How to develop WordPress themes

Although free WordPress themes are everywhere now, as a Geek, have you ever considered writing your own WordPress theme? This article teaches you how to create a WordPress theme from the very basics.
Theme file structure:
Before writing, you must first understand the structure of the WordPress theme.
The WordPress theme is placed under wp-content/themes/ and exists as an independent folder. The name of the folder is arbitrary, but do not use pure numbers, otherwise the theme will not be displayed properly in the theme list. The theme folder contains all style files, template files, function files, JavaScript script files, static files, etc. required by the theme.
A minimal theme usually consists of three types of files:
Style sheet file style.css
Function file functions.php (optional)
Template files
Note that the names of these files are fixed and cannot be changed at will.
Let’s take a look at the function of each file separately.
Style file:
style.css is a required file for a theme because it contains descriptive information for the theme. The header information of a style.css is as follows:
/* Theme Name: 主题名称(必选) Theme URI: 主题的地址,可选,格式为一个URL,如http://wordpress.org/ Description: 对主题的描述,会显示在主题列表中。 Author: 作者 Version: 版本,如1.0 Tags: 给主题加的一些标签,可选,一般是为了让用户更方便搜索到这个主题。 */
It should be noted that each theme should have its own theme name (Theme Name) so that it can be distinguished in the theme list.
Function file:
Unless you create a purely static theme, you will definitely call the WordPress API. The functions used by these themes are written in the functions.php file. You can use the functions file in the WordPress theme as a reference.
Template file:
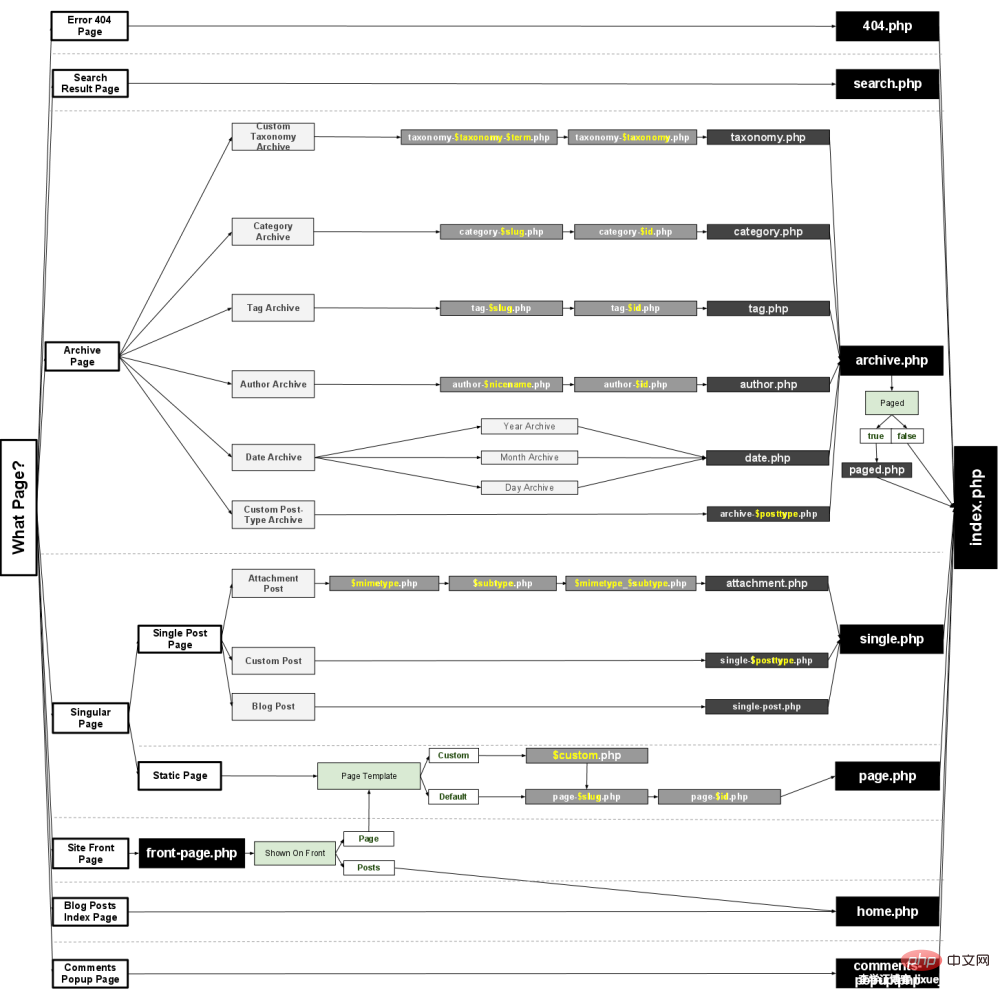
The template file is not a file, but a type of php file. They determine the final display of each of your pages. Template files follow certain naming rules. The following is the name and purpose of each template.
Template file description:
index.php
Main template. If your theme uses its own templates, index.php is required.
comments.php
Comment template.
front-page.php
Home page template, only used when the static home page is turned on.
home.php
Home page template, the default home page. If you enable the static homepage, this is a template page that displays the latest articles.
single.php
Single page template. Called when displaying a single article. For this and other request templates, index.php will be used if the template does not exist.
single-.php
Customize a single page template. For example, single-books.php displays articles with a custom article type of books. If the article type is not set, index.php is used.
page.php
Page template, independent page call.
category.php
Category template, category page call.
tag.php
Tag template, tag page call.
taxonomy.php
Term template, used when requesting terms for a custom taxonomy.
author.php
Author template, called by the author page.
date.php
Date/time template, the template used when querying by time.
archive.php
Archive template, the template used when querying categories, authors or dates. It should be noted that this template will be overwritten by category.php, author.php, and date.php respectively (if they exist).
search.php
Search result template, the template used when displaying search results.
attachment.php
Attachment template, the template used when viewing a single attachment.
image.php
Image attachment template, this template will be called when viewing a single image in wordpress. If this template does not exist, the attachment.php template will be called.
404.php
404 error page template, used when WordPress cannot find a log or page that matches the query, the 404.php file is used.
There is no special quantity requirement. You can even use just one file index.php as a template file. All pages will use this template. In most cases, you will have multiple templates to display different pages. The calling sequence of the specific template can refer to the figure below:
The simplest theme:
Know the above After that, let’s look at an example of the simplest theme. First of all, this theme contains the following files:
style.css
index.php
single.php
header.php
sidebar.php
footer.php
The content of style.css has been mentioned above. You only need to add the css you need.
Header.php, sidebar.php, footer.php categories are the top, sidebar, and tail of the page. Articles use single.php as the template, and other pages (such as the homepage) will use index.php as the template. The content of
index.php is:
<?php get_header(); ?> <?php get_sidebar(); ?> <?php get_footer(); ?>
The article page template single.php is:
<?php get_header(); ?> <h1><?php the_title(); ?></h1> <div><?php the_content(); ?></div> <?php get_sidebar(); ?> <?php get_footer(); ?>
这样,我们一个最简单的模板就完成了。剩下的就是你自己根据你的需要为其添加样式和内容了。另外在模板中所有你可能用到的Wordpress函数在这里都可以找到:Wordpress Function Reference。
更多wordpress相关技术文章,请访问wordpress教程栏目进行学习!
The above is the detailed content of How to develop WordPress themes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Is WordPress easy for beginners?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Is WordPress easy for beginners?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WordPress is easy for beginners to get started. 1. After logging into the background, the user interface is intuitive and the simple dashboard provides all the necessary function links. 2. Basic operations include creating and editing content. The WYSIWYG editor simplifies content creation. 3. Beginners can expand website functions through plug-ins and themes, and the learning curve exists but can be mastered through practice.
 Can I learn WordPress in 3 days?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Can I learn WordPress in 3 days?
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Can learn WordPress within three days. 1. Master basic knowledge, such as themes, plug-ins, etc. 2. Understand the core functions, including installation and working principles. 3. Learn basic and advanced usage through examples. 4. Understand debugging techniques and performance optimization suggestions.
 What is the WordPress good for?
Apr 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
What is the WordPress good for?
Apr 07, 2025 am 12:06 AM
WordPressisgoodforvirtuallyanywebprojectduetoitsversatilityasaCMS.Itexcelsin:1)user-friendliness,allowingeasywebsitesetup;2)flexibilityandcustomizationwithnumerousthemesandplugins;3)SEOoptimization;and4)strongcommunitysupport,thoughusersmustmanageper
 Should I use Wix or WordPress?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Should I use Wix or WordPress?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Wix is suitable for users who have no programming experience, and WordPress is suitable for users who want more control and expansion capabilities. 1) Wix provides drag-and-drop editors and rich templates, making it easy to quickly build a website. 2) As an open source CMS, WordPress has a huge community and plug-in ecosystem, supporting in-depth customization and expansion.
 How much does WordPress cost?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:13 AM
How much does WordPress cost?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:13 AM
WordPress itself is free, but it costs extra to use: 1. WordPress.com offers a package ranging from free to paid, with prices ranging from a few dollars per month to dozens of dollars; 2. WordPress.org requires purchasing a domain name (10-20 US dollars per year) and hosting services (5-50 US dollars per month); 3. Most plug-ins and themes are free, and the paid price ranges from tens to hundreds of dollars; by choosing the right hosting service, using plug-ins and themes reasonably, and regularly maintaining and optimizing, the cost of WordPress can be effectively controlled and optimized.
 Is WordPress a CMS?
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Is WordPress a CMS?
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WordPress is a Content Management System (CMS). It provides content management, user management, themes and plug-in capabilities to support the creation and management of website content. Its working principle includes database management, template systems and plug-in architecture, suitable for a variety of needs from blogs to corporate websites.
 Why would anyone use WordPress?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
Why would anyone use WordPress?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
People choose to use WordPress because of its power and flexibility. 1) WordPress is an open source CMS with strong ease of use and scalability, suitable for various website needs. 2) It has rich themes and plugins, a huge ecosystem and strong community support. 3) The working principle of WordPress is based on themes, plug-ins and core functions, and uses PHP and MySQL to process data, and supports performance optimization.
 Is WordPress still free?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Is WordPress still free?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The core version of WordPress is free, but other fees may be incurred during use. 1. Domain names and hosting services require payment. 2. Advanced themes and plug-ins may be charged. 3. Professional services and advanced features may be charged.




