 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 How to set an SSH password on Linux for passwordless login
How to set an SSH password on Linux for passwordless login
How to set an SSH password on Linux for passwordless login
This article will introduce about setting up ssh key on Linux system. In a Linux system using ssh key pair, we can also say it is passwordless ssh.
#ssh (secure shell) is widely used to log in to Linux servers remotely. When we log in to the remote system using ssh, it prompts for a password and then only allows us to log in to the server. Sometimes we need to configure an application or script (mainly shell script) to automate the tasks to be performed after ssh'ing to the remote system. However, if we do not configure key-based ssh, the script will prompt for a password every time it is run, and we will need to enter the password manually. To solve this problem, we can choose to use the public key/private key concept. Where the remote server allows other systems to ssh based on the key.
Step 1: Generate ssh key pair
First, you need to generate a key pair (rsa or dsa), you can use "- t" command line switch to specify the option rsa or dsa key. If you do not pass the -t parameter, it will create an RSA key by default.
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/rahul/.ssh/id_rsa): Created directory '/home/rahul/.ssh'. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/rahul/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/rahul/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: SHA256:GZQ3tJffEUimdMZHIG3LcpvdkOaogwXBtWeaM2ejzYY rahul@tecadmin The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 2048]----+ | ..+oo+*+o | | .+ +o** ..| | .oooB oo | | .o B =+..| | S.= *+=.o| | .X.+...| | oE.+ | | . o. | | . | +----[SHA256]-----+
The above command will create two files in the ~/.ssh directory as shown below.
1、~/.ssh/id_rsa [Private Key]
2、~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [Public Key]
Step 2: Copy the Public Key to the Remote System
Let’s copy the system’s public key to the key file of the remote system ~/.ssh/authorized_key. We can do this manually or using the ssh-copy-id command line tool.
$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub 192.168.10.20
Output:
21 root@192.168.10.20's password: Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '192.168.10.20'", and check in: .ssh/authorized_keys to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
It will prompt for the password of the remote system. Enter the remote machine password and press Enter.
Step 3: Verify SSH without Password
Now that we are done, just try to ssh to the remote system. You will log into the remote system without entering a password.
$ ssh root@192.168.10.20
The above command will not prompt for the login password. In any case, if the ssh command prompts for a password, it means your setup is not configured correctly, please retry all steps.
This article has ended here. For more exciting content, you can pay attention to other related column tutorials on the php Chinese website! ! !
The above is the detailed content of How to set an SSH password on Linux for passwordless login. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
![Telnet in Windows 11 Complete Tutorial [Installation/Enablement and Troubleshooting]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/164/168476253791019.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Telnet in Windows 11 Complete Tutorial [Installation/Enablement and Troubleshooting]
May 22, 2023 pm 09:35 PM
Telnet in Windows 11 Complete Tutorial [Installation/Enablement and Troubleshooting]
May 22, 2023 pm 09:35 PM
<p>Telnet is the abbreviation of "Terminal Network". It is a protocol that users can use to connect one computer to a local computer. </p><p>Here, the local computer refers to the device that initiates the connection, and the computer connected to the local computer is called the remote computer. </p><p>Telnet runs on a client/server principal, and although it is outdated, it is still used by many people in 2022. Many people have already switched to Windows 11 operating system, which is the latest operating system offered by Microsoft. &
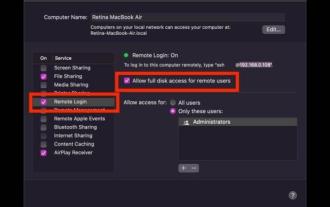 How to SSH from iPad to Mac
Apr 14, 2023 pm 12:22 PM
How to SSH from iPad to Mac
Apr 14, 2023 pm 12:22 PM
How to SSH from iPad to Mac This is a two-part walkthrough. First, you'll enable the SSH server on your Mac, and then you'll use the ssh client app to connect to it from your iPad. On Mac, start an SSH server You can enable an SSH server on your Mac by turning on a feature called Remote Login. Go to Apple Menu > System Preferences > Sharing > Enable "Remote Login" and check the "Allow remote users full access to disk" box Your Mac is now an SSH server, providing you with a shell to connect from your iPad. Notice
 Python server programming: Using Paramiko to implement SSH remote operation
Jun 18, 2023 pm 01:10 PM
Python server programming: Using Paramiko to implement SSH remote operation
Jun 18, 2023 pm 01:10 PM
With the development of cloud computing and the Internet of Things, remote operation of servers has become increasingly important. In Python, we can use the Paramiko module to easily implement SSH remote operations. In this article, we will introduce the basic usage of Paramiko and how to use Paramiko in Python to remotely manage servers. What is Paramiko Paramiko is a Python module for SSHv1 and SSHv2 that can be used to connect and control SSH clients
 OpenSSH on Windows: Installation, Configuration, and Usage Guide
Mar 08, 2024 am 09:31 AM
OpenSSH on Windows: Installation, Configuration, and Usage Guide
Mar 08, 2024 am 09:31 AM
For most Windows users, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) has always been the first choice for remote management because it provides a friendly graphical interface. However, for system administrators who require more granular control, SSH may better suit their needs. Through SSH, administrators can interact with remote devices through the command line, which can make management work more efficient. The advantage of SSH is its security and flexibility, making it easier for administrators to perform remote management and maintenance work, especially when dealing with a large number of devices or performing automated tasks. So while RDP excels in terms of user-friendliness, for system administrators, SSH is superior in terms of power and control. Previously, Windows users needed to borrow
 How to connect to Mysql database remotely using Python based on ssh
May 27, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
How to connect to Mysql database remotely using Python based on ssh
May 27, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
Background: If you need to access the Mysql database of a remote server, but for the security period of the Mysql database, the security measures are set to only allow local connections (that is, you need to log in to the server to use it), and other remote connections cannot be accessed directly, and The corresponding port has also been modified, so you need to connect to the database based on ssh. Connecting to the database in this way is the same as the interface in Navicat based on ssh connection. Navicat connects to the database installation support library. If you want to connect to Mysql, you first need to install pymysqlpipinstallpymysql to install the ssh-based library sshtunnelpipinstallsshtunnel#
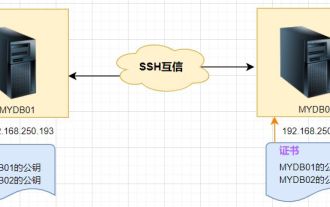 Linux SSH login mutual trust configuration
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
Linux SSH login mutual trust configuration
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
1. The purpose of ssh mutual trust 1. SSH mutual trust is required when building a cluster, which is conducive to convenient operation on another node. 2. When using scp remote copy operation, you need to enter the user name and password of the target server. At this time, you can configure SSH mutual trust between Linux servers, so that you can log in without a password when operating between multiple Linux servers. 2. The principle of ssh mutual trust configuration. In short, the server stores the certificate of the target host so that authentication can be completed automatically without entering a password. 3. SSH mutual trust configuration steps 1. Each node generates its own public key and private key pair. 2. Send your public key file to the other party. 3. Verify whether the mutual trust configuration is successful. 4. Configure ssh mutual trust here with MYDB01 and
 Does linux come with ssh?
Apr 06, 2023 pm 03:55 PM
Does linux come with ssh?
Apr 06, 2023 pm 03:55 PM
Linux comes with ssh. The Linux system will come with its own ssh software. The default is the OpenSSH related software package, and the ssh service is added to start automatically at boot. You can use the "ssh -V" command to view the installed ssh version information. Execute the "systemctl start sshd" command to start the sshd service. The default port is port 22.
 CentOS 7.9 installation and centos 7.9 installation ssh
Feb 13, 2024 pm 10:30 PM
CentOS 7.9 installation and centos 7.9 installation ssh
Feb 13, 2024 pm 10:30 PM
CentOS7.9 is a very commonly used operating system version when building servers or system management. This article will provide you with detailed steps and instructions for installing CentOS7.9 and installing SSH. CentOS7.9 is a free and open source Linux operating system. It is a binary compatible version based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The following are the steps to install CentOS7.9: 1. You need to download the ISO image file of CentOS7.9. You can download it from Download the latest CentOS7.9 ISO image file from the CentOS official website. 2. Create a new virtual machine or physical machine on your computer and install



