what is macro
The so-called macro is a series of commands that are organized together and used as a single command to complete a specific task; Microsoft Word defines macros as "A macro is a series of word commands that can be organized together and used as an independent command. , it makes everyday tasks easier”.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is a macro
The so-called macro is a group of commands organized together to complete a specific task as a single command. The definition of macro in Microsoft Word is: "A macro is a series of word commands that can be organized together as an independent command to make daily work easier." Word uses the macro language Visual Basic to write macros as a series of instructions.
A macro in computer science is an abstraction that replaces a certain text pattern according to a series of predefined rules. The Excel office software automatically integrates the "VBA" high-level programming language, and the program compiled in this language is called a "macro". Using "VBA" requires a certain programming foundation and consumes a lot of time. Therefore, the vast majority of users only use the general tabulation function of Excel and rarely use "VBA".
The interpreter or compiler will automatically perform this pattern replacement when encountering a macro. For compiled languages, macro expansion occurs at compile time, and the tool that performs macro expansion is often called a macro expander. The term macro is often used in many similar contexts, derived from the concept of macro expansion, including keyboard macros and macro languages. Most of the time, the use of the word "macro" implies the conversion of small commands or actions into a series of instructions.
The purpose of macros is to automate frequently used sequences or to gain a more powerful abstraction capability - but this is often the same thing.
Computer languages such as C or assembly language have simple macro systems, which are implemented by the preprocessor of the compiler or assembler. The job of C's macro preprocessor is just simple text search and replacement. Using additional text processing languages such as M4, C programmers can obtain more sophisticated macros.
Lisp-like languages such as Common Lisp and Scheme have more sophisticated macro systems: macros behave like functions that transform their own program text, and all languages can be used to express this transformation. A C macro can define a grammatical replacement, but a Lisp macro can control the calculation of a section of code. Gained the ability to control the order of execution of code (see lazy evaluation and unrestricted functions), making newly created syntax constructs indistinguishable from the language's built-in syntax constructs.
For example, if a Lisp dialect has cond but not if, you can use macros to define the latter from the former. Major extensions to Lisp syntax, such as the object-oriented CLOS system, can be defined by macros.
Typical applications of macros
Speed up daily editing and formatting. Combine multiple commands to make options in dialog boxes more accessible and automate a range of complex tasks.
Applications can also use a system similar to macros to allow users to customize a series of (usually the most commonly used operations) into a step. That is, the user performs a series of operations and lets the application "remember" these operations and their order. More advanced users can directly access the functionality of those applications through built-in macro programming. When programming in an unfamiliar macro language, a more effective method is to record a series of operations that the user hopes to obtain, and then understand the structure of the macro commands by reading the macro file recorded by the application.
Recommended courses: PHP Tutorial.
The above is the detailed content of what is macro. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 what is macro
Jun 01, 2019 pm 05:22 PM
what is macro
Jun 01, 2019 pm 05:22 PM
The so-called macro is a series of commands that are organized together and used as a single command to complete a specific task; Microsoft Word defines macros as "A macro is a series of word commands that can be organized together and used as an independent command. It can make daily work easier." becomes easier”.
 How to use macros to simplify code in C++ function overloading?
Apr 13, 2024 am 11:21 AM
How to use macros to simplify code in C++ function overloading?
Apr 13, 2024 am 11:21 AM
Macros simplify C++ function overloading: Create macros to extract common code into a single definition. Use macros to replace common sections of code in each overloaded function. Practical applications include creating functions that print input data type information, handling int, double, and string data types respectively.
 Discuss the concept and application of macros in Golang
Mar 05, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
Discuss the concept and application of macros in Golang
Mar 05, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
In Golang, macro (Macro) is an advanced programming technology that can help programmers simplify the code structure and improve the maintainability of the code. Macros are a source code level text replacement mechanism that replaces macro code snippets with actual code snippets during compilation. In this article, we will explore the concept and application of macros in Golang and provide specific code examples. 1. The concept of macros In Golang, macros are not a natively supported feature because the original design intention of Golang is to keep the language simple and clear.
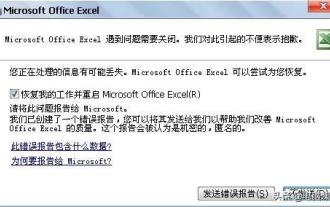 Macro cannot read USB disk
Mar 18, 2024 am 11:01 AM
Macro cannot read USB disk
Mar 18, 2024 am 11:01 AM
★Fault Phenomenon★: Every time you open the worksheet, it prompts that the macro cannot be found? After opening EXCEL, it closes for no reason and a sending error report appears. The Excel file cannot be opened and prompts an error report to be sent★Solution★: Download macro virus killing software and scan and kill the computer. Special Tips for Macro Virus Killer Software To ensure that this software can detect and remove viruses better, please pay attention to the following points when scanning: 1. Please close or delete 360 first (otherwise, you will be responsible for the problem of deleting data on 360.) 2. This special killer does not support virus scanning and killing of encrypted documents (please remove the password before checking.) 3. Documents set to read-only will cause the cleaning to fail (please remove read-only and check again.) 4. The special killer will check after you Remove viruses from your data files without damaging them. 5. Special Killer will back up before killing viruses.
 What is the name of the macro that can run automatically?
Jul 28, 2022 pm 03:21 PM
What is the name of the macro that can run automatically?
Jul 28, 2022 pm 03:21 PM
The name of the macro that can be automatically run when the database is opened is "Autoexec". The AutoExec macro can perform one or a series of specified operations when the database is first opened. When opening a database, Access will look for a macro called AutoExec and, if found, run it automatically.
 Comparison of C++ inline functions and macros
Apr 17, 2024 am 09:18 AM
Comparison of C++ inline functions and macros
Apr 17, 2024 am 09:18 AM
Inline functions are expanded into code, eliminating calling overhead, but avoiding excessively large function bodies and recursive calls; macros are text replacements, lightweight but difficult to maintain, used for constants and short code snippets. Practical case: Inline function implements Fibonacci sequence, macro defines constant PI.
 In-depth exploration of the usage scenarios of macros in Golang
Mar 05, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
In-depth exploration of the usage scenarios of macros in Golang
Mar 05, 2024 pm 03:33 PM
Golang is an open source programming language that has become increasingly popular among programmers in recent years. As a statically typed language, Golang provides many powerful features, one of which is macros. In this article, we will deeply explore the usage scenarios of macros in Golang and illustrate the functions and advantages of macros through specific code examples. What is a Macro? A macro is a feature in a programming language that can be replaced in the final code at compile time. It can help simplify code and improve
 Differences and comparison of advantages and disadvantages between C++ functions and macros
Apr 11, 2024 pm 04:03 PM
Differences and comparison of advantages and disadvantages between C++ functions and macros
Apr 11, 2024 pm 04:03 PM
Functions are code blocks that are executed during runtime and can return results; macros are constants or code fragments that are expanded during preprocessing and cannot return results. Functions are easy to read, reusable, and have high code readability, but low efficiency; macro compilation has low overhead and excellent performance, but poor code readability and is difficult to debug.



