A brief discussion of database knowledge starting with MongoDB
This article brings you a brief discussion of database knowledge starting from MongoDB. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Today’s topic is to talk about databases from MongoDB. In daily projects, we generally use mysql as the database, but once there is a problem, we often hear something like "How about replacing it with "Try MongoDB" sounds, so let us newbies come and talk about databases
What is a database
Let's put it in the simplest terms, a database is a place that saves data. Warehouse
The basic concept of database (Database)
A database is a warehouse that organizes, stores and manages data according to a certain data structure
The programs we write all run in memory. Once the program ends or the computer breaks, all the data in the program will be lost; so we need to persist some program data to the keyboard. , to ensure data security.
Database is a common choice for large-volume data persistence, 1. File 2. Database
Why use database to store data
The database is structured
The database can provide various interfaces to make data processing (addition, deletion, modification, and query) quick and convenient
Various languages (PHP, jsp, .net..) provide complete interfaces
Database popularity (source: https://db-engines.com /en/ranking)
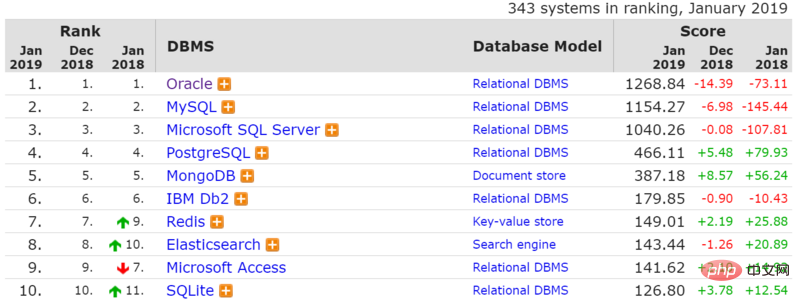
It can be seen from the statistical data that the most popular DBMS is "relational", among the top five Occupying four places, the data has been expanded to the top ten, and relational databases also account for seven places.
Why do most programmers prefer to use MySQL?
Open source, only enterprises need to purchase a license
-
Widely used: can be widely used on most platforms, such as Linux, Windows , Ubuntu, Mac OS
##Suitable for PHP (PHP is the best in the world), and can also be used with other programming languages, such as JAVA, PERL, C, C, etc. - Suitable for small and large Application
- So why is MongoDB still included in the top five if relational databases are so good? Let’s take a look at
- What are the shortcomings of relational databases and MySQL? ?
- Scalability: Adding more data to a specific record may involve scaling to multiple tables, columns, and rows, and because the data is stored row by row, even if it is only done for one of the columns Operation, the relational database will also read the entire row of data from the storage device into the memory, resulting in higher I/O.
- Before using it, you need to write a schema to define the table. At the same time, the table structure schema is inconvenient to expand if needed. Modifying the table structure requires executing DDL (data definition language) and statement modification. During the modification, the table will be locked.
- What makes MongoDB so attractive?
- Flexibility: The document structure is more consistent with the way developers code in their respective programming languages, which are clear and structured in key-value pairs so that they can be easily added at any time and edit data/documents
- Supports various queries: fields, expressions, range queries, JavaScript functions, etc.
- There is no strict schema: the document can be created before defining the document structure
- MongoDB’s features make it more suitable for processing large amounts of data
- Let us first compare the two and then explain in detail
-
MySQL MongoDB ##Version 1995- 2018 (mysql 8.0) 2009 Structure Relational Non-relational Flexibility Weak, database schema needs to be defined before use Considerable flexibility compared to MySQL - Define unnecessary schema Scalability It is possible, but it is more difficult. MySQL database can be expanded vertically and more resources can be added to a single server More efficient than MySQL Scalable. MongoDB is horizontally scalable and more servers can be added to grow your database Requires DB Administrator Yes No - Developers and Administration Accounting firms and banks, as well as other companies that require structured data with a clear schema. Ideal for businesses with more or less fixed requirements (with the exception of twitter) with real-time data, IoT, content management, mobile apps, social networks, big data/network analytics oriented systems and systems that do not require clear Ideal for businesses whose schema or structured data is constantly changing Flexibility
First of all, let’s talk about flexibility. For example, there will be many products in a mall, and these products all have their own unique attributes, such as TV screen size and screen resolution. efficiency, and air conditioners have attributes such as cooling type and outdoor unit noise. It is very difficult to put them into the product table, which adds extra work for programmers to design data tables, and MongoDB does not have Schema (schema, data model). It will seem very simple.
MongoDB’s flexibility is also reflected in unstructured and semi-structured data. MongoDB provides full-text indexing and also supports geolocation query and indexing. For example, a user wants to know where there are public restrooms within a five-kilometer radius. This is a "geographic range query." Then he searches for the nearest bike. Mobike uses MongoDB to complete such "distance sorting query".
Scalability
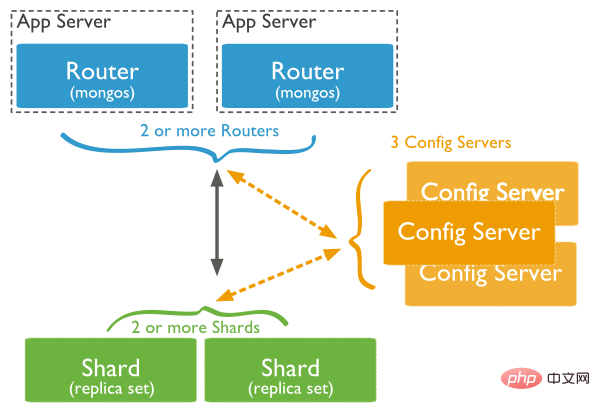
The data cannot be placed on one machine, so sharding is needed to put it on several machines. Sharding has been a native feature of MongoDB for many years and is efficiently integrated with other MongoDB features.
For example, a complex aggregation query in a sharded cluster will be automatically allocated to multiple nodes for running based on the Shard Key (shard key), and the computing tasks will be pushed down to the data nodes as much as possible. Finally, Aggregate the results of all nodes on one node. Sharding can also automatically migrate data between nodes to balance their data volume. At the same time, combined with MongoDB's replication (replica set) technology, data loss can be effectively avoided (during testing, it was found that mongo will automatically discover all machine addresses of the replica set. When a Mongo is stopped, the connected server will not Error report)
Using sharded cluster structure distribution in MongoDB:

Disadvantages of MongoDB
-
As we all know, MongoDB takes up a lot of server memory
MongoDB is slightly less secure
too free and flexible files Data errors caused by storage format (...)
The size of a single document is limited to 16 M
For array types Data operations are not rich enough
When to choose MongoDB
After saying so much shit, the most important thing is when do we choose to use MongoDB
Log system, the log information generated during the operation of the system generally has many types, a large scope, and the content is relatively messy. These messy logs can be collected and managed through MongoDB
Geographical location storage. MongoDB supports geographical location, two-dimensional spatial index, and can store longitude and latitude, so two points can be quickly calculated. The distance between them, and other location information
The data scale is growing rapidly (such as the supplied attention information)
Need to ensure a highly available environment
File storage requirements
Other scenarios, such as game development, user information, equipment, points, etc. can be stored through MongoDB. In addition Logistics systems, social systems, and even Internet of Things systems
Types of databases
Having said so much, why do we put mysql and MongoDB together to compare and choose? It is because they are different types of databases. From the development of databases to the present, they are roughly divided into three types
RDBMS (relational database)
The first thing to mention must be the one we are most familiar with. The relational database to which mysql database belongs.
Features of relational databases:
For example, MySql, sql server Oracle, etc.
Features are represented through tables Establish association
basically use SQL language to manage the database
Nosql (non-relational database)
NoSql, also It is the database type of MongoDB, originating from a Meetup held in San Francisco in 2009, where a description of NoSql technology appeared: open source, distributed, non relational databases
Characteristics of non-relational databases:
There is no concept of rows and columns and the json class is used to store data
A collection is equivalent to "Table", document is equivalent to "row"
Friction between normalization and non-standardization.
Standardization limits innovation, non-standard words cannot be unified
NoSql was interpreted as Non-Relational when it was first proposed, and there is also No-sql means, but with the rapid development in recent years, SQL has gradually been used in a wider range of fields. Therefore, SQL is no longer an exclusive feature of RDBMS. SQL capabilities have also been introduced in the NoSql technology system, thus evolving The concept of Not-Only-SQL came out
Most NoSql technologies weaken the support for ACID semantics and complex related queries, adopt a simpler or more professional data model, and optimize the read and write paths, thus Can be exchanged for higher read and write performance
NewSql
According to the definition in the wiki
NewSQL is a class of modern relational database management systems that seek to provide the same scalable performance of NoSQL systems for online transaction processing ( OLTP) read-write workloads while still maintaining the ACID guarantees of a traditional database system.
NewSql can be said to be the product of the combination of traditional RDBMS and NoSql technology. Therefore, the typical NewSql technology can be understood as distributed It is a basic prerequisite for a relational database to support distributed transactions. NoSQL and NewSQL have a lot of overlap in their technology stacks, but there are obvious differences in whether they support relational models and how well they support complex transactions. Since I don’t know much about it, I won’t say much here.
Here I will simply introduce the types of databases. A storage technology that belongs to NoSql, NewSql, or RDBMS cannot be simply classified. After all, technology is constantly improving. For example, MySQL is now also Compatible with nosql features:

Some people may wonder why transactions are not mentioned when introducing the shortcomings of MongoDB. This is because in In the MongoDB 4.0 version in the summer of 2018, MongoDB introduced transaction functions and supported multi-document ACID features, such as using the mongo shell for transaction operations

Specific stress test data will be added later
-
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion of database knowledge starting with MongoDB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle database and MySQL are both databases based on the relational model, but Oracle is superior in terms of compatibility, scalability, data types and security; while MySQL focuses on speed and flexibility and is more suitable for small to medium-sized data sets. . ① Oracle provides a wide range of data types, ② provides advanced security features, ③ is suitable for enterprise-level applications; ① MySQL supports NoSQL data types, ② has fewer security measures, and ③ is suitable for small to medium-sized applications.
 How to delete data from MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
How to delete data from MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 12:40 PM
PHP provides the following methods to delete data in MySQL tables: DELETE statement: used to delete rows matching conditions from the table. TRUNCATETABLE statement: used to clear all data in the table, including auto-incremented IDs. Practical case: You can delete users from the database using HTML forms and PHP code. The form submits the user ID, and the PHP code uses the DELETE statement to delete the record matching the ID from the users table.