Spring lazy-init原理的分析(代码示例)
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于Spring lazy-init原理的分析(代码示例),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
普通的bean的初始化是在容器启动初始化阶段执行的,而被lazy-init修饰的bean 则是在从容器里第一次进行context.getBean(“”)时进行触发。Spring 启动的时候会把所有bean信息(包括XML和注解)解析转化成Spring能够识别的BeanDefinition并存到Hashmap里供下面的初始化时用。接下来对每个BeanDefinition进行处理,如果是懒加载的则在容器初始化阶段不处理,其他的则在容器初始化阶段进行初始化并依赖注入。
本文我说了很多次 Spring 容器初始化和bean初始化,容器的初始化有可能包括bean的初始化主要取决于该bean是否是懒加载的,特此说明怕误会 。。。:)
一.先睹为快
话不多说先写个例子看下这属性到底有什么作用,我们定义了一个叫做coffee的普通bean,代码如下:
1.普通非懒加载bean的演示
package com.test.spring;
public class Coffee {
public Coffee() {
System.out.println("正在初始化bean !!!调用无参构造函数");
}
}<bean name="coffee" class="com.test.spring.Coffee"/>
@Test
public void testLazyInit() {
System.out.println("开始初始化Spring容器 ");
// 非懒加载的bean会在容器初始化时进行bean的初始化,后面会拿Spring启动时的源码进行分析
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-beans.xml");
// 非懒加载的bean 的构造函数会在这个位置打印
System.out.println("Spring容器初始化完毕");
System.out.println("开始从容器中获取Bean");
Coffee coffee = context.getBean("coffee", Coffee.class);
System.out.println("获取完毕 bean :" + coffee);
}运行结果如下:
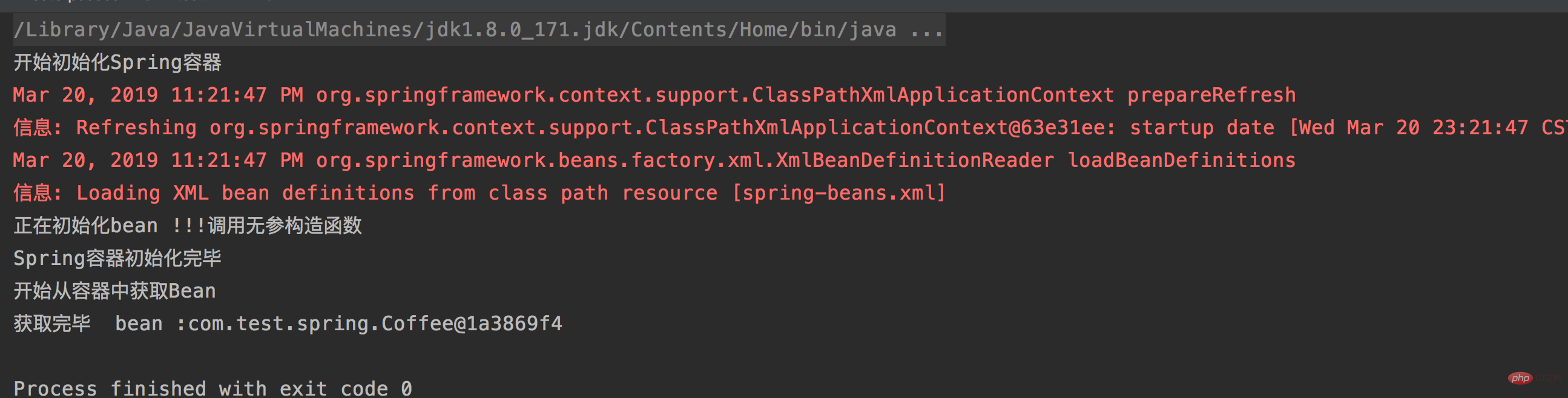
2.非懒加载bean的演示
<bean name="coffee" class="com.test.spring.Coffee" lazy-init="true" />
@Test
public void testLazyInit() {
System.out.println("开始初始化Spring容器 ");
// 在初始化容器阶段不会对懒加载的bean进行初始化
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-beans.xml");
System.out.println("Spring容器初始化完毕");
System.out.println("开始从容器中获取Bean");
// 在这一阶段会对懒加载的bean进行初始化
Coffee coffee = context.getBean("coffee", Coffee.class);
System.out.println("获取完毕 bean :" + coffee);
}运行结果如下:
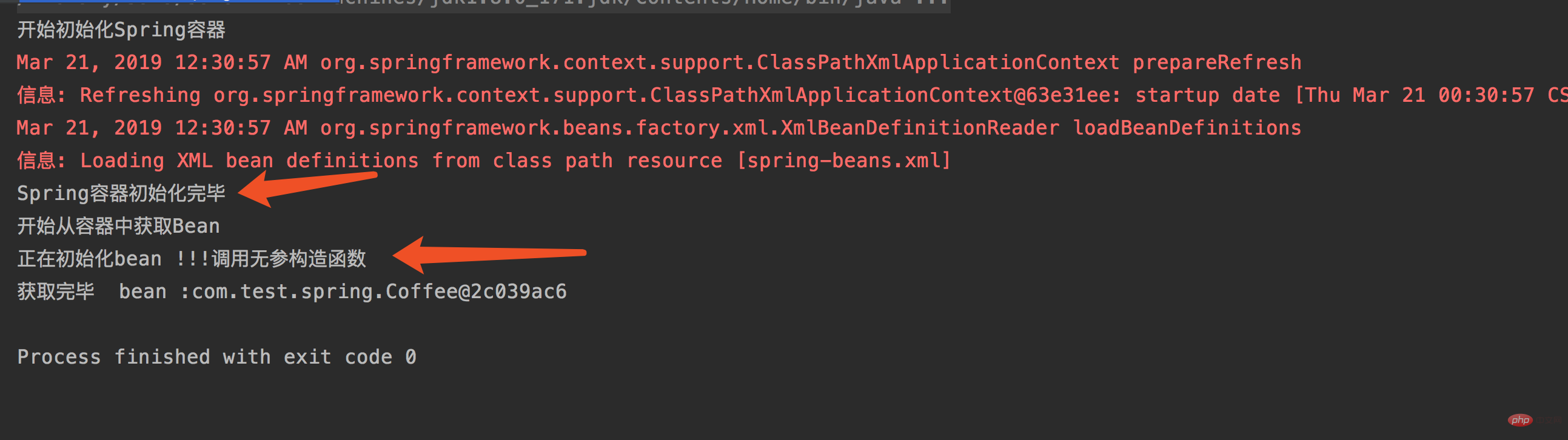
二,原理分析
Spring 启动时主要干俩件事 1.初始化容器 2.对bean进行初始化并依赖注入。(懒加载的bean不做第二件)
但是对于大多数bean来说,bean的初始化以及依赖注入就是在容器初始化阶段进行的,只有懒加载的bean是当应用程序第一次进行getBean时进行初始化并依赖注入。下面贴出代码看下
Spring 容器初始化代码如下就一行:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-beans.xml");public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// Spring ioc 启动入口 了解了refresh 就了解了ioc
refresh();
}
}Spring 初始化入口 refresh(省略了部分根本次无关的代码,望理解,太长了影响阅读体验)
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化所有非 懒加载的bean!!!!
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
}第20行则是跟本次主题有关的,就是说在容器启动的时候 只处理 non-lazy-init bean,懒加载的bean在Spring启动阶段根本不做任何处理下面看下源码就明白了
点进去第20行的finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)里头有个初始化non-lazy-init bean的函数 preInstantiateSingletons()
具体逻辑如下
1.对beanNames 集合遍历获取每个BeanDefinition
2.判断是否是懒加载的,如果不是则继续处理(non-lazy-init bean 不做处理)
3.判断是否是factorybean 如果不是则进行实例化并依赖注入
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
// 所有beanDefinition集合
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// 触发所有非懒加载单例bean的初始化
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 获取bean 定义
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 判断是否是懒加载单例bean,如果是单例的并且不是懒加载的则在Spring 容器
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 判断是否是FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
}else {
// 如果是普通bean则进行初始化依赖注入,此 getBean(beanName)接下来触发的逻辑跟
// context.getBean("beanName") 所触发的逻辑是一样的
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
}getBean() 方法是实现bean 初始化以及依赖注入的函数
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}三,总结
对于被修饰为lazy-init的bean Spring初始化阶段不会进行init并且依赖注入,当第一次进行getBean时候进行初始化并依赖注入
对于非懒加载的bean getBean的时候会从缓存里头取 因为容器初始化阶段已经初始化了
// 容器启动初始化 会初始化并依赖注入非懒加载的bean
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-beans.xml");
// lazy-init bean会进行第一次初始化并依赖注入 其他的会从缓存里取
Coffee coffee = context.getBean("coffee", Coffee.class);本篇文章到这里就已经全部结束了,更多其他精彩内容可以关注PHP中文网的Java教程视频栏目!
The above is the detailed content of Spring lazy-init原理的分析(代码示例). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
A new programming paradigm, when Spring Boot meets OpenAI
Feb 01, 2024 pm 09:18 PM
In 2023, AI technology has become a hot topic and has a huge impact on various industries, especially in the programming field. People are increasingly aware of the importance of AI technology, and the Spring community is no exception. With the continuous advancement of GenAI (General Artificial Intelligence) technology, it has become crucial and urgent to simplify the creation of applications with AI functions. Against this background, "SpringAI" emerged, aiming to simplify the process of developing AI functional applications, making it simple and intuitive and avoiding unnecessary complexity. Through "SpringAI", developers can more easily build applications with AI functions, making them easier to use and operate.
 Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
Use Spring Boot and Spring AI to build generative artificial intelligence applications
Apr 28, 2024 am 11:46 AM
As an industry leader, Spring+AI provides leading solutions for various industries through its powerful, flexible API and advanced functions. In this topic, we will delve into the application examples of Spring+AI in various fields. Each case will show how Spring+AI meets specific needs, achieves goals, and extends these LESSONSLEARNED to a wider range of applications. I hope this topic can inspire you to understand and utilize the infinite possibilities of Spring+AI more deeply. The Spring framework has a history of more than 20 years in the field of software development, and it has been 10 years since the Spring Boot 1.0 version was released. Now, no one can dispute that Spring
 What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
What are the implementation methods of spring programmatic transactions?
Jan 08, 2024 am 10:23 AM
How to implement spring programmatic transactions: 1. Use TransactionTemplate; 2. Use TransactionCallback and TransactionCallbackWithoutResult; 3. Use Transactional annotations; 4. Use TransactionTemplate in combination with @Transactional; 5. Customize the transaction manager.
 How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
May 24, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
May 24, 2023 pm 01:28 PM
Java implements scheduled tasks In the library that comes with Jdk, there are two ways to implement scheduled tasks, one is Timer, and the other is ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor. When Timer+TimerTask creates a Timer, it creates a thread, which can be used to schedule TimerTask tasks. Timer has four construction methods, and you can specify the name of the Timer thread and whether to set it as a daemon thread. The default name is Timer-number, and the default is not a daemon thread. There are three main methods: cancel(): terminate task scheduling, cancel all currently scheduled tasks, running tasks will not be affected purge(): remove tasks from the task queue
 The differences and connections between Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Jun 22, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
The differences and connections between Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Jun 22, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
SpringBoot and SpringCloud are both extensions of Spring Framework that help developers build and deploy microservice applications faster, but they each have different purposes and functions. SpringBoot is a framework for quickly building Java applications, allowing developers to create and deploy Spring-based applications faster. It provides a simple, easy-to-understand way to build stand-alone, executable Spring applications
 How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set transaction isolation level in Spring
Jan 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
How to set the transaction isolation level in Spring: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation; 2. Set it in the Spring configuration file; 3. Use PlatformTransactionManager; 4. Set it in the Java configuration class. Detailed introduction: 1. Use the @Transactional annotation, add the @Transactional annotation to the class or method that requires transaction management, and set the isolation level in the attribute; 2. In the Spring configuration file, etc.
 The 7 most commonly used annotations in Spring, the most powerful organization in history!
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
The 7 most commonly used annotations in Spring, the most powerful organization in history!
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
With the update and iteration of technology, Java5.0 began to support annotations. As the leading framework in Java, spring has slowly begun to abandon xml configuration since it was updated to version 2.5, and more annotations are used to control the spring framework.
 Learn Spring Cloud from scratch
Jun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
Learn Spring Cloud from scratch
Jun 22, 2023 am 08:11 AM
As a Java developer, learning and using the Spring framework is an essential skill. With the popularity of cloud computing and microservices, learning and using Spring Cloud has become another skill that must be mastered. SpringCloud is a development toolset based on SpringBoot for quickly building distributed systems. It provides developers with a series of components, including service registration and discovery, configuration center, load balancing and circuit breakers, etc., allowing developers to build micro




