
This article brings you a detailed introduction to commonly used functions in Python's numpy. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
numpy is a library related to scientific computing in python. This article will introduce some commonly used numpy functions. They need to be introduced before using numpy. Enter import numpy as np. We generally simplify numpy to np. .
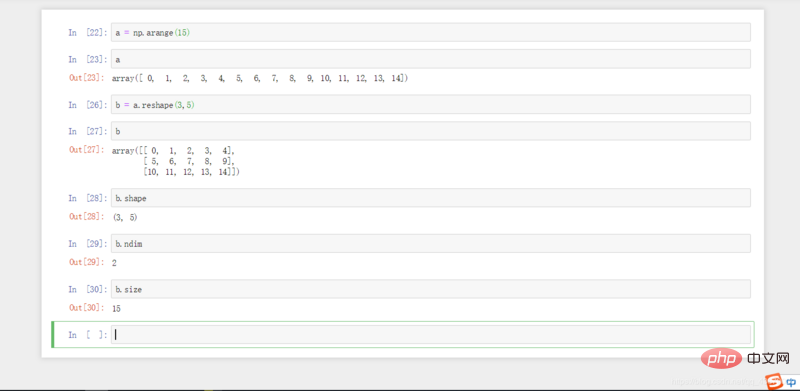
1.np.arange(n): Generates integers from 0 to n-1.
2.a.reshape(m,n): Redefine a as a matrix with m rows and n columns.
3.a.shape: Print the rows and columns of a.
4.a.ndim: Find the dimensions of a.
5.a.size: Output the number of elements in a.
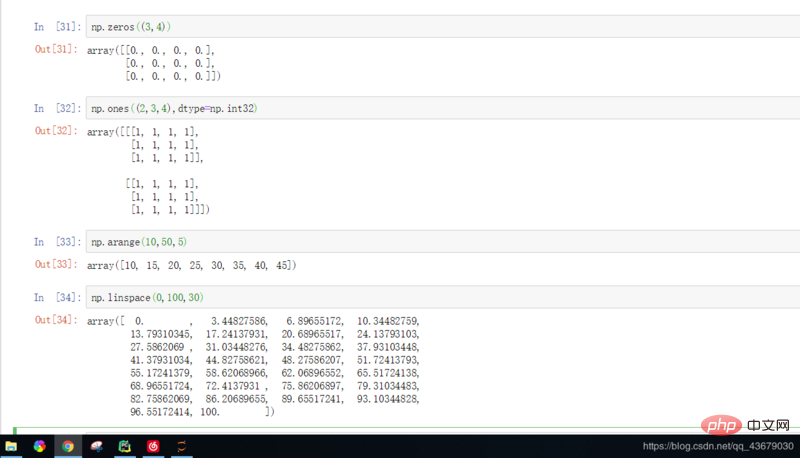
6.np.zeros((m,n)): Generate a zero matrix of m rows and n columns. It should be noted that in the function A tuple is passed in. The matrix 0 generated at this time has a decimal point after it, because the system default data type is floating point. To obtain the integer type, we should specify the data type in advance.
7.np.ones((k,m,n),dtype=np.int32): Generate k identity matrices with m rows and n columns, and the data type in the matrix is integer.
8.np.arange(m,n,k): Generate data sliced from m to n with step size k.
9.np.linspace(m,n,k): Take k values at equal intervals in the data from m to n.
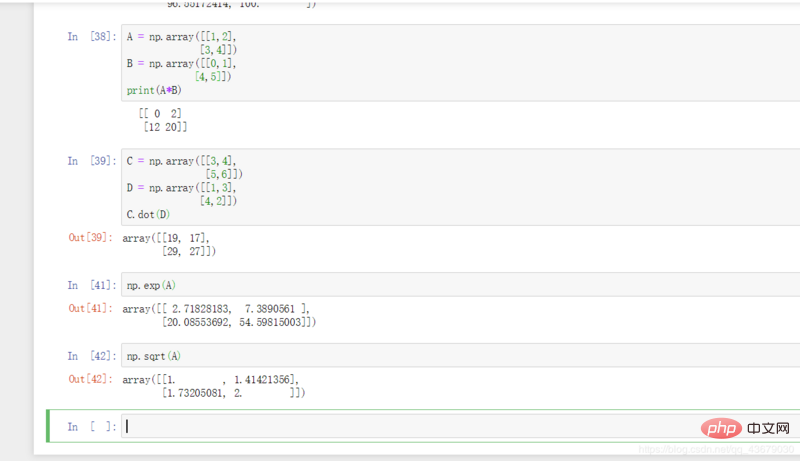
10. If A and B are matrices of the same dimension, A*B returns the result of multiplying the corresponding positions of the A and B matrices , A.dot(B) or np.dot(A,B) returns the result of matrix multiplication.
11.np.exp(A) or np.sqrt(B): Get the B power of e and the result of the square root of each number in matrix B respectively.
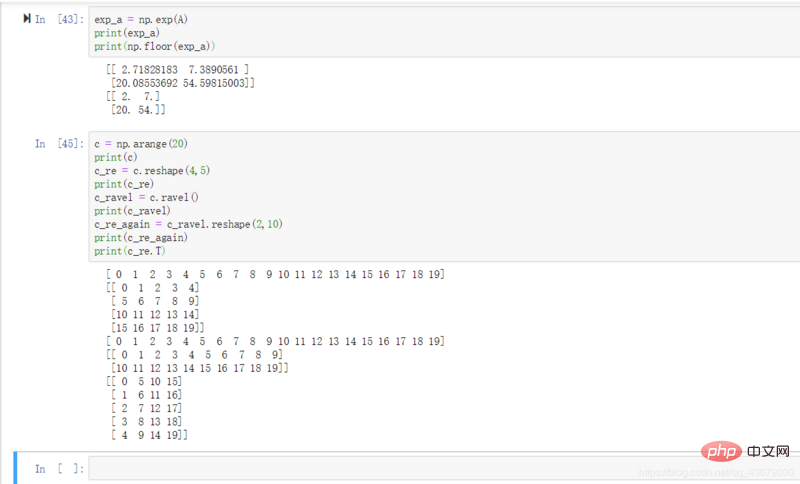
12.np.floor(): Round down.
13.a.ravel(): Re-stretch matrix a into a vector. After stretching, you can reshape it into a new matrix.
14.a.T: Find the transposed matrix of a.
15.a.reshape(n,-1) or a.reshape(-1,n): After determining the rows (columns) of a matrix, the corresponding columns (rows) are also directly determined, so Just enter -1.
16.np.hstack((a,b)): Splice matrices a and b horizontally.
17.np.vstack((a,b)): Splice matrices a and b vertically.
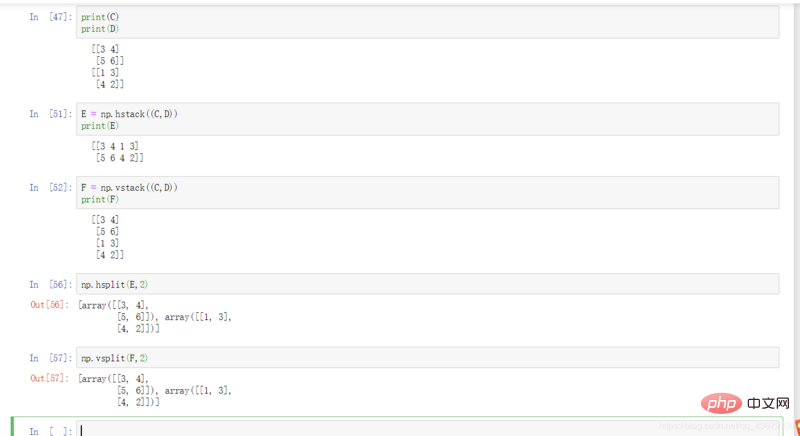
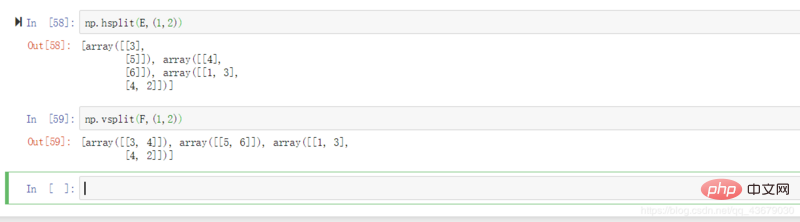
18.np.hsplit(a,n): Cut matrix a into n parts laterally.
19.np.hsplit(a,(m,n)): Cut horizontally in the gap between index m and n of a.
20.np.vsplit(a,n): Cut matrix a into n parts vertically.
21.np.hsplit(a,(m,n)): Cut vertically in the gap between index m and n of a.
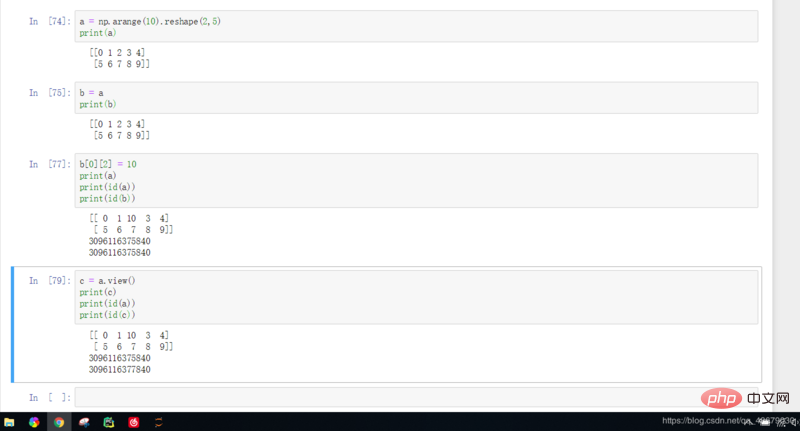
22. Copy of matrix:
b = a: The addresses of b and a obtained at this time are exactly the same, that is, a and b are just different names of the same matrix. Operations on any one matrix will cause the same change in the other matrix.
b = a.view(): The address of b obtained at this time is different from that of a, but the operation on b will change a.
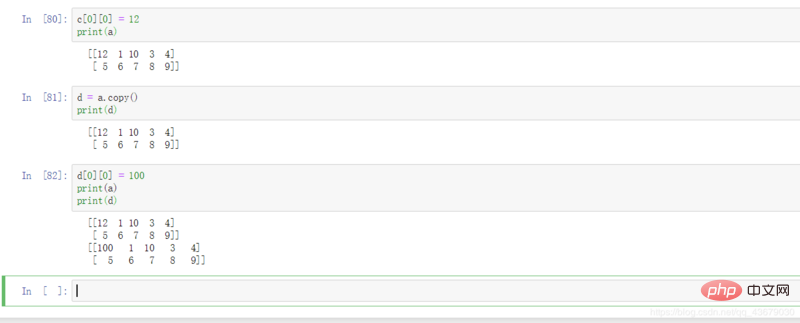
b = a.copy(): What you get at this time are two completely independent matrices.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to commonly used functions in Python's numpy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!