For Android application optimization encyclopedia
For technical practitioners, many times it’s not that they don’t know how to do it, but that they don’t know what to do? Today I have collected some experiences on how to optimize Android applications. , a total of eight dimensions.
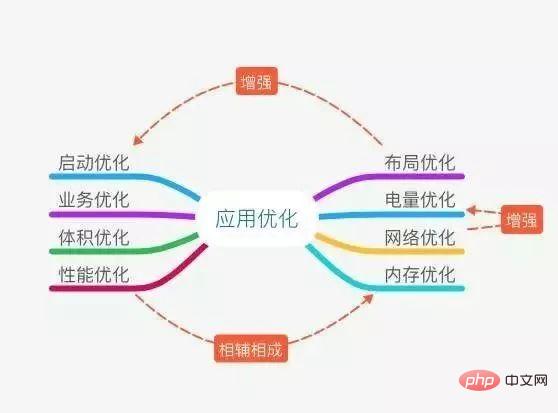
#1. Layout optimization
Why?
The Android system sends out a VSYNC signal every 16ms to trigger the rendering of the UI. To achieve a smooth interface, 60fps must be achieved, which means that most The operation must be completed within 16ms. In addition to the above interface being too complex and rendering not being completed in time, there is also the problem of over-drawing. The so-called over-drawing means that a certain pixel is drawn multiple times in the same frame. In a multi-level UI interface, if the invisible UI is also being drawn, then the pixels in these overlapping areas will be drawn multiple times, thus wasting a lot of CPU and GPU resources. Overdrawing also occurs when the background overlaps , for example, the Layout has its own background, and the sub-View has its own background.How to detect?
- Use HierarchyViewer to find Is the layout in the Activity too complex?
- Open the Show GPU Overdraw option in the developer options to observe whether there is overdrawing
- In the developer Select Profile GPU Rendering in the options, select On screen as bar
- Use TraceView to observe CPU execution
- Reduce the layout level and rationally use include, merge, and ViewStub
- Avoid a large number of creations in onDraw() of custom components Temporary objects, such as String, to avoid frequently triggering GC
- In onDraw() of custom components, consider using canvas.clipRect() to draw the area that needs to be drawn
- Consider using components with higher performance. For example, it is recommended to use RecycleView instead of ListView. Use staticlayout to achieve automatic line wrapping
Why?2. Memory optimization
Resources are always limited, and memory is also a resource. In Android, excessive/inappropriate occupation of memory resources will cause applications to be killed frequently, and eventually It will also affect the overall user experience. Any developer should keep saving memory in mind.
How to detect?- Use LeakCanary
- Use MAT to analyze Java heap
- Use Application Tracker in Android Device Monitor to track memory allocation information
- Android Monitor in Android Studio, select Memory
- Active Release memory, release memory appropriately in onLowMemory() and onTrimMemory()
- Avoid memory leaks and memory overflow
- When using Bitmap At this time, consider compressing it, using caching or changing the color mode. For example, the default color format of android is ARGB_8888. If the requirements are not high, you can use RGB__565, so that the memory occupied by each pixel can be 4byte to 2byte.
- Reduce the use of frame animation, if necessary, implement it through SurfaceView
- Use more lightweight data structures, such as ArrayMap/SparseArray
- Reasonably use related components, such as Service and Webview, and actively end their life cycles when they are not needed
Reasonable use of multiple processes, such as the music player class, can be divided into the main process and the playback process
Consider bounded queues when using asynchronous queues
If you can clearly know the size of HashMap, then set the capacity for it during initialization
3. Battery Optimization
Why?
Battery is a very precious resource for mobile devices. As a developer, you have It is necessary to consider the user and reduce power consumption. Surveys show that usually only about 30% of the power is consumed by the core functions of the program, such as interface rendering, and the remaining 70% is consumed by reporting data, location updates, and background notifications .
How to detect?
View the APP’s power consumption statistics in the phone options
Use Battery Historian Tool to view detailed power consumption
How to optimize?
Reduce the number of times you wake up the screen With the duration, use WakeLock correctly.
When delaying non-essential operations to the charging state, such as log reporting, it can be completed during night charging. This can be used in conjunction with JobScheduler
When using sensors to collect data, remember to cancel the registration once it is no longer needed.
Reduce network communication and merge communication.
Use the positioning function rationally, reduce the frequency of location updates and use different precision positioning requirements according to the actual situation
4. Network Optimization
Why?
Nowadays, almost all Apps need to be operated online. Network optimization can improve the experience on the one hand, and improve the experience on the other hand. Reduce traffic and power consumption. In addition, the network is also a resource, whether for users or network service providers, and no developer should assume that network resources are unlimited.
How Detection?
Use Network Traffic Tools in Android Studio to view network requests
-
Use Monitor in Android Studio
Use packet capture tools such as Fidder or Charles to analyze network data packets
How to optimize?
Be sure to cache when necessary, whether it is pictures or ordinary data, use LruCache and DiskLruCache to build your own caching system, and design caching strategies based on actual scenarios
Avoid excessive network synchronization and merge related network requests
Determine the request strategy according to the actual scenario and avoid using fixed interval frequencies for network operations. For example, when connecting to WiFi and charging The frequency can be high. After the first network request fails, double the time interval can be used for the next one.
Reduce the amount of data transmission and compress the transmitted data. If the transmission is For pictures, you need to choose the appropriate picture format and request pictures with appropriate specifications according to the display size. For ordinary data, you can consider using ProtocolBuffers to reduce the size of the transmitted data.
In some cases IP direct connection can be used, which on the one hand can reduce DNS resolution time and on the other hand can prevent domain name hijacking
5. Start optimization
##Why?
Startup optimization does not seem so necessary, but from a psychological point of view, faster startup speeds tend to give users With the psychological implication of good performance, efficiency and reliability, it is easy for users to have a good impression of it, leaving room for you to impress users later.How to detect?
- Use Method Tracing
- Use Systrace, such as adding trace.beginSection() and trace.endSection()
in onCreate
Use
adb shell am start -W [packageName]/[packageName.MainActivity]Measure cold start time
How to optimize?
Reduce complex and time-consuming operations in onCreate() of Activity
Application’s onCreate(), attachBaseContext () also reduces complex and time-consuming operations, but for many apps, a large number of initialization operations of components and services will be performed here. If possible, consider parallel initialization
Provide customized startup Window, such as displaying a picture as a startup window by setting a theme.
Optimize layout
6. Volume optimization
Why?
For users, whether it is user space or network, or Time is a resource. Volume optimization is an important part of saving resources for users. If you are currently making SDK products, then volume optimization is equally important.
How to detect?
Use Android Lint to check unused resources
How to optimize?
Reduce unnecessary dependent libraries/Jar, and give priority to small ones while meeting the needs.
Use the Proguard tool for code slimming, optimization, and obfuscation
Reduce the number of so files and provide so files according to the actual situation
Use shrinkResource in Gradle to exclude useless code and resources from the APK installation package
Reduce the size of image resources, consider image compression or use Vertor Drawable instead of png/jpeg
Selectively provide images with corresponding resolutions Resources
Reuse existing images, mostly by transforming existing images through code
Use plug-in technology (Don’t use it if the project is simple)
7. Performance optimization
can be used If you give 100% of your capabilities, don't only use 50% of them. This is not a bad thing for the application. If two cars are sold to users at the same price, I think most people will choose the one with better performance.
How to detect?
Use Lint to perform static analysis, in Android Studio's Analysis->Inspect Code
Turn on StrictMode in the developer options or turn it on in the code
Code Review
How to optimize?
Task parallelization, perform parallel operations on possible tasks, use thread pools instead of directly using threads
How to serialize data, give priority to Android Serializable provided by itself rather than provided by Java
Choose the appropriate data structure and clarify the complexity of List/Set/Map/Stack operations
Use Android to provide more efficient containers, such as using ArrayMap instead of HashMap. In addition, there are SparseBoolMap, SparseIntMap, SparseLongMap
- ##Using static constants instead of Enum types can reduce at least twice the memory Consumption
- Use object pool technology, such as providing an object pool like String
- Use caching technology
- String splicing operations are limited to using StringBuilder
- Optimize related algorithms and logic to reduce unnecessary processes
- Adopt JNI , for logic with a large amount of calculation, use its coroutine so file, such as image processing
Business Optimization
In addition to the above-mentioned more general optimizations In addition to the plan, you should also spend some time on business optimization. Many times, due to time pressure, the current business solution is not optimal. For example, in order to support the upload of multiple pictures, many people directly use serial operations. Although this It's easy to implement, but it's not the best.Since the business of each product is not the same, it is difficult to have a general optimization plan. Here are two more goals worth thinking about:
If possible, serial business Parallelization
If possible, simplify the business process. The way to put an elephant in the refrigerator is to open the refrigerator, put the elephant in, and finally close the refrigerator.
The fundamental reason why business optimization is put last is that business optimization has high risks and requires the overall cooperation of the team to complete.
There are four color formats for pictures in Android, which are
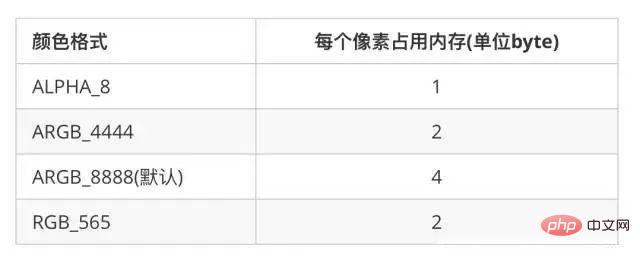
##The default is ARGB_8888<span style="font-size:14px;"></span>, where ARGB represents transparency, red, green, and blue respectively. Each value is recorded with 8 bits, that is, one pixel will occupy 4byte, a total of 32 bits. AndARGB_4444<span style="font-size:14px;"></span> is very similar to the above, but each value is recorded with 4 bits, that is, one pixel will occupy 2byte, a total of 16 bits . RGB_565<span style="font-size:14px;"></span> uses 5 bits, 6 bits, and 5 bits to record each value. There is no transparency, and each pixel will occupy 2 bytes. 16 bits in total. ALPHA_8<span style="font-size:14px;"></span>: This pixel only saves transparency and will occupy 1byte, 8 bits in total. In practical applications, it is recommended to use ARGB_8888<span style="font-size:14px;"></span> and RGB_565<span style="font-size:14px;"></span>, if you don’t need transparency, then choose RGB_565<span style="font-size:14px;"></span>, which can reduce the memory usage by half.
Android video tutorial]
The above is the detailed content of For Android application optimization encyclopedia. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 New report delivers damning assessment of rumoured Samsung Galaxy S25, Galaxy S25 Plus and Galaxy S25 Ultra camera upgrades
Sep 12, 2024 pm 12:23 PM
New report delivers damning assessment of rumoured Samsung Galaxy S25, Galaxy S25 Plus and Galaxy S25 Ultra camera upgrades
Sep 12, 2024 pm 12:23 PM
In recent days, Ice Universe has been steadily revealing details about the Galaxy S25 Ultra, which is widely believed to be Samsung's next flagship smartphone. Among other things, the leaker claimed that Samsung only plans to bring one camera upgrade
 Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra leaks in first render images with rumoured design changes revealed
Sep 11, 2024 am 06:37 AM
Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra leaks in first render images with rumoured design changes revealed
Sep 11, 2024 am 06:37 AM
OnLeaks has now partnered with Android Headlines to provide a first look at the Galaxy S25 Ultra, a few days after a failed attempt to generate upwards of $4,000 from his X (formerly Twitter) followers. For context, the render images embedded below h
 IFA 2024 | TCL\'s NXTPAPER 14 won\'t match the Galaxy Tab S10 Ultra in performance, but it nearly matches it in size
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:35 AM
IFA 2024 | TCL\'s NXTPAPER 14 won\'t match the Galaxy Tab S10 Ultra in performance, but it nearly matches it in size
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:35 AM
Alongside announcing two new smartphones, TCL has also announced a new Android tablet called the NXTPAPER 14, and its massive screen size is one of its selling points. The NXTPAPER 14 features version 3.0 of TCL's signature brand of matte LCD panels
 Vivo Y300 Pro packs 6,500 mAh battery in a slim 7.69 mm body
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:39 AM
Vivo Y300 Pro packs 6,500 mAh battery in a slim 7.69 mm body
Sep 07, 2024 am 06:39 AM
The Vivo Y300 Pro just got fully revealed, and it's one of the slimmest mid-range Android phones with a large battery. To be exact, the smartphone is only 7.69 mm thick but features a 6,500 mAh battery. This is the same capacity as the recently launc
 New report delivers damning assessment of rumoured Samsung Galaxy S25, Galaxy S25 Plus and Galaxy S25 Ultra camera upgrades
Sep 12, 2024 pm 12:22 PM
New report delivers damning assessment of rumoured Samsung Galaxy S25, Galaxy S25 Plus and Galaxy S25 Ultra camera upgrades
Sep 12, 2024 pm 12:22 PM
In recent days, Ice Universe has been steadily revealing details about the Galaxy S25 Ultra, which is widely believed to be Samsung's next flagship smartphone. Among other things, the leaker claimed that Samsung only plans to bring one camera upgrade
 Samsung Galaxy S24 FE billed to launch for less than expected in four colours and two memory options
Sep 12, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Samsung Galaxy S24 FE billed to launch for less than expected in four colours and two memory options
Sep 12, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Samsung has not offered any hints yet about when it will update its Fan Edition (FE) smartphone series. As it stands, the Galaxy S23 FE remains the company's most recent edition, having been presented at the start of October 2023. However, plenty of
 Motorola Razr 50s shows itself as possible new budget foldable in early leak
Sep 07, 2024 am 09:35 AM
Motorola Razr 50s shows itself as possible new budget foldable in early leak
Sep 07, 2024 am 09:35 AM
Motorola has released countless devices this year, although only two of them are foldables. For context, while most of the world has received the pair as the Razr 50 and Razr 50 Ultra, Motorola offers them in North America as the Razr 2024 and Razr 2
 Xiaomi Redmi Note 14 Pro Plus arrives as first Qualcomm Snapdragon 7s Gen 3 smartphone with Light Hunter 800 camera
Sep 27, 2024 am 06:23 AM
Xiaomi Redmi Note 14 Pro Plus arrives as first Qualcomm Snapdragon 7s Gen 3 smartphone with Light Hunter 800 camera
Sep 27, 2024 am 06:23 AM
The Redmi Note 14 Pro Plus is now official as a direct successor to last year'sRedmi Note 13 Pro Plus(curr. $375 on Amazon). As expected, the Redmi Note 14 Pro Plus heads up the Redmi Note 14 series alongside theRedmi Note 14and Redmi Note 14 Pro. Li





