What are cookies? how to work?
Many websites use small strings of characters called cookies to store persistent client-side state between connections. The following article will introduce you to cookies and briefly understand how they work. I hope it will be helpful to you.

What are cookies?
Cookies are small files that are stored on the user's computer. They are used to hold a modest amount of data specific to a particular client and website, and can be accessed via the web server or client computer.
Cookies are basically small documents that contain information about the website we browse (settings, records, etc.). For example, when we select the language in which we want to view a website, the website saves the information in a file called a cookie on our computer. The next time we visit the website, it will be able to read the previously saved cookie file (which contains The language of the set website). This way we can view the website in the preferred language without having to select the language again.
The information contained by cookies can be of any type, such as the time the website was visited, items added to the shopping basket, all links clicked on the website, etc.
If a cookie is created in a specific website and you later visit another website, the latter will not be able to read the content from the first website, in other words, only the same website where the information was saved will be accessible.
How do cookies work?
Cookies are passed from the server to the client and back in the HTTP headers of requests and responses. Servers can use cookies to indicate session IDs, shopping cart contents, login credentials, user preferences, etc. Let's take a look at how Cookies work.
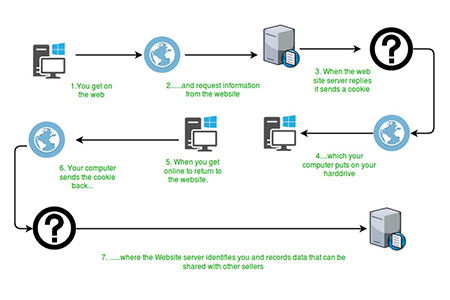
As you can see from the above figure, when the user requests a page for the first time, the server sends the cookie object together with the resource to be stored on the client. This object may contain details of the request. Now later, if the user requests the same resource again, it sends the request along with the stored cookie which can be used by the server to further enhance the user's experience.
Two types of Cookies
Session Cookie:
Session cookie means no The state of a defined life cycle, which only persists while the user is using the website, and the session cookie is usually deleted when the web browser is exited. If the user does not visit the website for a while on the server (idle timeout), the session cookie will expire. If someone comes to use our computer, they won't be able to see anything on a website that uses a session cookie because they will need to enter their username and password again.
Persistent Cookie:
Persistent cookie is the state when its life cycle is set. Persistent Cookie is more persistent than the user session. If you set the maximum age of a persistent cookie to 1 year, then within a year, every time the user visits the server, the initial value set in the cookie will be sent back to the server. This can be used to record important information, such as how a user originally arrived at the website. Therefore, persistent cookies are also called tracking cookies.
The above is the entire content of this article, I hope it will be helpful to everyone's study. For more exciting content, you can pay attention to the relevant tutorial columns of the PHP Chinese website! ! !
The above is the detailed content of What are cookies? how to work?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to Fix Roblox 403 Forbidden Error on Google Chrome
May 19, 2023 pm 01:49 PM
How to Fix Roblox 403 Forbidden Error on Google Chrome
May 19, 2023 pm 01:49 PM
Many Windows users have recently encountered an unusual error called Roblox403 Forbidden Error while trying to access website URLs in Google Chrome browser. Even after restarting the Chrome app multiple times, they were unable to do anything. There could be several potential causes for this error, some of which we've outlined and listed below. Browsing history and other cache of Chrome and corrupted data Unstable internet connection Incorrect website URLs Extensions installed from third-party sources After considering all the above aspects, we have come up with some fixes that can help users resolve this issue. If you encounter the same problem, check out the solutions in this article. Fix 1
 Where are cookies stored?
Dec 20, 2023 pm 03:07 PM
Where are cookies stored?
Dec 20, 2023 pm 03:07 PM
Cookies are usually stored in the cookie folder of the browser. Cookie files in the browser are usually stored in binary or SQLite format. If you open the cookie file directly, you may see some garbled or unreadable content, so it is best to use Use the cookie management interface provided by your browser to view and manage cookies.
 Where are the cookies on your computer?
Dec 22, 2023 pm 03:46 PM
Where are the cookies on your computer?
Dec 22, 2023 pm 03:46 PM
Cookies on your computer are stored in specific locations on your browser, depending on the browser and operating system used: 1. Google Chrome, stored in C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default \Cookies etc.
 Where are the mobile cookies?
Dec 22, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
Where are the mobile cookies?
Dec 22, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
Cookies on the mobile phone are stored in the browser application of the mobile device: 1. On iOS devices, Cookies are stored in Settings -> Safari -> Advanced -> Website Data of the Safari browser; 2. On Android devices, Cookies Stored in Settings -> Site settings -> Cookies of Chrome browser, etc.
 How cookies work
Sep 20, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
How cookies work
Sep 20, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
The working principle of cookies involves the server sending cookies, the browser storing cookies, and the browser processing and storing cookies. Detailed introduction: 1. The server sends a cookie, and the server sends an HTTP response header containing the cookie to the browser. This cookie contains some information, such as the user's identity authentication, preferences, or shopping cart contents. After the browser receives this cookie, it will be stored on the user's computer; 2. The browser stores cookies, etc.
 Detailed explanation of where browser cookies are stored
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:15 AM
Detailed explanation of where browser cookies are stored
Jan 19, 2024 am 09:15 AM
With the popularity of the Internet, we use browsers to surf the Internet have become a way of life. In the daily use of browsers, we often encounter situations where we need to enter account passwords, such as online shopping, social networking, emails, etc. This information needs to be recorded by the browser so that it does not need to be entered again the next time you visit. This is when cookies come in handy. What are cookies? Cookie refers to a small data file sent by the server to the user's browser and stored locally. It contains user behavior of some websites.
 Does clearing cookies have any impact?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 06:01 PM
Does clearing cookies have any impact?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 06:01 PM
The effects of clearing cookies include resetting personalization settings and preferences, affecting ad experience, and destroying login status and password remembering functions. Detailed introduction: 1. Reset personalized settings and preferences. If cookies are cleared, the shopping cart will be reset to empty and products need to be re-added. Clearing cookies will also cause the login status on social media platforms to be lost, requiring re-adding. Enter your username and password; 2. It affects the advertising experience. If cookies are cleared, the website will not be able to understand our interests and preferences, and will display irrelevant ads, etc.
 What are the dangers of cookie leakage?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
What are the dangers of cookie leakage?
Sep 20, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
The dangers of cookie leakage include theft of personal identity information, tracking of personal online behavior, and account theft. Detailed introduction: 1. Personal identity information is stolen, such as name, email address, phone number, etc. This information may be used by criminals to carry out identity theft, fraud and other illegal activities; 2. Personal online behavior is tracked and analyzed through cookies With the data in the account, criminals can learn about the user's browsing history, shopping preferences, hobbies, etc.; 3. The account is stolen, bypassing login verification, directly accessing the user's account, etc.




