How to use python third-party library
How to use the python third-party library: First enter the "pip install" command on the command line; then install the software package; finally use the import statement to call the third-party library.

#Independent developers have written thousands of third-party libraries! These libraries can be installed using pip. pip is the package manager included in Python 3. It is the standard Python package manager, but it is not the only one. Another popular manager is Anaconda, which is specifically targeted at data science.
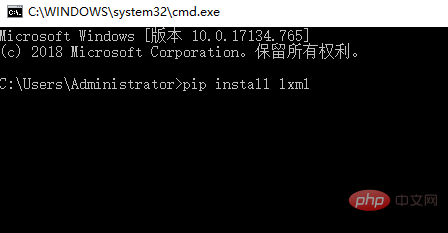
To install a package using pip, enter "pip install" at the command line, followed by the package name, as follows: pip install
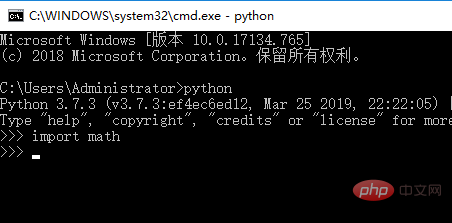
When using python's third-party libraries, you need to call them using the import statement
Practical third-party software packages
It is easy to install and import third-party libraries Useful, but to be a good programmer, you also need to know what libraries are available. People usually learn about useful new libraries through online recommendations or introductions from colleagues. If you're new to Python programming, you probably don't have many colleagues, so to help you get started, here's a list of packages that engineers love to use
IPython - A better interactive Python interpreter
python - Provides easy-to-use methods for making network requests. Suitable for accessing web APIs.
Flask - A small framework for building web applications and APIs.
Django - A richer web application building framework. Django is particularly suitable for designing complex, content-rich web applications.
Beautiful Soup - Used to parse HTML and extract information from it. Suitable for web page data extraction.
pytest- extends Python’s built-in assertions and is the most unitary module.
PyYAML - Used to read and write YAML files.
NumPy - The most basic package for scientific computing using Python. It contains a powerful N-dimensional array object, useful linear algebra functions, and more.
pandas - A library containing high-performance, data structure and data analysis tools. In particular, pandas provides dataframes!
matplotlib - A 2D plotting library that generates high-quality images that meet publishing standards in a variety of hardcopy formats and interactive environments.
ggplot - Another 2D drawing library based on R’s ggplot2 library.
Pillow - Python picture library that adds image processing capabilities to your Python interpreter.
pyglet - a cross-platform application framework specifically for game development.
Pygame - A series of Python modules for writing games.
pytz - Python's world time zone definition.
The above is the detailed content of How to use python third-party library. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
How to solve the permissions problem encountered when viewing Python version in Linux terminal?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Solution to permission issues when viewing Python version in Linux terminal When you try to view Python version in Linux terminal, enter python...
 How to teach computer novice programming basics in project and problem-driven methods within 10 hours?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
How to teach computer novice programming basics in project and problem-driven methods within 10 hours?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
How to teach computer novice programming basics within 10 hours? If you only have 10 hours to teach computer novice some programming knowledge, what would you choose to teach...
 How to efficiently copy the entire column of one DataFrame into another DataFrame with different structures in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
How to efficiently copy the entire column of one DataFrame into another DataFrame with different structures in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
When using Python's pandas library, how to copy whole columns between two DataFrames with different structures is a common problem. Suppose we have two Dats...
 How to avoid being detected by the browser when using Fiddler Everywhere for man-in-the-middle reading?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to avoid being detected by the browser when using Fiddler Everywhere for man-in-the-middle reading?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to avoid being detected when using FiddlerEverywhere for man-in-the-middle readings When you use FiddlerEverywhere...
 What are regular expressions?
Mar 20, 2025 pm 06:25 PM
What are regular expressions?
Mar 20, 2025 pm 06:25 PM
Regular expressions are powerful tools for pattern matching and text manipulation in programming, enhancing efficiency in text processing across various applications.
 How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests without serving_forever()?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests without serving_forever()?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How does Uvicorn continuously listen for HTTP requests? Uvicorn is a lightweight web server based on ASGI. One of its core functions is to listen for HTTP requests and proceed...
 What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
What are some popular Python libraries and their uses?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
The article discusses popular Python libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Django, Flask, and Requests, detailing their uses in scientific computing, data analysis, visualization, machine learning, web development, and H
 How to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
How to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods in Python?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
In Python, how to dynamically create an object through a string and call its methods? This is a common programming requirement, especially if it needs to be configured or run...




