Performance test of JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify() (example)
This article brings you the performance test (example) of JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify(). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you. helped.
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)) We generally use it for deep copying. To put it bluntly, the process is to use JSON.stringify to serialize js objects (JSON strings), and then use JSON.parse To deserialize (restore) js objects. As for why this line of code can achieve deep copy, what its limitations are, etc., this article does not introduce it. What this article wants to explore is, how efficient is the execution of this line of code? Will it cause any problems if used casually?
First two dependency functions for js performance testing
/**
* 一个简单的断言函数
* @param value {Boolean} 断言条件
* @param desc {String} 一个消息
*/
function assert(value, desc) {
let li = document.createElement('li');
li.className = value ? 'pass' : 'fail';
li.appendChild(document.createTextNode(desc));
document.getElementById('results').appendChild(li);
}/**
* 一个测试套件,定时器是为了多次执行减少误差
* @param fn {Function} 需要多次执行的代码块(需要测试、比对性能的代码块)
* @param config {Object} 配置项,maxCount: 执行代码块的for循环次数,times: 定时器执行次数
*/
function intervalTest(fn, config = {}) {
let maxCount = config.maxCount || 1000;
let times = config.times || 10;
let timeArr = [];
let timer = setInterval(function () {
let start = new Date().getTime();
for (let i = 0; i p + c) / times;
let p = document.createElement('p');
p.innerHTML = `for循环:${maxCount}次,定时器执行:${times}次,平均值:${average} ms`;
document.body.appendChild(p);
}
}, 1000);
}Define some initial data
let jsonData = {
title: 'hhhhh',
dateArr: [],
series: [
{
name: 'line1',
data: []
},
{
name: 'line2',
data: []
},
{
name: 'line3',
data: []
},
]
};
let res = [
{
name: 'line1',
value: 1
},
{
name: 'line2',
value: 2
},
{
name: 'line3',
value: 3
},
];Scenario 1: Simulate real-time update of chart data in a real environment
Data processing function
/**
* 处理json数据的函数。模拟真实环境中图表数据实时更新
* @param lastData {Object} 上一次的数据
* @param res {Array} 当前数据
* @returns data 处理完成后的结果集
*/
function handleJsonData(lastData, res) {
// 1. 使用 JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()) 深拷贝
let data = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(lastData));
// 2. 不使用JSON序列化,直接修改参数
// let data = lastData;
if (data.dateArr.length > 60) {
data.dateArr.shift();
for (let i = 0; i <h4 id="maxCount">maxCount=100</h4><p>Run it, first let maxCount=100, and loop for 100 times</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">let jsonTest = function () {
jsonData = handleJsonData(jsonData, res);
};
intervalTest(jsonTest, {maxCount: 100});1. Use JSON.parse(JSON.stringify ()) The result of deep copy:

2. The result of directly modifying parameters without using JSON serialization:
function handleJsonData(lastData, res) {
// 1. 使用 JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()) 深拷贝
// let data = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(lastData));
// 2. 不使用JSON序列化,直接修改参数
let data = lastData;
// ...
}
maxCount=1000
intervalTest(jsonTest, {maxCount: 1000});1. Use JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()) deep copy result:
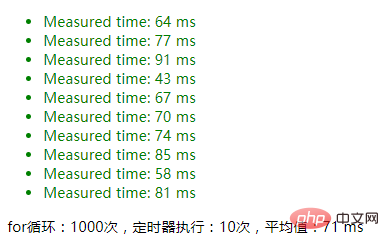
2. Do not use JSON serialization, the result of directly modifying parameters:

maxCount=10000
intervalTest(jsonTest, {maxCount: 10000});1. Use JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()) deep copy The result:
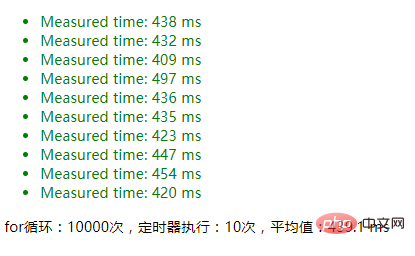
#2. Without using JSON serialization, the result of directly modifying the parameters:
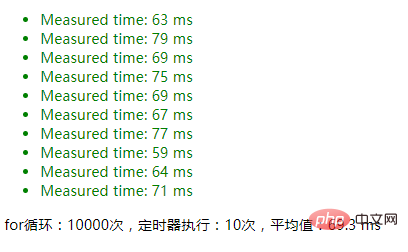
Scenario 2: Determine whether an object is an empty object
// 1. 使用 JSON.stringify() 判断一个对象是否为空对象
let isEmptyObject1 = function () {
if (JSON.stringify(jsonData) === '{}') {
// do something
}
};
// 2. 使用 Object.keys().length 判断一个对象是否为空对象
let isEmptyObject2 = function () {
if (Object.keys(jsonData).length === 0) {
// do something
}
};Just go through the judgment conditions, there is no execution code inside the if
maxCount=1000
1. Use JSON.stringify() to judge The result of whether an object is an empty object:
intervalTest(isEmptyObject1, {maxCount: 1000});
2. Use Object.keys().length to determine whether an object is an empty object. :
intervalTest(isEmptyObject2, {maxCount: 1000});
maxCount=10000
1. The result of using JSON.stringify() to determine whether an object is an empty object: 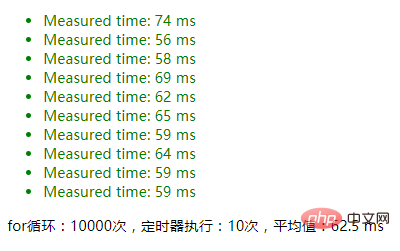
2. Use Object.keys().length to determine whether an object is an empty object. The result:
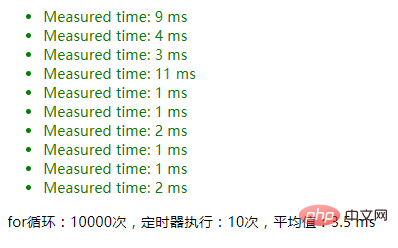
maxCount=100000
1. Use JSON.stringify() to determine whether an object is an empty object. The result:
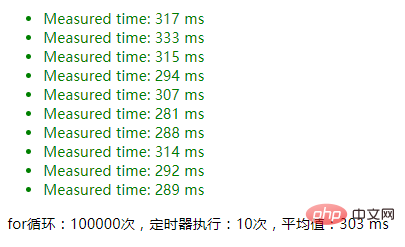
2. Use Object.keys().length to determine whether an object is an empty object. The result:

The tests on JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify() end here. Changing parameters and changing the executed code block may have different results. , the above results are for reference only.
Small conclusion: If you can not use JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify(), just use alternatives with better performance. PS: Especially code blocks that need to be executed multiple times, especially when the JSON data is relatively large
There is more knowledge about JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify() waiting for you. Go dig and welcome everyone to communicate and learn together~
About JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)): About the pitfalls that should be paid attention to when implementing deep copy of JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))
About deep copy: The ultimate exploration of deep copy (99% of people don’t know)
The above is the detailed content of Performance test of JSON.parse() and JSON.stringify() (example). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is the difference between MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What is the difference between MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0 are two different MySQL database versions. There are some main differences between them: Performance improvements: MySQL8.0 has some performance improvements compared to MySQL5.7. These include better query optimizers, more efficient query execution plan generation, better indexing algorithms and parallel queries, etc. These improvements can improve query performance and overall system performance. JSON support: MySQL 8.0 introduces native support for JSON data type, including storage, query and indexing of JSON data. This makes processing and manipulating JSON data in MySQL more convenient and efficient. Transaction features: MySQL8.0 introduces some new transaction features, such as atomic
 Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization methods for converting PHP arrays to JSON include: using JSON extensions and the json_encode() function; adding the JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE option to avoid character escaping; using buffers to improve loop encoding performance; caching JSON encoding results; and considering using a third-party JSON encoding library.
 Pandas usage tutorial: Quick start for reading JSON files
Jan 13, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Pandas usage tutorial: Quick start for reading JSON files
Jan 13, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Quick Start: Pandas method of reading JSON files, specific code examples are required Introduction: In the field of data analysis and data science, Pandas is one of the important Python libraries. It provides rich functions and flexible data structures, and can easily process and analyze various data. In practical applications, we often encounter situations where we need to read JSON files. This article will introduce how to use Pandas to read JSON files, and attach specific code examples. 1. Installation of Pandas
 How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
Annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization: Serialization: @JsonIgnore: Ignore the property @JsonProperty: Specify the name @JsonGetter: Use the get method @JsonSetter: Use the set method Deserialization: @JsonIgnoreProperties: Ignore the property @ JsonProperty: Specify name @JsonCreator: Use constructor @JsonDeserialize: Custom logic
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 In-depth understanding of PHP: Implementation method of converting JSON Unicode to Chinese
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP: Implementation method of converting JSON Unicode to Chinese
Mar 05, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
In-depth understanding of PHP: Implementation method of converting JSONUnicode to Chinese During development, we often encounter situations where we need to process JSON data, and Unicode encoding in JSON will cause us some problems in some scenarios, especially when Unicode needs to be converted When encoding is converted to Chinese characters. In PHP, there are some methods that can help us achieve this conversion process. A common method will be introduced below and specific code examples will be provided. First, let us first understand the Un in JSON
 Quick tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 03, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
Quick tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 03, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
PHP arrays can be converted to JSON strings through the json_encode() function (for example: $json=json_encode($array);), and conversely, the json_decode() function can be used to convert from JSON to arrays ($array=json_decode($json);) . Other tips include avoiding deep conversions, specifying custom options, and using third-party libraries.
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service




