5 commonly used annotations in springmvc

Recommended tutorial: Spring Tutorial
##1. Component-type annotations:
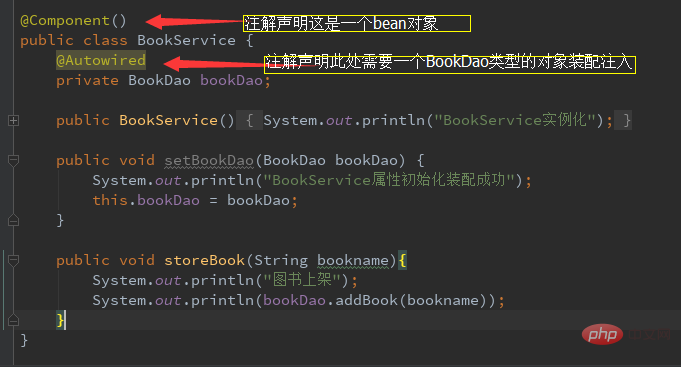
1. @Component Add the @Component annotation before the class definition, and it will be Spring Container identification and conversion to beans.
2. @Repository annotates the Dao implementation class (special @Component)
3. @Service is used to annotate the business logic layer, (special @Component)
4. @Controller is used to annotate the control layer, ( Special @Component)
The above four annotations are all annotated on the class. The annotated class will be initialized as a bean by spring and then managed uniformly.
## 2. Request and parameter type annotations:
1. @RequestMapping: used to process request address mapping, which can be applied to classes and methods.
Value: Define the mapping address of the request requestMethod: Define the method of request address request, including [GET , POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE.] The get request is accepted by default. If the request method is different from the defined method, the request will not succeed.
Params: Define the parameter values that must be included in the request request.
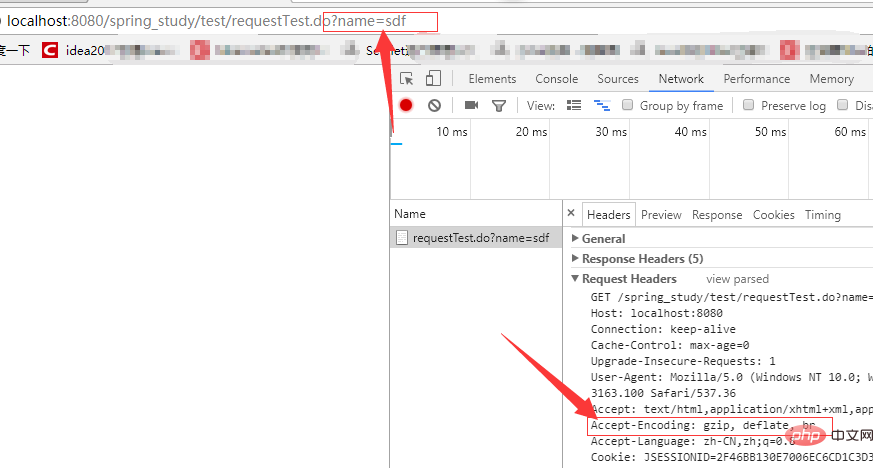
Headers: Define that the request request must contain certain specified request headers, such as: RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = "content-type=text/*" ) indicates that the request must contain the Content-type header of "text/html", "text/plain" to be a matching request.
●consumes: Define the type of content requested to be submitted.
●produces: Specify the content type to be returned. Only when the (Accept) type in the request header contains the specified type will it be returned
@RequestMapping(value="/requestTest.do",params = {"name=sdf"},headers = {"Accept-Encoding=gzip, deflate, br"},method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getIndex(){
System.out.println("请求成功");
return "index";
}
2.@RequestParam: used to get the value of the incoming parameter
Value: the name of the parameter
required: definition Whether the incoming parameter is required, the default is true, (similar to the params attribute of @RequestMapping)
@RequestMapping("/requestParams1.do")
public String requestParams1(@RequestParam(required = false) String name){
System.out.println("name = "+name);
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/requestParams2.do")
public String requestParams2(@RequestParam(value = "name",required = false) String names){
System.out.println("name = "+names);
return "index";
}##3.@PathViriable: used to define path parameter values
●value: the name of the parameter
●required: defines whether the incoming parameter is a required value@RequestMapping("/{myname}/pathVariable2.do") public String pathVariable2(@PathVariable(value = "myname") String name){
System.out.println("myname = "+name); return "index";
}This path declares {myname} as a path parameter, then this path will be Any value, @PathVariable will be able to get the value of the path based on value.
@RequestMapping("/{myname}/pathVariable2.do")
@ResponseBody
public String pathVariable2(@PathVariable(value = "myname") String name){
System.out.println("myname = "+name);
return "index";
}
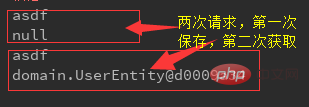
## It returns not a page, but the string " index" is printed directly on the page, which is actually similar to the following code. 5、@CookieValue:用于获取请求的Cookie值 6、@ModelAttribute: 用于把参数保存到model中,可以注解方法或参数,注解在方法上的时候,该方法将在处理器方法执行之前执行,然后把返回的对象存放在 session(前提时要有@SessionAttributes注解) 或模型属性中,@ModelAttribute(“attributeName”) 在标记方法的时候指定,若未指定,则使用返回类型的类名称(首字母小写)作为属性名称。 如上代码中,使用了@ModelAttribute("user")注解,在执行控制器前执行,然后将生成一个名称为user的model数据,在控制器中我们通过注解在参数上的@ModelAttribute获取参数,然后将model应用到控制器中,在jsp页面中我们同样可以使用它, 7、@SessionAttributes 默认情况下Spring MVC将模型中的数据存储到request域中。当一个请求结束后,数据就失效了。如果要跨页面使用。那么需要使用到session。而@SessionAttributes注解就可以使得模型中的数据存储一份到session域中。配合@ModelAttribute("user")使用的时候,会将对应的名称的model值存到session中, 结合上一个例子的代码,加了@SessionAttributes注解,然后请求了两次,第一次session中不存在属性名为user的值,第二次请求的时候发现session中又有了,这是因为,这是因为第一次请求时,model数据还未保存到session中请求结束返回的时候才保存,在第二次请求的时候已经可以获取上一次的model了 注意:@ModelAttribute("user") UserEntity user获取注解内容的时候,会先查询session中是否有对应的属性值,没有才去查询Model。PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.print("index");
out.flush(); @RequestMapping("/requestParams.do")
public String requestParams(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String cookie){
return "index";
}@ModelAttribute("user")
public UserEntity getUser(){
UserEntity userEntityr = new UserEntity();
userEntityr.setUsername("asdf");
return userEntityr;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelTest.do")
public String getUsers(@ModelAttribute("user") UserEntity user){
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
return "/index";
} <body>
${user.username}
</body>@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
@SessionAttributes(value = {"user","test1"})
public class LoginController{
@ModelAttribute("user")
public UserEntity getUser(){
UserEntity userEntityr = new UserEntity();
userEntityr.setUsername("asdf");
return userEntityr;
}
@RequestMapping("/modelTest.do")
public String getUsers(@ModelAttribute("user") UserEntity user ,HttpSession session){
System.out.println(user.getUsername());
System.out.println(session.getAttribute("user"));
return "/index";
}
}
The above is the detailed content of 5 commonly used annotations in springmvc. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






