
Global components in vue refer to components that can be used anywhere in the application, while local components refer to components that are not registered in global components and therefore can only be used locally.
The appearance of components in Vue is to split the code volume of Vue instances. Let us divide different functional modules into different components. In the code, we can just call the corresponding components for whatever functions we need. Next, I will introduce the difference between global components and local components. It has a certain reference effect and I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
【Recommended tutorial: Vue Tutorial】
Global components refer to components that can be used anywhere in the application, including in other components
Local components refer to components that are not registered in global components and therefore can only Use
on the component that registers it. Example:
<div id="app"> <contact-us></contact-us> </div>
Vue.component('contact-us', { data: function() {
return {
email: 'info@mycompany.com'
};
},
template: `
<div>
<h1>Contact Us</h1>
<p>Please send an e-mail to: {{ email }}</p>
</div>
`});new Vue({ el: '#app',});The component in the above code is actually a global component, because we use the component method on the global Vue object to register it. This means we can use it however we want.
How to set a global component to a local component
First store the component object in a variable
var contactUs = { data: function() {
return {
email: 'info@mycompany.com'
};
},
template: `
<div>
<h1>Contact Us</h1>
<p>Please send an e-mail to: {{ email }}</p>
</div>
`};Then in the Vue instance, We can add a components attribute that contains the components we want to register locally. This property should be an object and contain key-value pairs of the tag name and configuration object.
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'contact-us': contactUs
}});Note that in this example the components property has been added to the Vue instance, but it can also be added to another component.
After running the code, you will see that the component is working normally. But to prove that the component is local and not global would add another Vue instance and change the selector of the existing instance.
new Vue({
el: '#app1',
components: {
'contact-us': contactUs
}});new Vue({ el: '#app2',});<div id="app1"> <contact-us></contact-us> </div> <div id="app2"> <contact-us></contact-us> </div>

Now we only see the contact component rendered once, even though we used the tag twice in the template.
It appears in the first Vue instance because we have registered it as a local component, but the second Vue instance doesn't know what to do with the markup. Check the browser console. The browser reports an error saying that the component has not been registered
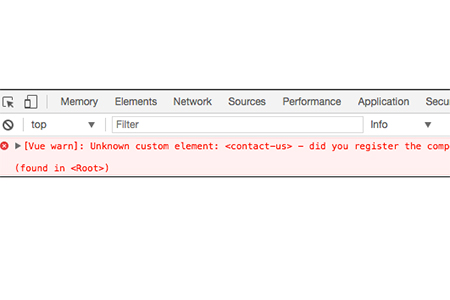
Therefore, to register a global component, please use the Vue.component method. For local components, you should Use the components property in a Vue instance or other component.
Summary: The above is the entire content of this article, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
The above is the detailed content of How to understand global components and local components in vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!