What is computer multithreading?
Multi-threading refers to the technology to realize the concurrent execution of multiple threads from software or hardware, and computer multi-threading refers to a computer with multi-threading capabilities that can execute more than one thread at the same time due to hardware support. Threads, thereby improving overall processing performance.

#A process is an activity in a computer regarding a certain data collection. It is the basic unit of resource allocation in the system and the basis of the computer structure. In the early process-oriented computer design structure, the process was the most basic execution entity of the program. A thread is the smallest unit that the operating system can perform operation scheduling. A process is a container for threads, a program is a collection of instructions, data and their organization, and a thread is the entity of the program.
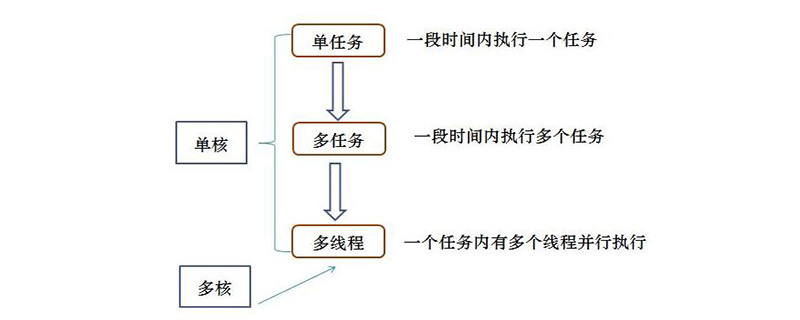
#A process can be understood as a program unit that can run independently. A process is composed of one or more threads. Each thread is an execution path in the process.
Computers with multi-threading capabilities can execute more than one thread at the same time due to hardware support, thus improving overall processing performance. Systems with this capability include symmetric multiprocessors, multicore processors, and chip-level multiprocessing or simultaneous multithreading processors.
What are the benefits of using multi-threading?
There are many time-consuming operations during the execution of a program, such as database reading and writing, disk IO operations, etc. It is very time-consuming. If you use a single thread, you must wait for these operations to be completed before performing other operations. Using multi-threading, you can put the time-consuming operations in the background and continue to execute other operations at the same time. To improve efficiency, to be precise, it means to increase CPU usage. For a single-core CPU, it is not used all the time. For example, when performing IO operations, IO operations are time-consuming. When reading the disk, The CPU is in a waiting state and is not performing any operations. At this time, we can use the waiting time of the CPU to perform other operations, thereby improving efficiency.
The above is the detailed content of What is computer multithreading?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 C++ function exceptions and multithreading: error handling in concurrent environments
May 04, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
C++ function exceptions and multithreading: error handling in concurrent environments
May 04, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
Function exception handling in C++ is particularly important for multi-threaded environments to ensure thread safety and data integrity. The try-catch statement allows you to catch and handle specific types of exceptions when they occur to prevent program crashes or data corruption.
 How to implement multi-threading in PHP?
May 06, 2024 pm 09:54 PM
How to implement multi-threading in PHP?
May 06, 2024 pm 09:54 PM
PHP multithreading refers to running multiple tasks simultaneously in one process, which is achieved by creating independently running threads. You can use the Pthreads extension in PHP to simulate multi-threading behavior. After installation, you can use the Thread class to create and start threads. For example, when processing a large amount of data, the data can be divided into multiple blocks and a corresponding number of threads can be created for simultaneous processing to improve efficiency.
 How can concurrency and multithreading of Java functions improve performance?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 04:15 PM
How can concurrency and multithreading of Java functions improve performance?
Apr 26, 2024 pm 04:15 PM
Concurrency and multithreading techniques using Java functions can improve application performance, including the following steps: Understand concurrency and multithreading concepts. Leverage Java's concurrency and multi-threading libraries such as ExecutorService and Callable. Practice cases such as multi-threaded matrix multiplication to greatly shorten execution time. Enjoy the advantages of increased application response speed and optimized processing efficiency brought by concurrency and multi-threading.
 Usage of JUnit unit testing framework in multi-threaded environment
Apr 18, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
Usage of JUnit unit testing framework in multi-threaded environment
Apr 18, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
There are two common approaches when using JUnit in a multi-threaded environment: single-threaded testing and multi-threaded testing. Single-threaded tests run on the main thread to avoid concurrency issues, while multi-threaded tests run on worker threads and require a synchronized testing approach to ensure shared resources are not disturbed. Common use cases include testing multi-thread-safe methods, such as using ConcurrentHashMap to store key-value pairs, and concurrent threads to operate on the key-value pairs and verify their correctness, reflecting the application of JUnit in a multi-threaded environment.
 How do PHP functions behave in a multi-threaded environment?
Apr 16, 2024 am 10:48 AM
How do PHP functions behave in a multi-threaded environment?
Apr 16, 2024 am 10:48 AM
In a multi-threaded environment, the behavior of PHP functions depends on their type: Normal functions: thread-safe, can be executed concurrently. Functions that modify global variables: unsafe, need to use synchronization mechanism. File operation function: unsafe, need to use synchronization mechanism to coordinate access. Database operation function: Unsafe, database system mechanism needs to be used to prevent conflicts.
 C++ Concurrent Programming: How to avoid thread starvation and priority inversion?
May 06, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
C++ Concurrent Programming: How to avoid thread starvation and priority inversion?
May 06, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To avoid thread starvation, you can use fair locks to ensure fair allocation of resources, or set thread priorities. To solve priority inversion, you can use priority inheritance, which temporarily increases the priority of the thread holding the resource; or use lock promotion, which increases the priority of the thread that needs the resource.
 How to deal with shared resources in multi-threading in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 am 10:28 AM
How to deal with shared resources in multi-threading in C++?
Jun 03, 2024 am 10:28 AM
Mutexes are used in C++ to handle multi-threaded shared resources: create mutexes through std::mutex. Use mtx.lock() to obtain a mutex and provide exclusive access to shared resources. Use mtx.unlock() to release the mutex.
 Challenges and countermeasures of C++ memory management in multi-threaded environment?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 01:08 PM
Challenges and countermeasures of C++ memory management in multi-threaded environment?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 01:08 PM
In a multi-threaded environment, C++ memory management faces the following challenges: data races, deadlocks, and memory leaks. Countermeasures include: 1. Use synchronization mechanisms, such as mutexes and atomic variables; 2. Use lock-free data structures; 3. Use smart pointers; 4. (Optional) implement garbage collection.





