
Linux File Permissions
Before learning more, let’s first understand the basic information about file permissions. [Recommended: Linux Video Tutorial]
First create an information file
>$ touch new_file >$ ll new_file >$ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 4月 23 22:59 new_file
filenew_file Has the following three sets of permissions:
rw-: The owner of the file, the permissions of the logged-in user r w are read and write respectively
r--: The permissions of the group to which the file owner belongs r Read
r--: Others The user's permission r is read
. Of course, there is also an x executable permission which is not available here and can be increased through the chmod command. More on this later. Let’s first talk about the origin of file permissions and how the default permissions after the touch command come from. To know, you first need to know that umask exists. The default value can be obtained through the umask command. This value is very useful.
>$ umask >$ 0022 // 这是我机器上面的值
To understand how this umask works, you must first understand the security settings of octal mode. The security setting in octal mode first obtains the values of these three rwx permissions and then converts them into three-digit binary values, represented by an octal value. In this binary representation, each position represents a binary bit. For example, the only read permission r-- converted into binary is 100, then the represented octal is 4.
As shown in the following table:
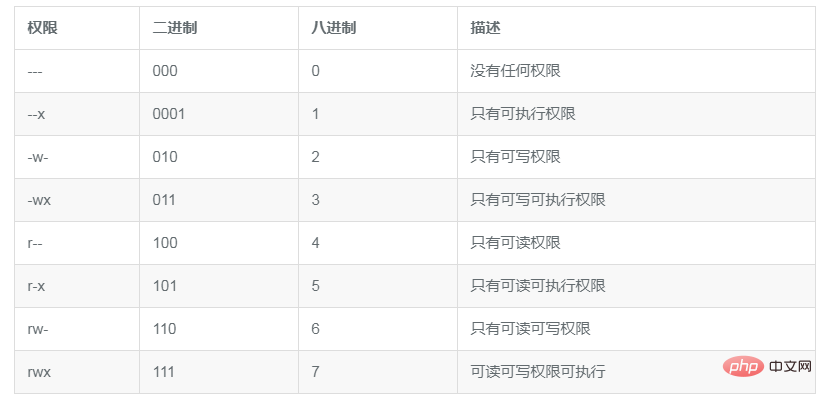
After understanding the corresponding permissions and octal values, see that the permissions of new_file above are 644. So I'm a little confused here, how is this value obtained? What is the significance of umask 0022? In fact, this value is just a mask.
He will block permissions that are not granted to that security level. For files, the full permission is 666, minus the value of umask, which is the permission of the newly created file. 644 is exactly what we expected. The w permissions of the group to which the file belongs and other users are blocked by default. It is explained here that the full permission of the folder is 777. If you want to block more permissions, you can modify the value of umask.
>$ umask 026
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Linux file permissions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!