What are the basic algorithms of PHP?
Many people say that algorithms are the core of programs. The key to whether a program is good or bad is the quality of the program's algorithm. As a junior PHPer, although I have little exposure to algorithmic things. But I think we still need to master the four basic algorithms of bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, and quick sort.

Related recommendations: "PHP Tutorial"
Requirements: Use bubble sorting, quick sorting, and selection sorting respectively. , the insertion sort method sorts the values in the array below in ascending order.
1 |
|
1. Bubble sort
Introduction:
Bubble Sort (Bubble Sort, Taiwanese translation: bubble sort or bubble sort) is A simple sorting algorithm. It repeatedly walks through the sequence to be sorted, comparing the two elements in turn, and swapping them if they are in the wrong order. The work of visiting the array is repeated until no more exchanges are needed, which means that the array has been sorted. The name of this algorithm comes from the fact that smaller elements will slowly "float" to the top of the array through swapping.
Steps:
1. Compare adjacent elements. If the first one is bigger than the second one, swap them both.
2. Do the same work for each pair of adjacent elements, from the first pair at the beginning to the last pair at the end. At this point, the last element should be the largest number.
3. Repeat the above steps for all elements except the last one.
4. Continue to repeat the above steps for fewer and fewer elements each time until there are no pairs of numbers to compare.
Specific code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
|
Sort effect: 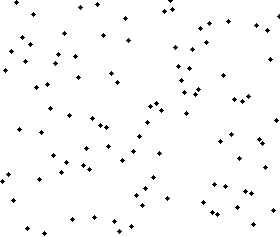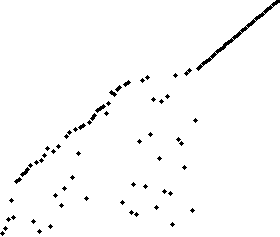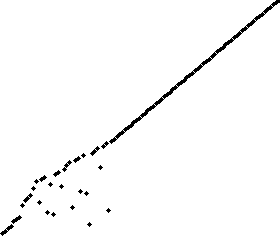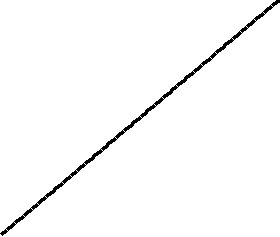
2. Select sorting
Introduction:
Selection sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. Here's how it works. First, find the smallest element in the unsorted sequence and store it at the beginning of the sorted sequence. Then, continue to find the smallest element from the remaining unsorted elements, and then put it at the end of the sorted sequence. And so on until all elements are sorted.
Specific code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
Sort effect:

##3. Insertion sort
Introduction: The algorithm description of Insertion Sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. It works by constructing an ordered sequence. For unsorted data, it scans from back to front in the sorted sequence, finds the corresponding position and inserts it. In the implementation of insertion sort, in-place sorting is usually used (that is, sorting that only uses O(1) extra space). Therefore, during the scanning process from back to front, it is necessary to repeatedly and gradually shift the sorted elements backward. , providing insertion space for the latest element. Steps:1. Starting from the first element, this element can be considered to have been sorted1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
|
4. Quick sort
Introduction:Quick sort It is a sorting algorithm developed by Tony Hall. On average, sorting n items requires O(n log n) comparisons. In the worst case, O(n2) comparisons are required, but this situation is uncommon. In fact, quicksort is often significantly faster than other Ο(n log n) algorithms because its inner loop can be implemented efficiently on most architectures and works well on most real-world applications. Data can determine design choices, reducing the possibility of quadratic terms in time required. Steps: 1. Pick an element from the sequence, called the "pivot",1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
The above is the detailed content of What are the basic algorithms of PHP?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the common algorithms in PHP programming?
Jun 12, 2023 am 08:30 AM
What are the common algorithms in PHP programming?
Jun 12, 2023 am 08:30 AM
In PHP programming, algorithms are an integral part. Mastering common algorithms can not only improve code efficiency, but also help with subsequent program design. The following are common algorithms in PHP programming: Sorting algorithm Sorting algorithm refers to arranging a set of data into an ordered sequence according to certain rules. In PHP programming, commonly used sorting algorithms include bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, etc. Among them, quick sort is the sorting algorithm with the lowest time complexity and is suitable for processing large-scale data. search algorithm search algorithm
 Array sorting and search algorithm in PHP
Jun 23, 2023 am 09:45 AM
Array sorting and search algorithm in PHP
Jun 23, 2023 am 09:45 AM
PHP is a very popular programming language that supports various data types and algorithms, of which array sorting and search algorithms are basic and important parts. This article will introduce commonly used array sorting and search algorithms in PHP, as well as their application scenarios and efficiency analysis. 1. Array sorting PHP provides a variety of array sorting methods, including bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, merge sort, etc. The following is an introduction and sample code for several commonly used algorithms: Bubble Sort (BubbleSort)
 Understand PHP data structures and algorithms
May 24, 2023 am 08:15 AM
Understand PHP data structures and algorithms
May 24, 2023 am 08:15 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used in web development and is getting better and better at building dynamic websites. In Web development, data structures and algorithms are no less important than other programming categories, and their impact on program running efficiency is particularly significant. Especially in scenarios involving large amounts of data storage and processing, or high program performance requirements, data structures and algorithms have become a part that cannot be ignored. This article mainly introduces some commonly used data structures and algorithms in PHP. 1. Data structure array PHP array is a very common
 How to represent knowledge and automatically generate algorithms in PHP?
May 22, 2023 pm 08:10 PM
How to represent knowledge and automatically generate algorithms in PHP?
May 22, 2023 pm 08:10 PM
With the popularity of the Internet and the continuous expansion of applications, the development of programming languages has become increasingly important. As a very popular programming language, PHP is also constantly developing. In the process of programming with PHP, PHP developers may face the need to represent some knowledge and automatically generate algorithms. So, how to represent knowledge and automatically generate algorithms in PHP? This article will discuss this below. 1. Knowledge representation Knowledge representation is a very important issue in the field of artificial intelligence. Know
 In-depth understanding of the core algorithms of PHP and Vue in the brain mapping function
Aug 15, 2023 pm 01:00 PM
In-depth understanding of the core algorithms of PHP and Vue in the brain mapping function
Aug 15, 2023 pm 01:00 PM
In-depth understanding of the core algorithms of PHP and Vue in the brain mapping function Introduction: In the modern Internet era, we often use a variety of applications to help us organize and manage information. Brain mapping is a common and practical way of organizing information, which can graphically display complex thinking processes. In this article, we will focus on the core algorithms of PHP and Vue in the brain mapping function and give code examples. 1. Characteristics of mind maps. Mind maps are a type of brain map that takes a central theme as its core and displays information related to that theme through a tree structure.
 PHP algorithm analysis: How to use binary search algorithm to quickly locate elements in an ordered array?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 01:14 PM
PHP algorithm analysis: How to use binary search algorithm to quickly locate elements in an ordered array?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 01:14 PM
PHP algorithm analysis: How to use binary search algorithm to quickly locate elements in an ordered array? Overview: The binary search algorithm is an efficient search algorithm that is suitable for finding specific elements in an ordered array. This article will introduce the principle of binary search algorithm in detail and give PHP code examples. Principle: The binary search algorithm quickly locates the target element by repeatedly reducing the search range by half. The process is as follows: first, narrow the search range to the beginning and end of the array; then, calculate the index of the middle element and compare it with the target element;
 PHP algorithm analysis: How to use dynamic programming algorithm to solve the 0-1 knapsack problem?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
PHP algorithm analysis: How to use dynamic programming algorithm to solve the 0-1 knapsack problem?
Sep 19, 2023 pm 12:33 PM
PHP algorithm analysis: How to use dynamic programming algorithm to solve the 0-1 knapsack problem? Introduction: Dynamic programming is an algorithmic idea commonly used to solve optimization problems. In program development, the 0-1 knapsack problem is a classic dynamic programming application scenario. This article will introduce how to use PHP to write a dynamic programming algorithm to solve the 0-1 knapsack problem, and provide specific code examples. What is the 0-1 knapsack problem? The 0-1 knapsack problem is a classic combinatorial optimization problem. The problem is set as follows: There is a backpack with a capacity of C. There are n objects
 Algorithms and data structures in PHP
May 25, 2023 am 08:51 AM
Algorithms and data structures in PHP
May 25, 2023 am 08:51 AM
PHP is a widely used development language commonly used for the development of web applications. However, Web applications often need to process large amounts of data, including data processing, storage, query, etc. Therefore, applying algorithms and data structures in PHP is a very critical technology. An algorithm is a general method used in computer programming to solve problems. In programming, we solve problems by designing and implementing algorithms to improve the efficiency, maintainability, and scalability of our programs. Commonly used algorithms include sorting, search, divide and conquer, greedy, etc.








