
1. this keyword
a. There is an object pointing to the object;
b. There is no object pointing to the global variable (window);
c. There is new pointing to the new object produced by new;
d. Bind, call&apply changes the pointing of this;
e. SetTimeout/setInterval this points to window;
f. Arrow function this is determined when the function is defined;
var adder = {
base : 1,
add : function(a) {
var f = v => v + this.base;
return f(a);
},
addThruCall: function inFun(a) {
var f = v => v + this.base;
var b = {
base : 2
};
return f.call(b, a);
}
};var obj = {
i: 10,
b: () => console.log(this.i, this),
c: function() {
console.log( this.i, this)
}
}
obj.b(); // undefined window{...}原型
obj.c(); // 10 Object {...}2. Prototype
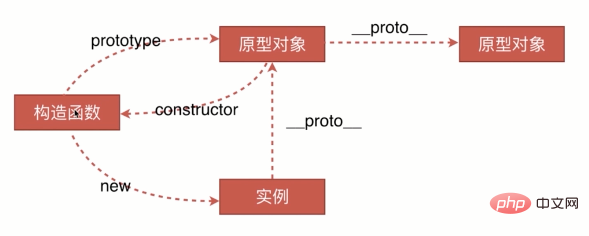
prototype:
prototype:every An object will initialize an attribute inside it: prototype;
Prototype chain: When we access the properties of an object, if this property does not exist inside the object, then go back__proto__ Look for this attribute in , and keep looking for it: prototype chain;
instanceof The principle is to determine whether the __proto__ of the instance object and the prototype of the constructor that generated the instance refer to the same an address.
hasOwnProperty is the only function in JavaScript that handles properties without looking up the prototype chain.
Execution context:
The scope of variable declaration and function declaration will be raised to the top of the method body; Scope: a. JavaScript does not have block-level scopeb. In addition to the global scope, JavaScript only has scopes that functions can create. The scope is determined when the function is defined. rather than when the function is called. Closure: Concept: Internal functions can access variables in external functions; Use: function as return value; function as parameter; Function: encapsulate variables, converge permissions; Disadvantages: consumes memoryMethod to create objects:
Object literal;Constructor; Immediately execute function;Object.create();new object procedure:
Create new Object; this points to this new object;Execute code;Return this;Class and inheritance:
Class declaration:
function Animal(){
this.name = 'name';
}
// es6
class Animal2{
constructor(){
this.name = 'name2';
}
}Inheritance:
1. Implement inheritance with the help of constructorfunction Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child1';
}function Parent(){
this.name = 'name';
}
function Child(){
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();缺点:原型链上原型对象是共用的。(原型的属性修改,所有继承自该原型的类的属性都会一起改变)
3.组合方式
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();缺点:
父类执行函数执行两次;
constructor指向父类;
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;缺点:
子类constructor指向父类
function Parent(){
this.name = 'parent';
}
function Child(){
Parent.call(this);
this.type = 'child';
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;优点:
子类的原型指向Object.create(Parent.prototype),实现了子类和父类构造函数的分离,但是这时子类中还是没有自己的构造函数,
所以紧接着又设置了子类的构造函数,由此实现了完美的组合继承。(也就是把父类的prototype写入子类的prototype,在定义子类的constructor)
4. es6
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(){
}
}希望本文中的内容能够帮到学习JavaScript的同学。谢谢!
更多JavaScript的相关问题请访问PHP中文网:https://www.php.cn/
The above is the detailed content of In-depth understanding of this, prototype and closure in js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!