
对数组中的每一项运行给定函数,返回该函数会返回true的项组成的数组。
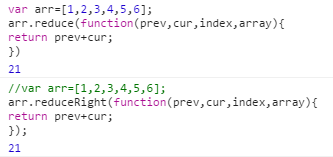
13:reduce()和reduceRight();
两个方法都会迭代数组的所有项,然后构建一个最终返回的值。其中reduce()方法从数组的第一项开始,逐个遍历到最后。而reduceRight()则从数组的最后一项开始,向前遍历到第一项。数组未被修改。
二、扩展方法
1:数组去重
function unique(array){
return array.filter(function(item,index){
return array.indexOf(item)==index;
})
};
var arr=[1,2,3,3,4,2,1,5];
console.log(unique(arr)); //[1,2,3,4,5];
function unique(arr){
var arr2=[arr[0]],
len=arr.length;
if(!len){
return;
}
for(var i=0;i<len;i++){
arr2.join(" ").indexOf(arr[i])<0?arr2.push(arr[i]):"";
}
return arr2;
}
var arr=[1,2,3,3,4,2,1,5];
console.log(uniq(arr)); //[1,2,3,4,5]
2:去掉数组中的空元素
function deleteNullInArray(array){
return array.filter(function(item){
return item!=null;
})
}
var arr=[1,2,null,,,5];
console.log(deleteNullInArray(arr)); //[1,2,5];
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1374
1374
 52
52
 Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Replace String Characters in JavaScript
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Detailed explanation of JavaScript string replacement method and FAQ This article will explore two ways to replace string characters in JavaScript: internal JavaScript code and internal HTML for web pages. Replace string inside JavaScript code The most direct way is to use the replace() method: str = str.replace("find","replace"); This method replaces only the first match. To replace all matches, use a regular expression and add the global flag g: str = str.replace(/fi
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Article discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.
 How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
How do I optimize JavaScript code for performance in the browser?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:14 PM
The article discusses strategies for optimizing JavaScript performance in browsers, focusing on reducing execution time and minimizing impact on page load speed.
 How do I debug JavaScript code effectively using browser developer tools?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
How do I debug JavaScript code effectively using browser developer tools?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:16 PM
The article discusses effective JavaScript debugging using browser developer tools, focusing on setting breakpoints, using the console, and analyzing performance.
 jQuery Matrix Effects
Mar 10, 2025 am 12:52 AM
jQuery Matrix Effects
Mar 10, 2025 am 12:52 AM
Bring matrix movie effects to your page! This is a cool jQuery plugin based on the famous movie "The Matrix". The plugin simulates the classic green character effects in the movie, and just select a picture and the plugin will convert it into a matrix-style picture filled with numeric characters. Come and try it, it's very interesting! How it works The plugin loads the image onto the canvas and reads the pixel and color values: data = ctx.getImageData(x, y, settings.grainSize, settings.grainSize).data The plugin cleverly reads the rectangular area of the picture and uses jQuery to calculate the average color of each area. Then, use
 How to Build a Simple jQuery Slider
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:19 AM
How to Build a Simple jQuery Slider
Mar 11, 2025 am 12:19 AM
This article will guide you to create a simple picture carousel using the jQuery library. We will use the bxSlider library, which is built on jQuery and provides many configuration options to set up the carousel. Nowadays, picture carousel has become a must-have feature on the website - one picture is better than a thousand words! After deciding to use the picture carousel, the next question is how to create it. First, you need to collect high-quality, high-resolution pictures. Next, you need to create a picture carousel using HTML and some JavaScript code. There are many libraries on the web that can help you create carousels in different ways. We will use the open source bxSlider library. The bxSlider library supports responsive design, so the carousel built with this library can be adapted to any
 Enhancing Structural Markup with JavaScript
Mar 10, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Enhancing Structural Markup with JavaScript
Mar 10, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Key Points Enhanced structured tagging with JavaScript can significantly improve the accessibility and maintainability of web page content while reducing file size. JavaScript can be effectively used to dynamically add functionality to HTML elements, such as using the cite attribute to automatically insert reference links into block references. Integrating JavaScript with structured tags allows you to create dynamic user interfaces, such as tab panels that do not require page refresh. It is crucial to ensure that JavaScript enhancements do not hinder the basic functionality of web pages; even if JavaScript is disabled, the page should remain functional. Advanced JavaScript technology can be used (
 How to Upload and Download CSV Files With Angular
Mar 10, 2025 am 01:01 AM
How to Upload and Download CSV Files With Angular
Mar 10, 2025 am 01:01 AM
Data sets are extremely essential in building API models and various business processes. This is why importing and exporting CSV is an often-needed functionality.In this tutorial, you will learn how to download and import a CSV file within an Angular




