Crawler parsing method five: XPath
Many languages can crawl, but crawlers based on python are more concise and convenient. Crawlers have also become an essential part of the python language. There are also many ways to parse crawlers. The previous article told you about the fourth method of parsing crawlers: PyQuery. Today I bring you another method, XPath.

The basic use of xpath for python crawlers
1. Introduction
XPath is a language for finding information in XML documents. XPath can be used to traverse elements and attributes in XML documents. XPath is a major element of the W3C XSLT standard, and both XQuery and XPointer are built on XPath expressions.
2. Installation
pip3 install lxml
3. Use
1 , Import
from lxml import etree
2. Basic usage
from lxml import etree
wb_data = """
<div>
<ul>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link1.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul>
</div>
"""
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
print(html)
result = etree.tostring(html)
print(result.decode("utf-8"))From the results below, our printer html is actually a python object, and etree.tostring(html) is The basic writing method of html in Buquanli completes the tags that are missing arms and legs.
<Element html at 0x39e58f0>
<html><body><div>
<ul>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link1.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</li></ul>
</div>
</body></html> 3. Get the content of a certain tag (basic use). Note that to get all the content of the a tag, there is no need to add a forward slash after a, otherwise an error will be reported.
Writing method one
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('/html/body/div/ul/li/a')
print(html)
for i in html_data:
print(i.text)
<Element html at 0x12fe4b8> first item second item third item fourth item fifth item
Writing method two (Directly in the tag where you need to find the content Just add a /text() after it)
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('/html/body/div/ul/li/a/text()')
print(html)
for i in html_data:
print(i)<Element html at 0x138e4b8> first item second item third item fourth item fifth item
#使用parse打开html的文件
html = etree.parse('test.html')
html_data = html.xpath('//*')<br>#打印是一个列表,需要遍历
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i.text)html = etree.parse('test.html') html_data = etree.tostring(html,pretty_print=True) res = html_data.decode('utf-8') print(res)
<div>
<ul>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link1.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a></li>
</ul>
</div>html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('/html/body/div/ul/li/a/@href')
for i in html_data:
print(i)link1.html link2.html link3.html link4.html link5.html
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('/html/body/div/ul/li/a[@href="link2.html"]/text()')
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i)7. Above we found all absolute paths (each one is searched from the root), below we find relative paths, for example, find the a tag content under all li tags.
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('//li/a/text()')
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i)['first item', 'second item', 'third item', 'fourth item', 'fifth item'] first item second item third item fourth item fifth item
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('//li/a//@href')
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i)['link1.html', 'link2.html', 'link3.html', 'link4.html', 'link5.html'] link1.html link2.html link3.html link4.html link5.html
9. The method of checking specific attributes under relative paths is similar to that under absolute paths, or it can be said to be the same.
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('//li/a[@href="link2.html"]')
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i.text)[<Element a at 0x216e468>] second item
10、查找最后一个li标签里的a标签的href属性
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('//li[last()]/a/text()')
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i)
打印:
['fifth item'] fifth item
11、查找倒数第二个li标签里的a标签的href属性
html = etree.HTML(wb_data)
html_data = html.xpath('//li[last()-1]/a/text()')
print(html_data)
for i in html_data:
print(i)
打印:
['fourth item'] fourth item
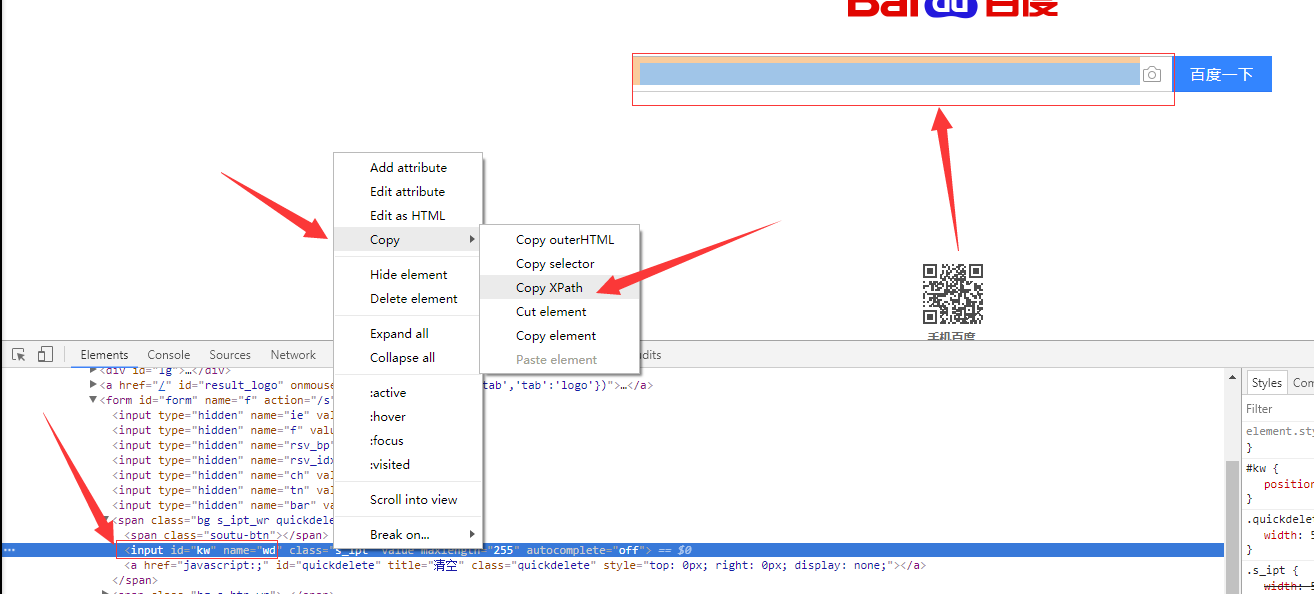
12、如果在提取某个页面的某个标签的xpath路径的话,可以如下图:
//*[@id="kw"]
解释:使用相对路径查找所有的标签,属性id等于kw的标签。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from scrapy.selector import Selector, HtmlXPathSelector
from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse
html = """<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li><a id='i1' href="link.html">first item</a></li>
<li><a id='i2' href="llink.html">first item</a></li>
<li><a href="llink2.html">second item<span>vv</span></a></li>
</ul>
<div><a href="llink2.html">second item</a></div>
</body>
</html>
"""
response = HtmlResponse(url='http://example.com', body=html,encoding='utf-8')
# hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[2]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id="i1"]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@href="link.html"][@id="i1"]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[contains(@href, "link")]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[starts-with(@href, "link")]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/text()').extract()
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/@href').extract()
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href').extract()
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li/a/@href').extract_first()
# print(hxs)
# ul_list = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li')
# for item in ul_list:
# v = item.xpath('./a/span')
# # 或
# # v = item.xpath('a/span')
# # 或
# # v = item.xpath('*/a/span')
# print(v)The above is the detailed content of Crawler parsing method five: XPath. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 Is distinctIdistinguish related?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
Is distinctIdistinguish related?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
Although distinct and distinct are related to distinction, they are used differently: distinct (adjective) describes the uniqueness of things themselves and is used to emphasize differences between things; distinct (verb) represents the distinction behavior or ability, and is used to describe the discrimination process. In programming, distinct is often used to represent the uniqueness of elements in a collection, such as deduplication operations; distinct is reflected in the design of algorithms or functions, such as distinguishing odd and even numbers. When optimizing, the distinct operation should select the appropriate algorithm and data structure, while the distinct operation should optimize the distinction between logical efficiency and pay attention to writing clear and readable code.
 How to understand !x in C?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
How to understand !x in C?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
!x Understanding !x is a logical non-operator in C language. It booleans the value of x, that is, true changes to false, false changes to true. But be aware that truth and falsehood in C are represented by numerical values rather than boolean types, non-zero is regarded as true, and only 0 is regarded as false. Therefore, !x deals with negative numbers the same as positive numbers and is considered true.
 Can C language user identifiers contain spaces?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:51 PM
Can C language user identifiers contain spaces?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:51 PM
C language identifiers cannot contain spaces because they can cause confusion and difficulty in maintaining. The specific rules are as follows: they must start with letters or underscores. Can contain letters, numbers, or underscores. Cannot contain illegal characters (such as special symbols).
 What does sum mean in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
What does sum mean in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C for sum, but it can be implemented by: using a loop to accumulate elements one by one; using a pointer to access and accumulate elements one by one; for large data volumes, consider parallel calculations.
 How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
In C language, snake nomenclature is a coding style convention, which uses underscores to connect multiple words to form variable names or function names to enhance readability. Although it won't affect compilation and operation, lengthy naming, IDE support issues, and historical baggage need to be considered.
 Does H5 page production require continuous maintenance?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Does H5 page production require continuous maintenance?
Apr 05, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
The H5 page needs to be maintained continuously, because of factors such as code vulnerabilities, browser compatibility, performance optimization, security updates and user experience improvements. Effective maintenance methods include establishing a complete testing system, using version control tools, regularly monitoring page performance, collecting user feedback and formulating maintenance plans.




