what is apache server
Apache server is an open source cross-platform web server. It has a variety of free and open source web technologies and is adaptable to a variety of operating systems. In addition, it has modules that add more functionality to the software, making it the most feature-rich HTTP web server.
Apache is a popular open source, cross-platform web server. It is also the most popular web server in existence. Next, we will introduce this server in detail in the article. I hope it will be helpful to you. Everyone helps.

【Recommended course: Database Tutorial】
Apache Server
In addition to its popularity, Apache server is also one of the oldest web servers. Its first version was released in 1995, unlike other web servers. Likewise, Apache provides the backend aspect of serving website files to visitors. It promotes a variety of free and open source advanced web technologies. The Apache web server provides a full range of functionality, including CGI, SSL, and virtual domains; it also supports plug-in modules for extension. Although Apache was originally designed for Unix environments, more than 90% of installations run on Linux. However, it also works on other operating systems such as Windows.

How the Apache server works
The basic task of all Web servers is to accept requests from clients (such as a visitor web browser), which then sends the request to the response page (such as the page component a visitor wants to see).
The Apache web server has modules that add more functionality to its software, such as MPM (for handling multiprocessing mode) or mod_ssl to enable SSL v3 and TLS support. Here are some common features in Apache:
IPv6
FTP
- ##Bandwidth Limit
- WebDAV
- Load Balancing
- URL Rewriting
- Session Tracking
- Geolocation based on IP address
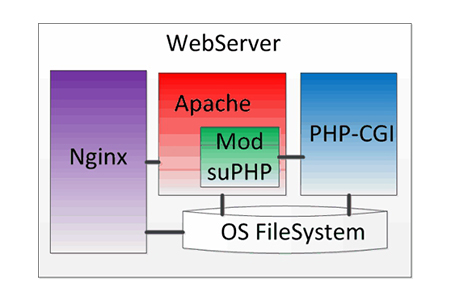
Why use Apache Server
The most important benefit of Apache is that it is free for personal and commercial use, plus it is a reliable software framework and is still actively maintained, so it gets frequent feature upgrades as well Security patches and bug improvements. Although Apache is a free and newer product, it doesn't skimp on features. The fact that it is one of the most feature-rich HTTP web servers is another reason why it is so popular. Apache adds more functionality to the software through the use of modules. Apache supports: Password verification and digital certificatesCustomizable error messagesSupports multiple functions through virtual host functionality WebsiteProxy serviceSSL and TLSGZIP compression can speed up web pagesSummary: The above is the entire content of this article, I hope Helpful to everyone.The above is the detailed content of what is apache server. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
To set up a CGI directory in Apache, you need to perform the following steps: Create a CGI directory such as "cgi-bin", and grant Apache write permissions. Add the "ScriptAlias" directive block in the Apache configuration file to map the CGI directory to the "/cgi-bin" URL. Restart Apache.
 How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
How to start apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:06 PM
The steps to start Apache are as follows: Install Apache (command: sudo apt-get install apache2 or download it from the official website) Start Apache (Linux: sudo systemctl start apache2; Windows: Right-click the "Apache2.4" service and select "Start") Check whether it has been started (Linux: sudo systemctl status apache2; Windows: Check the status of the "Apache2.4" service in the service manager) Enable boot automatically (optional, Linux: sudo systemctl
 How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
To delete an extra ServerName directive from Apache, you can take the following steps: Identify and delete the extra ServerName directive. Restart Apache to make the changes take effect. Check the configuration file to verify changes. Test the server to make sure the problem is resolved.
 How to check Debian OpenSSL configuration
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
How to check Debian OpenSSL configuration
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
This article introduces several methods to check the OpenSSL configuration of the Debian system to help you quickly grasp the security status of the system. 1. Confirm the OpenSSL version First, verify whether OpenSSL has been installed and version information. Enter the following command in the terminal: If opensslversion is not installed, the system will prompt an error. 2. View the configuration file. The main configuration file of OpenSSL is usually located in /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf. You can use a text editor (such as nano) to view: sudonano/etc/ssl/openssl.cnf This file contains important configuration information such as key, certificate path, and encryption algorithm. 3. Utilize OPE
 How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
This article will explain how to improve website performance by analyzing Apache logs under the Debian system. 1. Log Analysis Basics Apache log records the detailed information of all HTTP requests, including IP address, timestamp, request URL, HTTP method and response code. In Debian systems, these logs are usually located in the /var/log/apache2/access.log and /var/log/apache2/error.log directories. Understanding the log structure is the first step in effective analysis. 2. Log analysis tool You can use a variety of tools to analyze Apache logs: Command line tools: grep, awk, sed and other command line tools.
 How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
There are 3 ways to view the version on the Apache server: via the command line (apachectl -v or apache2ctl -v), check the server status page (http://<server IP or domain name>/server-status), or view the Apache configuration file (ServerVersion: Apache/<version number>).
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.




