How to expand redis
A classmate in the team used Redis as a cache in his project and stored hotspot data in Redis. In order to improve performance, the pipeline method is used when writing Redis. When used normally, the performance and resource usage of Redis can meet the project requirements. However, when the number of visits increases, the QPS of Redis can still meet the requirements, but the CPU usage is high. has reached 90%, usually only 30%. As we all know, Redis is a single process and can only occupy 1 CPU core. When it is full, it will be 100%. It cannot use the multi-core of the machine. When the CPU reaches 100% When, it will inevitably cause a performance bottleneck. How to deal with it?

Recommended: "Redis Video Tutorial"
Option 1:
The first thing that comes to mind is to increase the number of Redis servers, perform a hash operation on the stored keys on the client, and store them in different Redis servers. When reading, the same hash operation is also performed to find the corresponding Redis server. Solve the problem, but the disadvantages:
First, the client needs to change the code;
Second, the client needs to remember the addresses of all Redis servers;
This solution can be used, but can it be expanded without changing the code?
Option 2:
Build a cluster. Since the version used by the Redis server is lower than 3.0, it does not support clusters. You can only use a proxy, so I thought of the famous Redis proxy twemproxy.
The performance of twemproxy is also very good. Although it is a proxy, its impact on access performance is very small. Even the Redis author recommends it.
twemproxy is easy to use. A novice can learn to use it in less than an hour, and the key is that there is no need to change the client code. It supports almost all Redis commands and pipeline operations. You only need to change the client code. The Redis IP and PORT configured in the configuration file are changed from the original Redis IP and Port to the IP and PORT of the twemproxy service.
The client does not need to consider hash issues, twemproxy will do these, and the client is just like operating a Redis.
The word "almost" is used above because some commands, such as "keys *" are not supported
We quickly deployed twemproxy and the four following Redis machines. The test found that the CPU usage of the following four Redis units dropped, but a new problem came, twemproxy is also a single process! The performance bottleneck comes to twemproxy again!
Option 3:
Access to Redis is divided into writing and reading, similar to producers and consumers. After careful analysis, it is found that there is less writing and relatively less reading. More, this can separate reading and writing, writing to the primary, and reading from the backup. The situation encountered happens to be that reading and writing are two services. To achieve separation of reading and writing, just change the configuration information. It can be done very simply, thus dispersing the pressure on the main Redis.
The access pressure on Redis has improved here, but it is not a long-term solution. For example, when events are held and the amount of data increases, there will still be performance risks.
The final method adopted is comprehensive plan two and three, as shown in the figure below: 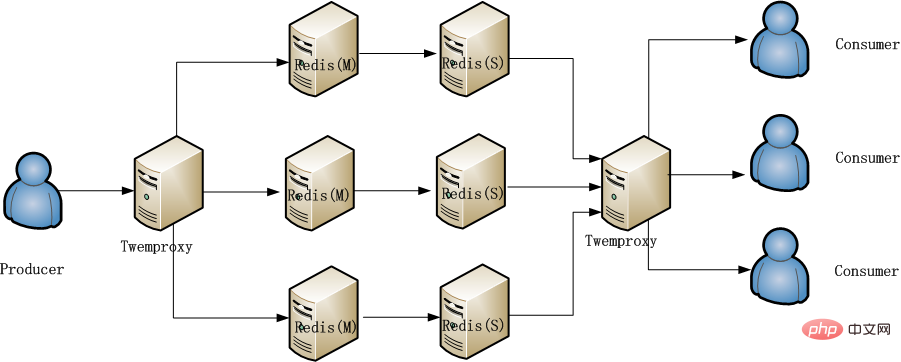
This method has minimal changes to existing services and can be effective The problem of alleviating redis pressure
The hash algorithm used by twemproxy on the producer side and the consumer side must be consistent, otherwise the key will not be found.
If plan 1 is also added, it will be more complicated and will not be used for the time being.
The above is the detailed content of How to expand redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
How to view server version of Redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 01:27 PM
Question: How to view the Redis server version? Use the command line tool redis-cli --version to view the version of the connected server. Use the INFO server command to view the server's internal version and need to parse and return information. In a cluster environment, check the version consistency of each node and can be automatically checked using scripts. Use scripts to automate viewing versions, such as connecting with Python scripts and printing version information.




