Changes brought about by PHP7's Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)

What is an abstract syntax tree?
Abstract syntax tree (AST) is a tree representation of the abstract syntax structure of the source code. Each node on the tree represents a structure in the source code. This is why It is abstract because the abstract syntax tree does not represent every detail of the real grammar. For example, nested brackets are implicit in the structure of the tree and are not presented in the form of nodes. The abstract syntax tree does not depend on the grammar of the source language, which means that the context-free grammar used in the syntax analysis stage [Grammar is the formal rules used to describe the grammatical structure of a language. Any language has its own grammar, whether it is machine language or natural language. 】, because when writing grammar, equivalent transformations are often performed on the grammar (elimination of left recursion, backtracking, ambiguity, etc.), which will introduce some redundant components into the grammar analysis, adversely affect the subsequent stages, and even Make the whole stage confusing. For this reason, many compilers often need to construct syntax analysis trees independently to establish a clear interface for the front end and back end
PHP-Parser’s project homepage is https://github.com/nikic/PHP- Parser. It can perfectly parse multiple versions of PHP and generate an abstract syntax tree.
New execution process
An important change in the core of PHP7 is the addition of AST. In PHP5, the execution process from php scripts to opcodes is:
1.Lexing: lexical scanning analysis, converting source files into token streams;
2.Parsing: syntax analysis, Op arrays are generated at this stage.
In PHP7, op arrays are no longer directly generated during the syntax analysis phase, but AST is generated first, so there is one more step in the process:
1.Lexing: lexical scanning analysis, converting the source file into token stream;
2.Parsing: syntax analysis, generating abstract syntax tree from token stream;
3.Compilation: generating op arrays from abstract syntax tree.
Execution time and memory consumption
From the above steps, this is one more step than the previous process, so according to common sense, this will increase the program execution time and memory usage. But in fact, the memory usage has indeed increased, but the execution time has decreased.
The following results are obtained by testing three scripts: small (about 100 lines of code), medium (about 700 lines), and large (about 2800 lines). Test script: https://gist.github .com/nikic/289b0c7538b46c2220bc.
Execution time of compiling each file 100 times (note that the test results of the article are from 14 years, when PHP7 was still called PHP-NG):
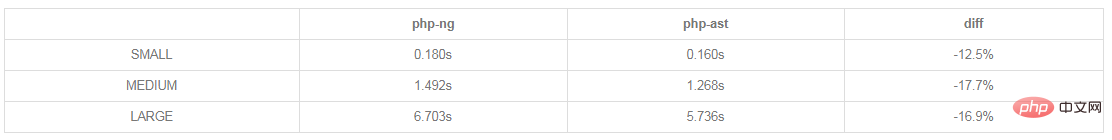
Memory peak value in a single compilation:
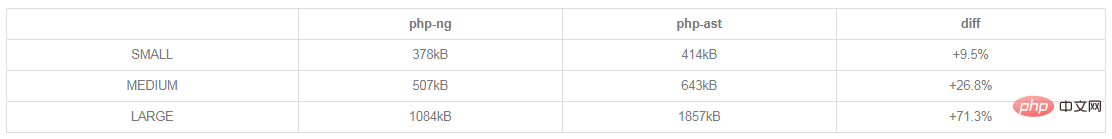
The test results of a single compilation may not represent actual usage. The following is using PhpParser The results of the complete project test:

The test shows that after using AST, the overall execution time of the program is improved by about 10% to 15%, but the memory consumption is also increased. , the increase is obvious in a single compilation of large files, but it is not a serious problem during the entire project execution.
Also note that the above results are all without Opcache. When Opcache is turned on in a production environment, the increase in memory consumption is not a big problem.
Semantic changes
If it is just a time optimization, it does not seem to be a sufficient reason to use AST. In fact, the implementation of AST is not based on time optimization considerations, but to solve syntax problems. Let’s take a look at some changes in semantics.
yield does not require parentheses
In the PHP5 implementation, if you use yield in an expression context (such as on the right side of an assignment expression), you You must use parentheses on both sides of the yield declaration:
<?php $result = yield fn(); // 不合法的 $result = (yield fn()); // 合法的
This behavior is only due to the implementation limitations of PHP5. In PHP7, parentheses are no longer necessary. Therefore, the following writing methods are also legal:
<?php $result = yield; $result = yield $v; $result = yield $k => $v;
Of course, you must follow the application scenarios of yield.
Brackets do not affect behavior
In PHP5,
<?php ($foo)['bar'] = 'baz'; # PHP Parse error: Syntax error, unexpected '[' on line 1
But in PHP7, the two writing methods mean the same thing.
Similarly, if the parameters of the function are wrapped in parentheses, there is a problem with type checking. This problem has also been solved in PHP7:
<?php
function func() {
return [];
}
function byRef(array &$a) {
}
byRef((func()));The above code will not alarm in PHP5 unless byRef is used (func()), but in PHP7, the following error will occur regardless of whether there are parentheses on both sides of func():
PHP Strict standards: Only variables should be passed by reference ...
Changes in list()
list 关键字的行为改变了很多。list 给变量赋值的顺序(等号左右同时的顺序)以前是从右至左,现在是从左到右:
<?php list($array[], $array[], $array[]) = [1, 2, 3]; var_dump($array); // PHP5: $array = [3, 2, 1] // PHP7: $array = [1, 2, 3] # 注意这里的左右的顺序指的是等号左右同时的顺序, # list($a, $b) = [1, 2] 这种使用中 $a == 1, $b == 2 是没有疑问的。
产生上面变化的原因正是因为在 PHP5 的赋值过程中,3 会最先被填入数组,1 最后,但是现在顺序改变了。
同样的变化还有:
<?php $a = [1, 2]; list($a, $b) = $a; // PHP5: $a = 1, $b = 2 // PHP7: $a = 1, $b = null + "Undefined index 1"
这是因为在以前的赋值过程中 $b 先得到 2,然后 $a 的值才变成1,但是现在 $a 先变成了 1,不再是数组,所以 $b 就成了null。
list 现在只会访问每个偏移量一次
<?php list(list($a, $b)) = $array; // PHP5: $b = $array[0][1]; $a = $array[0][0]; // PHP7: // 会产生一个中间变量,得到 $array[0] 的值 $_tmp = $array[0]; $a = $_tmp[0]; $b = $_tmp[1];
空的 list 成员现在是全部禁止的,以前只是在某些情况下:
<?php list() = $a; // 不合法 list($b, list()) = $a; // 不合法 foreach ($a as list()) // 不合法 (PHP5 中也不合法)
引用赋值的顺序
引用赋值的顺序在 PHP5 中是从右到左的,现在时从左到右:
<?php
$obj = new stdClass;
$obj->a = &$obj->b;
$obj->b = 1;
var_dump($obj);
// PHP5:
object(stdClass)#1 (2) {
["b"] => &int(1)
["a"] => &int(1)
}
// PHP7:
object(stdClass)#1 (2) {
["a"] => &int(1)
["b"] => &int(1)
}__clone 方法可以直接调用
现在可以直接使用 $obj->__clone() 的写法去调用 __clone 方法。 __clone 是之前唯一一个被禁止直接调用的魔术方法,之前你会得到一个这样的错误:
Fatal error:Cannot call __clone() method on objects -use 'clone $obj' instead in...
变量语法一致性
AST 也解决了一些语法一致性的问题,这些问题是在另外一个 RFC 中被提出的:https://wiki.php.net/rfc/uniform_variable_syntax.
在新的实现上,以前的一些语法表达的含义和现在有些不同,具体的可以参照下面的表格:

整体上还是以前的顺序是从右到左,现在从左到右,同时也遵循括号不影响行为的原则。这些复杂的变量写法是在实际开发中需要注意的。
相关推荐:《PHP教程》
The above is the detailed content of Changes brought about by PHP7's Abstract Syntax Tree (AST). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to install mongo extension in php7.0
Nov 21, 2022 am 10:25 AM
How to install mongo extension in php7.0
Nov 21, 2022 am 10:25 AM
How to install the mongo extension in php7.0: 1. Create the mongodb user group and user; 2. Download the mongodb source code package and place the source code package in the "/usr/local/src/" directory; 3. Enter "src/" directory; 4. Unzip the source code package; 5. Create the mongodb file directory; 6. Copy the files to the "mongodb/" directory; 7. Create the mongodb configuration file and modify the configuration.
 How to solve the problem when php7 detects that the tcp port is not working
Mar 22, 2023 am 09:30 AM
How to solve the problem when php7 detects that the tcp port is not working
Mar 22, 2023 am 09:30 AM
In php5, we can use the fsockopen() function to detect the TCP port. This function can be used to open a network connection and perform some network communication. But in php7, the fsockopen() function may encounter some problems, such as being unable to open the port, unable to connect to the server, etc. In order to solve this problem, we can use the socket_create() function and socket_connect() function to detect the TCP port.
 What should I do if the plug-in is installed in php7.0 but it still shows that it is not installed?
Apr 02, 2024 pm 07:39 PM
What should I do if the plug-in is installed in php7.0 but it still shows that it is not installed?
Apr 02, 2024 pm 07:39 PM
To resolve the plugin not showing installed issue in PHP 7.0: Check the plugin configuration and enable the plugin. Restart PHP to apply configuration changes. Check the plugin file permissions to make sure they are correct. Install missing dependencies to ensure the plugin functions properly. If all other steps fail, rebuild PHP. Other possible causes include incompatible plugin versions, loading the wrong version, or PHP configuration issues.
 What is AST Inspector? How to use the PHP AST step debugger?
Nov 08, 2022 pm 04:39 PM
What is AST Inspector? How to use the PHP AST step debugger?
Nov 08, 2022 pm 04:39 PM
This article will introduce to you what AST Inspector is and how to use the PHP AST step debugger. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need~
 How to install and deploy php7.0
Nov 30, 2022 am 09:56 AM
How to install and deploy php7.0
Nov 30, 2022 am 09:56 AM
How to install and deploy php7.0: 1. Go to the PHP official website to download the installation version corresponding to the local system; 2. Extract the downloaded zip file to the specified directory; 3. Open the command line window and go to the "E:\php7" directory Just run the "php -v" command.
 PHP Server Environment FAQ Guide: Quickly Solve Common Problems
Apr 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
PHP Server Environment FAQ Guide: Quickly Solve Common Problems
Apr 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
Common solutions for PHP server environments include ensuring that the correct PHP version is installed and that relevant files have been copied to the module directory. Disable SELinux temporarily or permanently. Check and configure PHP.ini to ensure that necessary extensions have been added and set up correctly. Start or restart the PHP-FPM service. Check the DNS settings for resolution issues.
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 How should Python Ast abstract syntax tree be used?
May 09, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
How should Python Ast abstract syntax tree be used?
May 09, 2023 pm 12:49 PM
IntroductionAbstractSyntaxTrees are abstract syntax trees. Ast is an intermediate product from Python source code to bytecode. With the help of the ast module, the source code structure can be analyzed from the perspective of a syntax tree. In addition, we can not only modify and execute the syntax tree, but also unparse the syntax tree generated by Source into python source code. Therefore, ast leaves enough room for Python source code checking, syntax analysis, code modification, and code debugging. 1. Introduction to AST. The CPython interpreter officially provided by Python processes python source code as follows: Parsesourcecodeintoaparsetree(Parse




