What are the common annotations for springboot?
Commonly used annotations in springboot include: 1. SpringBootApplication; 2. Repository; 3. Service; 4. RestController; 5. ResponseBody; 6. Component, etc.

Commonly used annotations in springboot are:
1, @SpringBootApplication
This annotation is the core annotation of Spring Boot. It is used on the main class of Spring Boot to identify this as a Spring Boot application and is used to enable various capabilities of Spring Boot. In fact, this annotation is a combination of three annotations: @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan. Since these annotations are generally used together, Spring Boot provides a unified annotation @SpringBootApplication.
2. @EnableAutoConfiguration
Allow Spring Boot to automatically configure annotations. After turning on this annotation, Spring Boot can configure Spring based on the packages or classes in the current class path. Beans.
For example: There is the Mybatis JAR package under the current class path, and the MybatisAutoConfiguration annotation can configure each Spring Bean of Mybatis according to relevant parameters.
The key to the implementation of @EnableAutoConfiguration is the introduction of AutoConfigurationImportSelector. Its core logic is the selectImports method. The logic is roughly as follows:
● Load all possible components from the configuration file META-INF/spring.factories Automatic configuration classes;
● Remove duplication and exclude classes carried by the exclude and excludeName attributes;
● Filter and return automatic configuration classes that meet the conditions (@Conditional);
3. @Configuration
is used to define the configuration class, indicating that this class is the information source for Bean configuration, which is equivalent to the traditional xml configuration file and is generally added to the main class. If some third-party libraries need to use xml files, it is recommended to still use the @Configuration class as the main configuration class of the project - you can use the @ImportResource annotation to load the xml configuration file.
4. @ComponentScan
Component scan. Let spring Boot scan the Configuration class and add it to the program context.
The @ComponentScan annotation will assemble classes annotated with @Controller, @Service, @Repository, and @Component into the spring container by default.
5, @Repository
is used to mark data access components, that is, DAO components.
Using the @Repository annotation can ensure that DAO or repositories provide exception translation. The DAO or repositories class modified by this annotation will be discovered and configured by ComponentScan, and there is no need to provide XML configuration items for them.
6, @Service
Generally used to modify the components of the service layer
7, @RestController
is used to mark control layer components (such as action in struts), indicating that this is a controller bean, and the return value of the function is directly filled in the HTTP response body. It is a REST style controller; it is @Controller and Collection of @ResponseBody.
8, @ResponseBody
means that the return result of this method is directly written into the HTTP response body
is generally used when obtaining data asynchronously. After using @RequestMapping, the return value is usually parsed as a jump path. After adding @responsebody, the return result will not be parsed as a jump path, but will be written directly into the HTTP response body. For example, if you obtain json data asynchronously and add @responsebody, the json data will be returned directly.
9. @Component
refers to components in general. When components are difficult to classify, we can use this annotation to annotate them.
10. @Bean
is equivalent to
11, @AutoWired
byType method. Use the configured beans to complete the assembly of properties and methods. It can annotate class member variables, methods and constructors to complete automatic assembly.
When (required=false) is added, no error will be reported even if the bean cannot be found.
12. @Qualifier
When there are multiple beans of the same type, you can use @Qualifier("name") to specify. Used in conjunction with @Autowired
13, @Resource(name="name",type="type")
If there is no content in brackets, byName will be used by default. Do similar things with @Autowired.
14, @RequestMapping
RequestMapping is an annotation used to process request address mapping; provides routing information and is responsible for mapping URLs to specific functions in Controller. Available on a class or method. Used on a class, it means that all methods in the class that respond to requests use this address as the parent path.
15. @RequestParam
is used in front of the parameters of the method. Example:
@RequestParam String a =request.getParameter("a")。16, @PathVariable
Path variable. The parameters must be the same as the names in the curly brackets. Example:
RequestMapping("user/get/mac/{macAddress}")
public String getByMacAddress(@PathVariable String macAddress){
//do something;
}17, @Profiles
Spring Profiles provide a way to isolate application configurations and allow these configurations to only take effect in specific environments .
任何@Component或@Configuration都能被@Profile标记,从而限制加载它的时机。
@Configuration
@Profile("prod")
public class ProductionConfiguration {
// ...
}18、@ConfigurationProperties
Spring Boot可使用注解的方式将自定义的properties文件映射到实体bean中,比如config.properties文件。
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties("rocketmq.consumer")
public class RocketMQConsumerProperties extends RocketMQProperties {
private boolean enabled = true;
private String consumerGroup;
private MessageModel messageModel = MessageModel.CLUSTERING;
private ConsumeFromWhere consumeFromWhere = ConsumeFromWhere.CONSUME_FROM_LAST_OFFSET;
private int consumeThreadMin = 20;
private int consumeThreadMax = 64;
private int consumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan = 2000;
private int pullThresholdForQueue = 1000;
private int pullInterval = 0;
private int consumeMessageBatchMaxSize = 1;
private int pullBatchSize = 32;
}以上就是本篇文章的全部内容,希望能对大家的学习有所帮助。更多精彩内容大家可以关注php中文网相关教程栏目!!!
The above is the detailed content of What are the common annotations for springboot?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
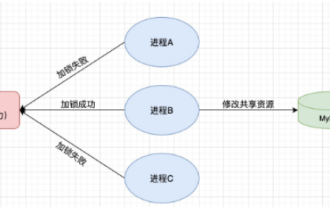 How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
1. Redis implements distributed lock principle and why distributed locks are needed. Before talking about distributed locks, it is necessary to explain why distributed locks are needed. The opposite of distributed locks is stand-alone locks. When we write multi-threaded programs, we avoid data problems caused by operating a shared variable at the same time. We usually use a lock to mutually exclude the shared variables to ensure the correctness of the shared variables. Its scope of use is in the same process. If there are multiple processes that need to operate a shared resource at the same time, how can they be mutually exclusive? Today's business applications are usually microservice architecture, which also means that one application will deploy multiple processes. If multiple processes need to modify the same row of records in MySQL, in order to avoid dirty data caused by out-of-order operations, distribution needs to be introduced at this time. The style is locked. Want to achieve points
 How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot reads the file, but cannot access the latest development after packaging it into a jar package. There is a situation where springboot cannot read the file after packaging it into a jar package. The reason is that after packaging, the virtual path of the file is invalid and can only be accessed through the stream. Read. The file is under resources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 How are annotations used for test methods in the JUnit framework?
May 06, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
How are annotations used for test methods in the JUnit framework?
May 06, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
Annotations in the JUnit framework are used to declare and configure test methods. The main annotations include: @Test (declaration of test methods), @Before (method run before the test method is executed), @After (method run after the test method is executed), @ BeforeClass (method that runs before all test methods are executed), @AfterClass (method that runs after all test methods are executed), these annotations help organize and simplify the test code, and improve the reliability of the test code by providing clear intentions and configurations. Readability and maintainability.
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
When Springboot+Mybatis-plus does not use SQL statements to perform multi-table adding operations, the problems I encountered are decomposed by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object with parameters to simulate passing parameters to the background. We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use tools such as Mybatis-plus-join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper.xml file and configure The smelly and long ResultMap, and then write the corresponding sql statement. Although this method seems cumbersome, it is highly flexible and allows us to
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 The King of PHP Code Documentation: An Advanced Guide to PHPDoc
Mar 02, 2024 am 08:43 AM
The King of PHP Code Documentation: An Advanced Guide to PHPDoc
Mar 02, 2024 am 08:43 AM
Introduction: PHPDoc is a comment standard for PHP code that produces easy-to-understand and informative documentation. By using specific comment tags, PHPDoc allows developers to provide important details about functions, classes, methods, and other code elements. This advanced guide takes an in-depth look at PHPDoc, demonstrating its capabilities and providing effective documentation strategies. Syntax and tags: PHPDoc comments start with double slashes (//) or multi-line comments (/**/). Here are some common annotation tags: @param: Defines the parameters of a function or method. @return: Specifies the return value of the function or method. @throws: Describes exceptions that may be thrown by a function or method. @var: defines the attributes or instances of the class
 How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. Customize RedisTemplate1.1, RedisAPI default serialization mechanism. The API-based Redis cache implementation uses the RedisTemplate template for data caching operations. Here, open the RedisTemplate class and view the source code information of the class. publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations, BeanClassLoaderAware{//Declare key, Various serialization methods of value, the initial value is empty @NullableprivateRedisSe
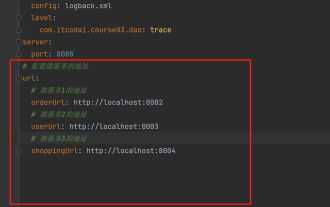 How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
In projects, some configuration information is often needed. This information may have different configurations in the test environment and the production environment, and may need to be modified later based on actual business conditions. We cannot hard-code these configurations in the code. It is best to write them in the configuration file. For example, you can write this information in the application.yml file. So, how to get or use this address in the code? There are 2 methods. Method 1: We can get the value corresponding to the key in the configuration file (application.yml) through the ${key} annotated with @Value. This method is suitable for situations where there are relatively few microservices. Method 2: In actual projects, When business is complicated, logic



