Comparison of MySQL and Redis transactions (picture and text)
The content of this article is about the comparison of MySQL and Redis transactions (pictures and texts). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
In short: Generally speaking, transactions must meet four conditions (ACID): atomicity (Atomicity, or indivisibility), consistency (Consistency), isolation (Isolation, also known as independence), durability (Durability).
Judging from the title, since they are both transactions, what is the difference between them? Let’s unravel them one by one, starting with the two databases.
MySQL belongs to relational database, and Redis belongs to non-relational database. They have different interpretations of transactions.
(Related recommendations: MySQL Tutorial, Redis Tutorial)
Redis
[1] Redis transactions can execute multiple transactions at one time command, and comes with the following two important guarantees:
- Batch operations are put into the queue cache before sending the EXEC command.
- Enter transaction execution after receiving the EXEC command. If any command in the transaction fails to execute, the remaining commands are still executed.
- During the transaction execution process, command requests submitted by other clients will not be inserted into the transaction execution command sequence.
A transaction will go through the following three stages from start to execution:
- Start transaction.
- Command to join the queue.
- Execute transactions.
The execution of a single Redis command is atomic, but Redis does not add any mechanism to maintain atomicity on the transaction, so the execution of the Redis transaction is not atomic.
A transaction can be understood as a packaged batch execution script, but batch instructions are not atomic operations. The failure of an instruction in the middle will not cause the rollback of the previous instructions, nor It will not cause subsequent instructions not to be executed.
Operation error
It seems a bit convoluted, so let’s actually execute it and see the results.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
In the above transaction, a string data with key tr_1 is set, and then elements are added through lpush. This is obviously wrong. Operation mode, when we submit the transaction, an operation error occurs. At this time, let’s take a look at the value of tr_1.
1 2 |
|
The content of tr_1 obtained through the get command is still 233 and has not changed. Let’s take a look at the others.
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
Here you can see that tr_2 exists and the value is printed. At this time, we found that even if an operation error occurred, the error did not No Causes the execution to stop, and the statement after the error is also executed and executed successfully, which seems to be in line with the above mentioned The failure of a certain instruction in the middle will not cause the rollback of the previous instruction, nor will it cause subsequent instructions Don't do it.
Syntax error
NO~, there is another situation at this timeSyntax error
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
When we execute to No parameters were given when setting, and one parameter was deliberately given during the second execution. You can see that syntax error was reported, and the transaction was finally submitted, which also told us that the transaction was lost due to the error. Then we used keys * to search and found that this was indeed the case.
Document Interpretation
Here you can find the
Errors inside a transaction mentioned in the official document
// You may encounter during execution to two wrong command errors.
During a transaction it is possible to encounter two kind of command errors:
//
1. The command cannot be entered into the queue, such as: wrong number of parameters, wrong command name ..., or some critical errors such as insufficient memory
- A command may fail to be queued, so there may be an error before EXEC is called. For instance the command may be syntactically wrong (wrong number of arguments, wrong command name, ...), or there may be some critical condition like an out of memory condition (if the server is configured to have a memory limit using the
maxmemorydirective).//
2. Perform wrong operations on keys, such as using lpush on strings above
- A command may fail after EXEC is called, for instance since we performed an operation against a key with the wrong value (like calling a list operation against a string value).
// The client checks the typed command, Most of the time, a
first typeerror will be found before callingexec. If the command execution returns QUEUED, it means that the command enters the queue normally. Otherwise, there is an error. In most cases, the client will terminate. Abandon this transaction.Clients used to sense the first kind of errors, happening before the EXEC call, by checking the return value of the queued command: if the command replies with QUEUED it was queued correctly, otherwise Redis returns an error. If there is an error while queueing a command, most clients will abort the transaction discarding it.
关于 Redis 暂时看到这里 接下来看到 MySQL
MySQL
众所周知,MySQL 只有 InnoDB 引擎支持 事务,在启用 MySQL 事务之前需要先停掉自动提交
测试表结构 user
| 列 | 类型 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|
| id | int(11) 自动增量 | 主键ID |
| money | int(11) [0] | 金钱 |
| title | varchar(500) NULL | 称呼 |
在这里来模拟一个转账的操作:A给B转100元。
步骤解析 A+100 元,B -100元,即两步虽然很简单,简单走一下流程。
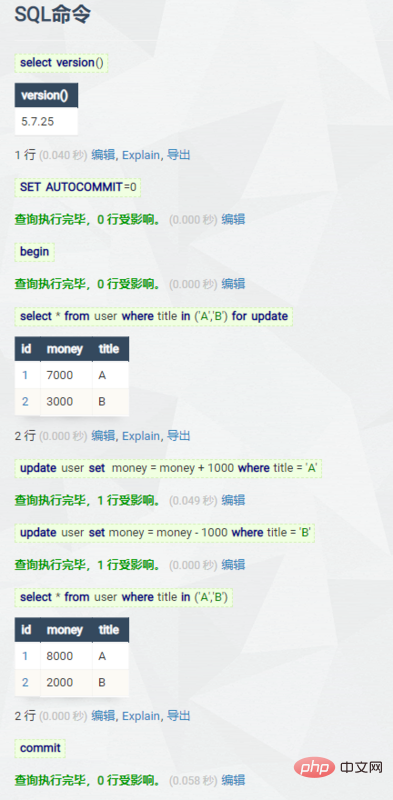
可以看到,没有问题,那么我们从中人为的制造一些问题呢?
操作错误
| 列 | 类型 | 注释 |
| id | int(11) 自动增量 | |
| money | int(11) unsigned [0]
|
|
| title | varchar(500) NULL |
这里我们把 money 字段变成了无符号,即不能小于 0,并且,调整数据库中的数据如下。
1 |
|
| 修改 | id | money | title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 编辑 | 1 | 10000 | A |
| 编辑 | 2 | 0 | B |
接着执行下面的 SQL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
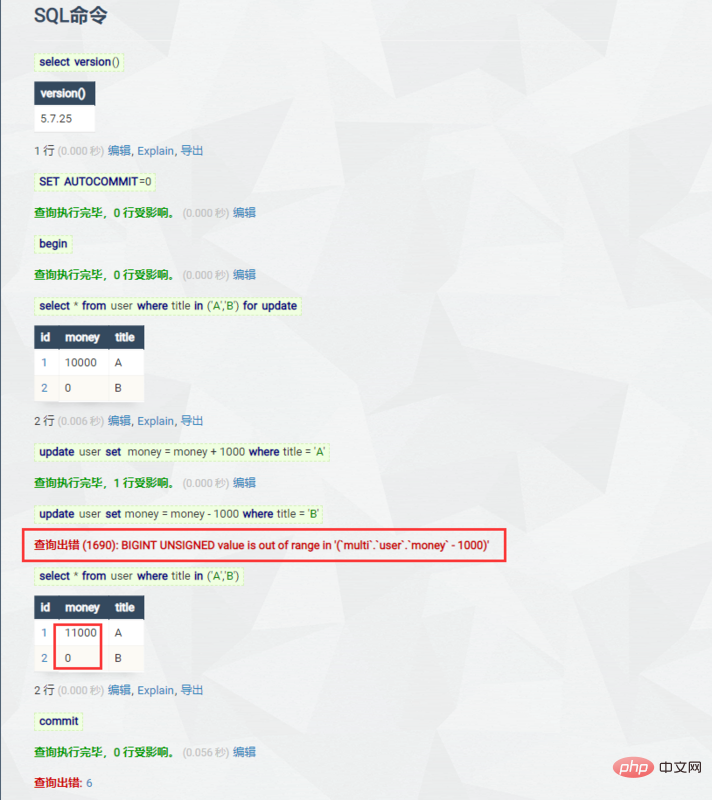
问题出现了,这里报出了错误,但是可以看到 前面的 SQL 已经是已执行的了,结果已经发生了变化,从这里看,似乎和 Redis 的处理差不多,除了错误之后语句继续执行。但是 值的注意的是, 在我们实际开发中,这种情况程序会直接抛出异常,以供我们在 catch 块中执行 rollback ,以回滚操作确保数据完整,即使是单独使用 MySQL 命令行 我们也可以用存储过程来对异常进行回滚。
语法错误
刚刚看到 Redis 当遇到 语法错误 时会自动丢弃事务,阻止提交,那 MySQL 呢?
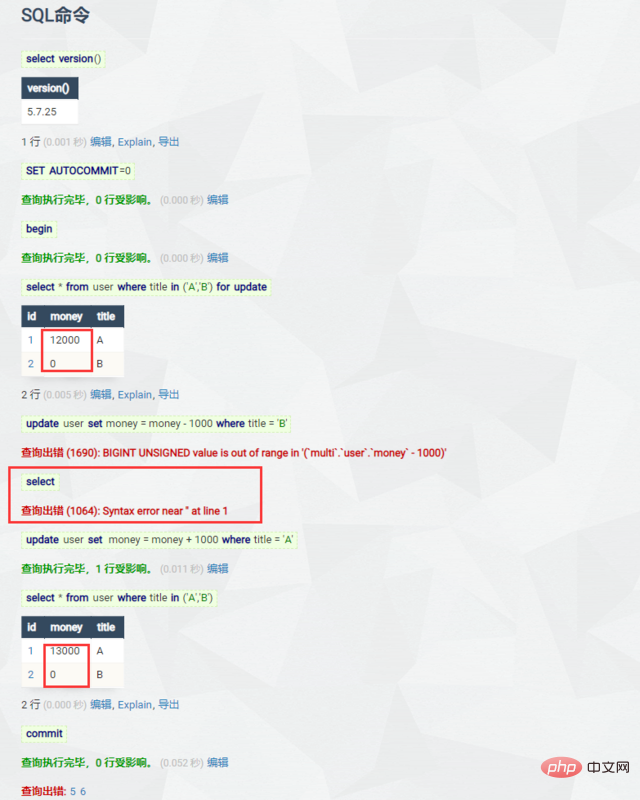
答案:不会,MySQL 在顺序执行时,如果未对异常进行处理,总会将成功执行的的提交,而不会触发自动终止,但是我们可以在程序执行时进行放弃提交。
Redis 为什么没有回滚?
Redis 的官方文档给出了这样的解释
// 只有在使用错误的语法调用时才会失败Redis命令(并且在命令排队期间无法检测到问题),或者对于持有错误数据类型的键,Redis命令可能会失败:这意味着实际上失败的命令是编程错误的结果,以及在开发过程中很可能检测到的一种错误,而不是在生产中。
- Redis commands can fail only if called with a wrong syntax (and the problem is not detectable during the command queueing), or against keys holding the wrong data type: this means that in practical terms a failing command is the result of a programming errors, and a kind of error that is very likely to be detected during development, and not in production.
// Redis内部简化且速度更快,因为它不需要回滚的能力。
- Redis is internally simplified and faster because it does not need the ability to roll back.
总结
| 数据库 自动回滚条件 | 操作错误 | 语法错误 |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | ✖ | ✖ |
| Redis | ✖ | ✔ |
但是 MySQL 支持手动回滚,实际开发过程中可以自行手动对已提交的操作进行回滚操作,更加友好。
The above is the detailed content of Comparison of MySQL and Redis transactions (picture and text). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.




