Java interview knowledge points

1. Java files are compiled into bytecode files by JVM, that is, .class files. When the bytecode files are run in different operating systems, the operating system then converts the bytecode files into bytecode files. Code files are compiled into machine code files. This is Java cross-platform
2. First of all, let’s make it clear that java’s GC recycling is completely automatic. There is no relevant API for manual recycling. All memory allocation and recycling permissions are in the jvm and in the developer’s hands. There is no absolute way to force garbage collection, but you can do it like this:
1) For objects that are no longer referenced, assign their references to null in a timely manner. obj = null;
2) If the memory is really tight, call the System.gc () method to suggest the garbage collector to start collecting garbage and notify the GC to run. However, the Java language specification does not guarantee that the GC will be executed.
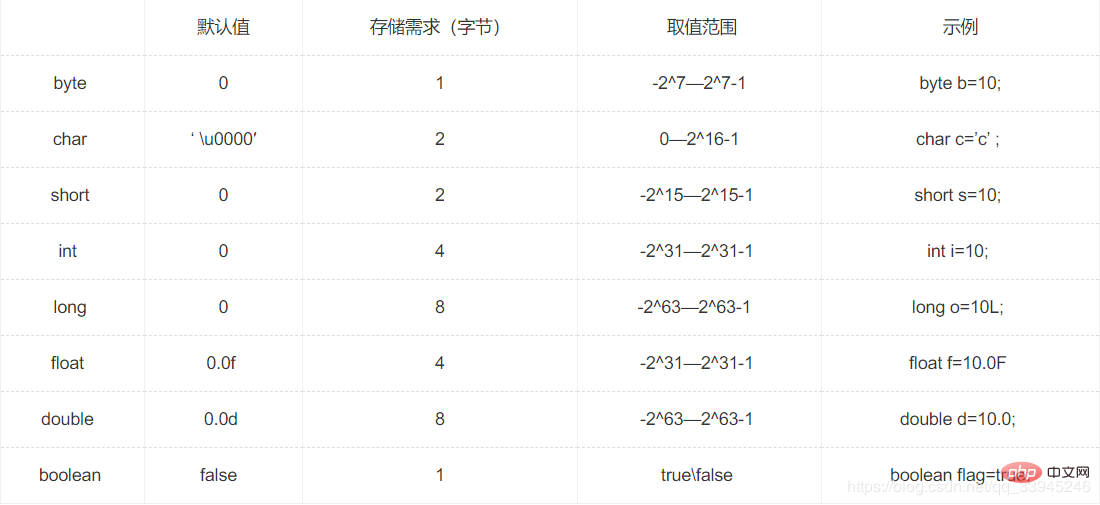
3. Default value and value range of java basic types
Integer type byte (1 byte) short (2 bytes) int (4 bytes) long (8 bytes)
Character type char (2 bytes)
Floating point type float (4 bytes) double (8 bytes)
4. The ASCII code values of common characters are as follows: the ASCII code value of a space is 32; the ASCII code values of numbers 0 to 9 are 48 to 57 respectively; the capital letter "A" The ASCII code values of "Z" are 65 to 90 respectively; the ASCII code values of lowercase letters "a" to "z" are 97 to 122 respectively.
5. Java identifiers have the following naming rules:
1) Composed of 26 English letters in upper and lower case, numbers: 0-9, symbols: _ $ ¥
2) The identifier should start with letters, _, $.
3) The identifier cannot be a keyword.
6、Abstract classes and interfaces
1) About abstract classes
Before JDK 1.8, the default access permission of abstract class methods was protected
When JDK 1.8, the default access permission of abstract class methods becomes default
2) About the interface
Before JDK 1.8, the methods in the interface must be public
JDK In JDK 1.8, the methods in the interface can be public or default. When JDK 1.9, the methods in the interface can be private.
7. Boxing and unpacking BoxThe basic data type is converted into a packaging class by boxing (such as: int --> Integer).
Converting a wrapper class into a basic data type is unboxing (such as: Integer --> int).
The wrapper class is the reference type, and the basic data type is the value type.
Through boxing and unboxing operations, a bridge can be built between value types and reference types. In other words, value types and reference types can be easily converted to each other, boxing and unboxing can uniformly examine the system, and any type of value can ultimately be processed as an object.
8. Serialization and deserializationJava will not instantiate static variables and transient-modified variables during serialization, because static represents members of the class and transient represents objects. Temporary data, it is declared that these two types of data members cannot be serialized
9. Java has two transfer methods, value transfer and reference transfer. Basic types and those created in this way with string str = "aaa"; are all passed by value. Object creation and arrays are all passed by reference, so special attention needs to be paid when judging the formal parameters of the function.10. Java garbage collection mechanism
Garbage collection is mainly aimed at recycling the heap area, because the memory in the stack area is released along with the thread. The heap is divided into three areas: Young Generation, Old Generation, and Permanent Generation (Method Area).
1) Young generation: When an object is created (new), the object is usually placed in Young (except for some objects that occupy relatively large memory). After a certain Minor GC (memory recycling for the young generation), it is still Live objects will be moved to the old generation (some specific movement details are omitted).
2) Old generation: It is the above-mentioned young generation moved over and some larger objects. Major GC (FullGC) is for the collection of the old generation.
3) Permanent generation: stores final constants, static variables, and constant pools.
11. Package referenceImport java.util.* ;
Can access all classes in the java/util directory, but cannot access the java/util subdirectory All classes under
12. The constructor cannot be inherited, and the constructor can only be called explicitly or implicitly. (This is true both with and without ginseng)13. Files are divided into text files and binary files. Computers only understand binary, so they are actually different ways of interpreting binary. Text files are characters displayed in different encoding formats, such as Ascii, Unicode, etc. The suffix names of text files in window include ".txt", ".log", source code files of various programming languages, etc. Binary files are text documents. You can't read garbled characters when you open them. As long as the file can be opened with text, it can be regarded as a text file, but the displayed result is not what you want. Binary files can only be read with special applications, such as ".png"," .bmp", etc., most of the files in the computer are still binary files
14. try is only suitable for handling runtime exceptions, while try catch is suitable for handling ordinary runtime exceptions. In other words, if you only use try to handle ordinary exceptions without using catch, the compilation will not pass, because the compiler rigidly stipulates that if ordinary exceptions are caught, they must be explicitly declared with catch for further processing. There is no such provision for runtime exceptions at compile time, so catch can be omitted. It is understandable for the compiler to add catch.
15. Pipeline
For pipelines, there are the following types:
① Ordinary pipeline (PIPE): There are usually two restrictions, one is single Work, that is, it can only be transmitted in one direction; second, blood, which is often used between father and son processes (or between processes with blood relationships).
②Stream pipe (s_pipe): The first restriction mentioned above is removed and bidirectional transmission is realized.
③Named pipe (name_pipe): Removes the second restriction mentioned above and realizes communication between different processes that are not related by blood.
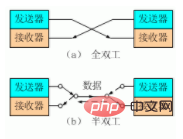
The requirement is that the communication between different servers must be in full-duplex form, while the pipeline can only be half-duplex. Although it can be bidirectional, there can only be transmission in one direction at the same time. The difference between duplex and half-duplex can be understood as follows:
Recommended tutorial: Java Basic Introduction Video
Original address: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33945246/article/details/90040041
The above is the detailed content of Java interview knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




