How to optimize mysql database
Methods to optimize mysql database: establish Index index, use less select statements, enable query caching, choose a suitable storage engine, avoid using or in the where clause to connect and avoid returning large amounts of data, etc.
For a data-centric application, the quality of the database directly affects the performance of the program, so database performance is crucial. Therefore, everyone must understand the optimization operations of mysql database. This article mainly summarizes the common optimization operations in mysql database. I won’t go into more details below, let’s take a look at the detailed introduction.
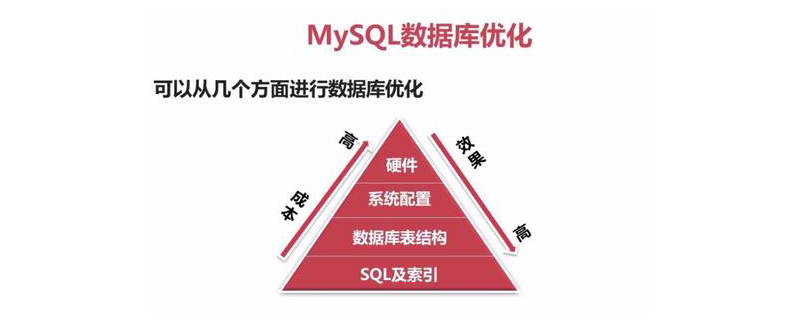
1. Index index
Put Index first. Needless to say, we have been quietly doing this optimization method Use, that is the primary key index. Sometimes we may not care. If a suitable index is defined, the database query performance (speed) will be improved several times or even dozens of times.
2. Use SELECT sparingly*
Some people may select whatever they want to query when querying the database. This is inappropriate behavior. We should get the data we want to use, not all, because when we select, it will increase the burden on the web server, increase the load on network transmission, and the query speed will naturally decrease.
3. EXPLAIN SELECT
It is estimated that many people have never seen this function, but it is highly recommended to use it. explain shows how mysql uses indexes to handle select statements and join tables. It can help choose better indexes and write more optimized query statements. The main use is to add explain before select.
EXPLAIN SELECT [查找字段名] FROM tab_name ...
4. Turn on query cache
Most MySQL servers have query cache turned on. This is one of the most effective ways to improve performance, and it's handled by the MySQL database engine. When many of the same queries are executed multiple times, these query results will be placed in a cache, so that subsequent identical queries do not need to operate the table but directly access the cached results.
The first step is to set query_cache_type to ON, and then query whether the system variable have_query_cache is available:
show variables like 'have_query_cache'
After that, allocate the memory size to the query cache and control the maximum value of cached query results. Relevant operations are modified in the configuration file.
5. Use NOT NULL
Many tables contain columns that can be NULL (null value), even if the application does not need to save NULL, this is Because NULL is the default property of the column. It is usually best to specify columns as NOT NULL unless you really need to store NULL values.
If the query contains NULL columns, it is more difficult for MySQL to optimize because NULL columns make indexes, index statistics, and value comparisons more complex. Columns that can be NULL use more storage space and require special handling in MySQL. When NULLable columns are indexed, each index record requires an extra byte, which in MyISAM can even cause a fixed-size index (such as an index with only one integer column) to become a variable-size index.
Usually the performance improvement brought by changing the NULL column to NOT NULL is relatively small, so (when tuning) there is no need to first search and modify this situation in the existing schema. Unless you are sure this will cause a problem. However, if you plan to build an index on a column, you should try to avoid designing the column to be NULL. Of course, there are exceptions. For example, it is worth mentioning that InnoDB uses a separate bit to store NULL values, so it has good space efficiency for sparse data. But this does not apply to MyISAM.
6. Selection of storage engine
Regarding how to choose MyISAM and InnoDB, if you need transaction processing or foreign keys, then InnoDB may be a better way. If you need full-text indexing, then MyISAM is usually a good choice because it is built into the system. However, we don't actually test 2 million rows of records very often. So, even if it's a little slower, we can get a full-text index from InnoDB by using Sphinx.
The size of the data is an important factor that affects what storage engine you choose. Large-size data sets tend to choose InnoDB because it supports transaction processing and failure recovery. The size of the database determines the length of fault recovery time. InnoDB can use transaction logs for data recovery, which will be faster. While MyISAM may take
several hours or even days to do these things, InnoDB only takes a few minutes.
Your habit of operating database tables may also be a factor that greatly affects performance. For example: COUNT() will be very fast in MyISAM table, but may be painful in InnoDB table. The primary key query will be quite fast under InnoDB, but we need to be careful that if our primary key is too long, it will also cause performance problems. A large number of inserts statements will be faster under MyISAM, but updates will be faster under InnoDB - especially when the amount of concurrency is large.
所以,到底你检使用哪一个呢?根据经验来看,如果是一些小型的应用或项目,那么MyISAM也许会更适合。当然,在大型的环境下使用MyISAM也会有很大成功的时候,但却不总是这样的。如果你正在计划使用一个超大数据量的项目,而且需要事务处理或外键支持,那么你真的应该直接使用InnoDB方式。但需要记住InnoDB的表需要更多的内存和存储,转换100GB的MyISAM 表到InnoDB 表可能会让你有非常坏的体验。
七、避免在 where 子句中使用 or 来连接
如果一个字段有索引,一个字段没有索引,将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描,如:
select id from t where num=10 or Name = 'admin'
可以这样查询:
select id from t where num = 10 union all select id from t where Name = 'admin'
八、多使用varchar/nvarchar
使用varchar/nvarchar代替 char/nchar ,因为首先变长字段存储空间小,可以节省存储空间,其次对于查询来说,在一个相对较小的字段内搜索效率显然要高些。
九、避免大数据量返回
这里要考虑使用limit,来限制返回的数据量,如果每次返回大量自己不需要的数据,也会降低查询速度。
十、where子句优化
where 子句中使用参数,会导致全表扫描,因为SQL只有在运行时才会解析局部变量,但优化程序不能将访问计划的选择推迟到运行时;它必须在编译时进行选择。然 而,如果在编译时建立访问计划,变量的值还是未知的,因而无法作为索引选择的输入项。
应尽量避免在 where 子句中对字段进行表达式操作,避免在where子句中对字段进行函数操作这将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描。不要在 where 子句中的“=”左边进行函数、算术运算或其他表达式运算,否则系统将可能无法正确使用索引。
相关学习推荐:mysql教程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of How to optimize mysql database. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to optimize settings and improve performance after receiving a new Win11 computer?
Mar 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
How to optimize settings and improve performance after receiving a new Win11 computer?
Mar 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
How do we set up and optimize performance after receiving a new computer? Users can directly open Privacy and Security, and then click General (Advertising ID, Local Content, Application Launch, Setting Recommendations, Productivity Tools or directly open Local Group Policy Just use the editor to operate it. Let me introduce to you in detail how to optimize settings and improve performance after receiving a new Win11 computer. How to optimize settings and improve performance after receiving a new Win11 computer. One: 1. Press the [Win+i] key combination to open Settings, then click [Privacy and Security] on the left, and click [General (Advertising ID, Local Content, App Launch, Setting Suggestions, Productivity) under Windows Permissions on the right Tools)】.Method 2
 In-depth interpretation: Why is Laravel as slow as a snail?
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:54 AM
In-depth interpretation: Why is Laravel as slow as a snail?
Mar 07, 2024 am 09:54 AM
Laravel is a popular PHP development framework, but it is sometimes criticized for being as slow as a snail. What exactly causes Laravel's unsatisfactory speed? This article will provide an in-depth explanation of the reasons why Laravel is as slow as a snail from multiple aspects, and combine it with specific code examples to help readers gain a deeper understanding of this problem. 1. ORM query performance issues In Laravel, ORM (Object Relational Mapping) is a very powerful feature that allows
 Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed!
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed!
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed! Laravel, as a popular PHP framework, provides developers with rich functions and a convenient development experience. However, as the size of the project increases and the number of visits increases, we may face the challenge of performance bottlenecks. This article will delve into Laravel performance optimization techniques to help developers discover and solve potential performance problems. 1. Database query optimization using Eloquent delayed loading When using Eloquent to query the database, avoid
 Discussion on Golang's gc optimization strategy
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:39 PM
Discussion on Golang's gc optimization strategy
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:39 PM
Golang's garbage collection (GC) has always been a hot topic among developers. As a fast programming language, Golang's built-in garbage collector can manage memory very well, but as the size of the program increases, some performance problems sometimes occur. This article will explore Golang’s GC optimization strategies and provide some specific code examples. Garbage collection in Golang Golang's garbage collector is based on concurrent mark-sweep (concurrentmark-s
 C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
C++ program optimization: time complexity reduction techniques
Jun 01, 2024 am 11:19 AM
Time complexity measures the execution time of an algorithm relative to the size of the input. Tips for reducing the time complexity of C++ programs include: choosing appropriate containers (such as vector, list) to optimize data storage and management. Utilize efficient algorithms such as quick sort to reduce computation time. Eliminate multiple operations to reduce double counting. Use conditional branches to avoid unnecessary calculations. Optimize linear search by using faster algorithms such as binary search.
 Laravel performance bottleneck revealed: optimization solution revealed!
Mar 07, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
Laravel performance bottleneck revealed: optimization solution revealed!
Mar 07, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
Laravel performance bottleneck revealed: optimization solution revealed! With the development of Internet technology, the performance optimization of websites and applications has become increasingly important. As a popular PHP framework, Laravel may face performance bottlenecks during the development process. This article will explore the performance problems that Laravel applications may encounter, and provide some optimization solutions and specific code examples so that developers can better solve these problems. 1. Database query optimization Database query is one of the common performance bottlenecks in Web applications. exist
 How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
How to optimize the startup items of WIN7 system
Mar 26, 2024 pm 06:20 PM
1. Press the key combination (win key + R) on the desktop to open the run window, then enter [regedit] and press Enter to confirm. 2. After opening the Registry Editor, we click to expand [HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorer], and then see if there is a Serialize item in the directory. If not, we can right-click Explorer, create a new item, and name it Serialize. 3. Then click Serialize, then right-click the blank space in the right pane, create a new DWORD (32) bit value, and name it Star
 Vivox100s parameter configuration revealed: How to optimize processor performance?
Mar 24, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Vivox100s parameter configuration revealed: How to optimize processor performance?
Mar 24, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Vivox100s parameter configuration revealed: How to optimize processor performance? In today's era of rapid technological development, smartphones have become an indispensable part of our daily lives. As an important part of a smartphone, the performance optimization of the processor is directly related to the user experience of the mobile phone. As a high-profile smartphone, Vivox100s's parameter configuration has attracted much attention, especially the optimization of processor performance has attracted much attention from users. As the "brain" of the mobile phone, the processor directly affects the running speed of the mobile phone.




