How composer works

The meaning of Composer
1. What is Composer?
Composer is a dependency management tool for PHP. Simply put, our projects usually use other code libraries. At this time, we only declare which code libraries we depend on in the project. By default, it will not be globally Install anything.
2. What is the meaning of Composer?
For modern languages, dependency management tools are basically standard. Java has Maven, Python has pip, Ruby has gem, and Nodejs has npm. PHP is PEAR, but PEAR has many pitfalls: dependency processing is prone to problems, configuration is very complex, command line interface is difficult to use, etc.
It is precisely because of the emergence of Composer that the problem of project dependency has been solved and PHP development work has become like stacking blocks.
Related recommendations: "Composer command usage graphic tutorial"
Through a simple example, let us understand how to use Composer.
1. Create a new composer.json file in the project root directory and write the following content:
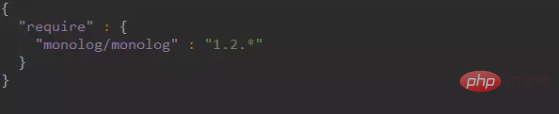
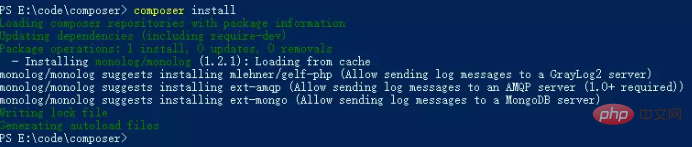
2. Execute the composer install command to install the package dependencies
3. Directory structure

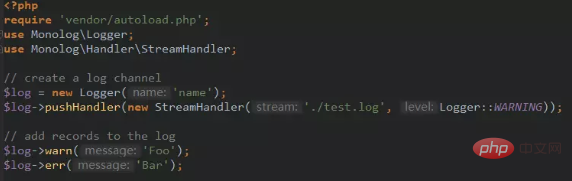
4. Development using packages
Working Principle of Composer
How does Composer work? For example, when we install a software, we usually install it through the app store. When we develop PHP projects, we will also face the same problem. For example, if we need a tool to record business logs, can we download the tools we need through a PHP application store?
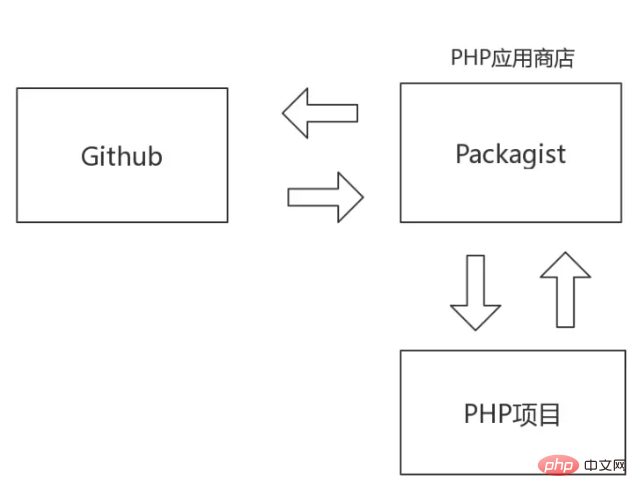
Packagist is Composer’s default development package repository. You can submit your installation package to packagist. In the future, if you create a new tag or update the code in your VCS (source code management software, such as Github) warehouse, packagist will automatically build a new development package. This is how packagist currently works, in the future packagist will allow you to directly upload development packages and publish your own packages.
The above is the detailed content of How composer works. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Composer's advanced features: aliases, scripts, and conflict resolution
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:37 PM
Composer's advanced features: aliases, scripts, and conflict resolution
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:37 PM
Composer provides advanced features, including: 1. Aliases: define convenient names for packages for repeated reference; 2. Scripts: execute custom commands when installing/updating packages, used to create database tables or compile resources; 3. Conflict resolution: use priorities Rules, satisfaction constraints, and package aliases resolve the different requirements of multiple packages for the same dependency version to avoid installation conflicts.
 Agile development and operation of PHP microservice containerization
May 08, 2024 pm 02:21 PM
Agile development and operation of PHP microservice containerization
May 08, 2024 pm 02:21 PM
Answer: PHP microservices are deployed with HelmCharts for agile development and containerized with DockerContainer for isolation and scalability. Detailed description: Use HelmCharts to automatically deploy PHP microservices to achieve agile development. Docker images allow for rapid iteration and version control of microservices. The DockerContainer standard isolates microservices, and Kubernetes manages the availability and scalability of the containers. Use Prometheus and Grafana to monitor microservice performance and health, and create alarms and automatic repair mechanisms.
 The role of PHP CI/CD in DevOps projects
May 08, 2024 pm 09:09 PM
The role of PHP CI/CD in DevOps projects
May 08, 2024 pm 09:09 PM
PHPCI/CD is a key practice in DevOps projects that automates the build, test, and deployment processes to improve development efficiency and software quality. A typical PHPCI/CD pipeline consists of the following stages: 1) Continuous Integration: Whenever the code changes, the code is automatically built and tested. 2) Continuous deployment: Speed up delivery by automatically deploying tested and integrated code to the production environment. By implementing the PHPCI/CD pipeline, you can increase development efficiency, improve software quality, shorten time to market, and improve reliability.
 PHP code version control and collaboration
May 07, 2024 am 08:54 AM
PHP code version control and collaboration
May 07, 2024 am 08:54 AM
PHP code version control: There are two version control systems (VCS) commonly used in PHP development: Git: distributed VCS, where developers store copies of the code base locally to facilitate collaboration and offline work. Subversion: Centralized VCS, a unique copy of the code base is stored on a central server, providing more control. VCS helps teams track changes, collaborate and roll back to earlier versions.
 Visualization technology of PHP data structure
May 07, 2024 pm 06:06 PM
Visualization technology of PHP data structure
May 07, 2024 pm 06:06 PM
There are three main technologies for visualizing data structures in PHP: Graphviz: an open source tool that can create graphical representations such as charts, directed acyclic graphs, and decision trees. D3.js: JavaScript library for creating interactive, data-driven visualizations, generating HTML and data from PHP, and then visualizing it on the client side using D3.js. ASCIIFlow: A library for creating textual representation of data flow diagrams, suitable for visualization of processes and algorithms.
 How to use PHP CI/CD to iterate quickly?
May 08, 2024 pm 10:15 PM
How to use PHP CI/CD to iterate quickly?
May 08, 2024 pm 10:15 PM
Answer: Use PHPCI/CD to achieve rapid iteration, including setting up CI/CD pipelines, automated testing and deployment processes. Set up a CI/CD pipeline: Select a CI/CD tool, configure the code repository, and define the build pipeline. Automated testing: Write unit and integration tests and use testing frameworks to simplify testing. Practical case: Using TravisCI: install TravisCI, define the pipeline, enable the pipeline, and view the results. Implement continuous delivery: select deployment tools, define deployment pipelines, and automate deployment. Benefits: Improve development efficiency, reduce errors, and shorten delivery time.
 How to use Redis cache in PHP array pagination?
May 01, 2024 am 10:48 AM
How to use Redis cache in PHP array pagination?
May 01, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Using Redis cache can greatly optimize the performance of PHP array paging. This can be achieved through the following steps: Install the Redis client. Connect to the Redis server. Create cache data and store each page of data into a Redis hash with the key "page:{page_number}". Get data from cache and avoid expensive operations on large arrays.
 How does Composer handle the composer.lock file?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
How does Composer handle the composer.lock file?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
Composer manages dependencies by using the composer.lock file, which records all installed dependencies and their exact versions, making it: Ensure consistency and avoid version conflicts. Improve performance without having to search for packages repeatedly. Track changes, recording installed dependency versions after each install command.




