 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (6) - bytecode execution engine
Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (6) - bytecode execution engine
Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (6) - bytecode execution engine
When the execution engine in the JVM executes java code, it generally has two options: interpreted execution (execution through an interpreter) and compiled execution (local code execution generated through a just-in-time compiler).
Stack frame
Definition:
Stack frame is data used to support method calling and method execution by the virtual machine Structure, which is located inside the virtual machine stack.
Function:
Every method from the beginning of the call to the completion of execution corresponds to a stack frame from the stack to the stack in the virtual machine stack. the process of.
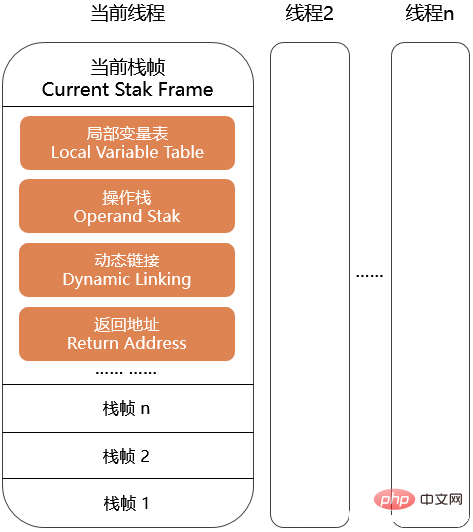
Features:
(1) The stack frame includes the local variable table, operand stack, etc. How big is it needed? The local variable table and the depth of the operand stack are determined at compile time. Because how much memory needs to be allocated for a stack frame will not be affected by variable data during program runtime.
(2) Data sharing between two stack frames. In the conceptual model, the two stack frames are completely independent, but in the implementation of the virtual machine, some optimization processing will be done to partially overlap the two stack frames. In this way, part of the data can be shared when making method calls, without the need for additional parameter copying and passing.
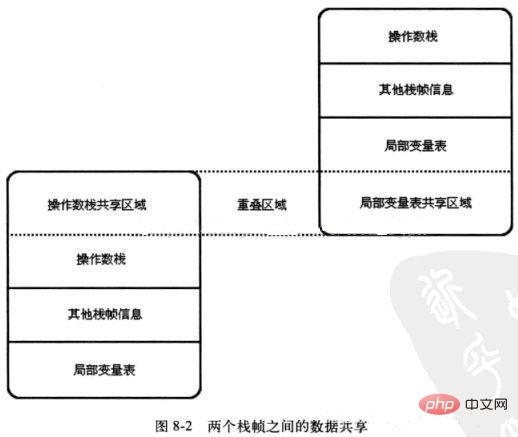
(1) Local variable table
The local variable table is a set of variable value storage spaces. Used to store method parameters and local variables defined within the method.
//方法参数 max(int a,int b)
int a;//全局变量
void say(){
int b=0;//局部变量
}Local variables are different from class variables (variables modified with static)
Class variables have two processes of assigning initial values: the preparation phase (assigning the system initial value) and the initialization phase (assigning Programmer-defined initial value). So it doesn't matter even if the class variable is not assigned a value during the initialization phase, it still has a certain initial value.
But local variables are different. If they are defined but not assigned an initial value, they cannot be used.
(2) Operation stack
When a method just starts executing, the operand stack of this method is empty. During the execution process, there will be various bytecode instructions to write and extract content from the operand stack, that is, pop and push operations.
For example, calculate:
int a=2+3
The two elements closest to the top of the operand stack are 2 and 3. When the iadd instruction is executed, 2 and 3 will be popped off the stack and added. , and then push the added result 5 onto the stack.
(3) Dynamic link
#There are a large number of symbol references in the constant pool of the Class file, and method calling instructions in the bytecode Just take a symbolic reference to the method in the constant pool as a parameter. These symbol references are divided into two parts:
Static analysis: converted into direct references during the class loading phase or when used for the first time. Dynamic link: converted into a direct reference during each run.
(4) Return address
当一个方法开始执行后,只有两种方式可以退出这个方法:正常退出、异常退出。无论采用何种退出方式,在方法退出之后,都需要返回到方法被调用的位置,程序才能继续执行。
当方法正常退出时
调用者的PC计数器作为返回地址。栈帧中一般会保存这个计数器值。
当方法异常退出时
返回地址是要通过异常处理器表来确定的。栈帧中一般不会保存这部分信息。
方法调用
方法调用是确定调用哪一个方法。
(1)解析
对“编译器可知,运行期不可变”的方法进行调用称为解析。符合这种要求的方法主要包括
静态方法,用static修饰的方法私有方法,用private修饰的方法
(2)分派
分派讲解了虚拟机如何确定正确的目标方法。分派分为静态分派和动态分派。讲解静动态分派之前,我们先看个多态的例子。
Human man=new Man();
在这段代码中,Human为静态类型,其在编译期是可知的。Man是实际类型,结果在运行期才可确定,编译期在编译程序的时候并不知道一个对象的实际类型是什么。
静态分派:
所有依赖静态类型来定位方法执行版本的分派动作称为静态分派。它的典型应用是重载。
public class StaticDispatch{
static abstract class Human{
}
static class Man extends Human{
}
static class Woman extends Human{
}
public void say(Human hum){
System.out.println("I am human");
}
public void say(Man hum){
System.out.println("I am man");
}
public void say(Woman hum){
System.out.println("I am woman");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Human man = new Man();
Human woman = new Woman();
StaticDispatch sr = new StaticDispatch();
sr.say(man);
sr.say(woman);
}
}运行结果是:
I am human I am human
为什么会产生这个结果呢?
因为编译器在重载时,是通过参数的静态类型而不是实际类型作为判断依据的。在编译阶段,javac编译器会根据参数的静态类型决定使用哪个重载版本,所以两个对say()方法的调用实际为sr.say(Human)。
动态分派:
在运行期根据实际类型确定方法执行版本的分派过程。它的典型应用是重写。
public class DynamicDispatch{
static abstract class Human{
protected abstract void say();
}
static class Man extends Human{
@Override
protected abstract void say(){
System.out.println("I am man");
}
}
static class Woman extends Human{
@Override
protected abstract void say(){
System.out.println("I am woman ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Human man = new Man();
Human woman = new Woman();
man.say();
woman.say();
man=new Woman();
man.say();
}
}运行结果:
I am man I am woman I am woman
这似乎才是我们平时敲的java代码。对于方法重写,在运行时才确定调用哪个方法。由于Human的实际类型是man,因此调用的是man的name方法。其余的同理。
动态分派的实现依赖于方法区中的虚方法表,它里面存放着各个方法的实际入口地址。如果某个方法在子类中被重写了,那子类方法表中的地址将会替换为指向子类实现版本的入口地址,否则,指向父类的实现入口。
单分派和多分派:
方法的接收者与方法的参数统称为方法的宗量,根据分派基于多少种宗量,分为单分派和多分派。
在静态分派中,需要调用者的实际类型和方法参数的类型才能确定方法版本,所以其是多分派类型。在动态分派中,已经知道了参数的实际类型,所以此时只需知道方法调用者的实际类型就可以确定出方法版本,所以其是单分派类型。综上,java是一门静态多分派,动态单分派的语言。
字节码解释执行引擎
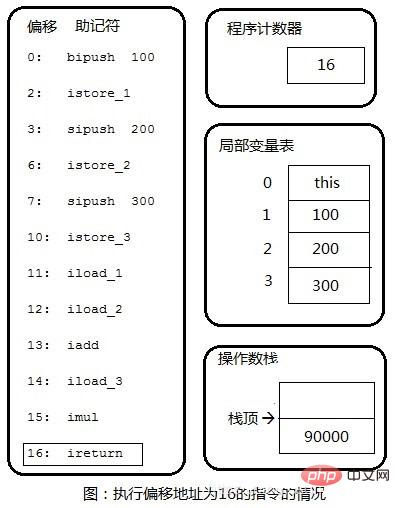
虚拟机中的字节码解释执行引擎是基于栈的。下面通过一段代码来仔细看一下其解释的执行过程。
public int calc(){
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
int c = 300;
return (a + b) * c;
}第一步:将100入栈。
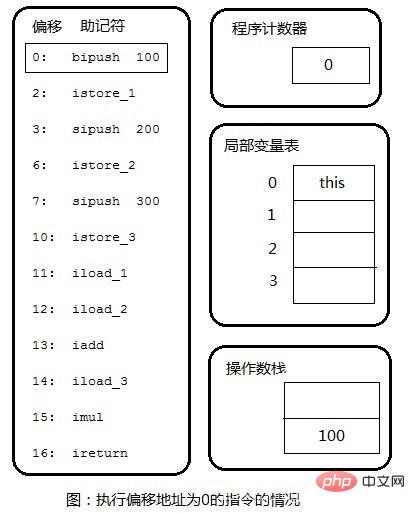
Step 2: Pop 100 from the operation stack and store it in local variables. The same applies to the subsequent 200,300.
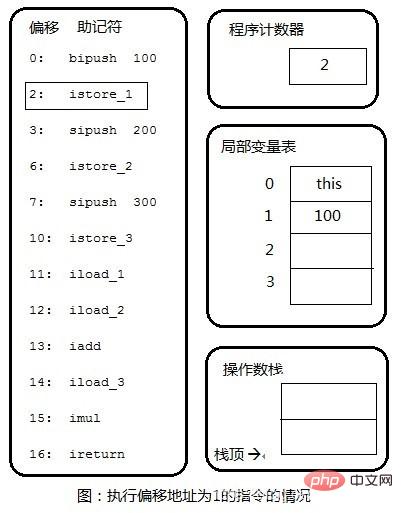
Step 3: Copy 100 in the local variable table to the top of the operand stack.
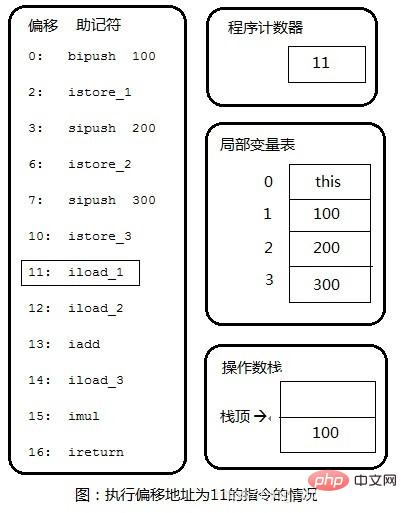
Step 4: Copy 200 in the local variable table to the top of the operand stack.
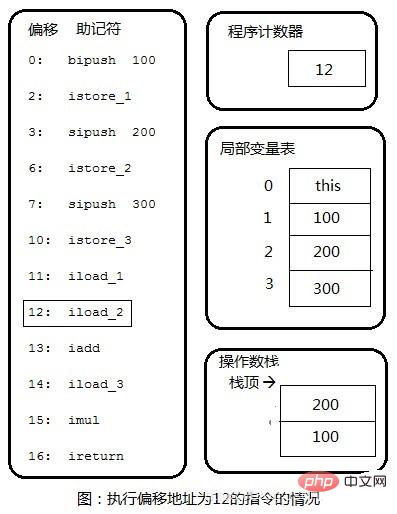
Step 5: Pop 100 and 200 off the stack, perform integer addition, and finally push the result 300 back onto the stack.
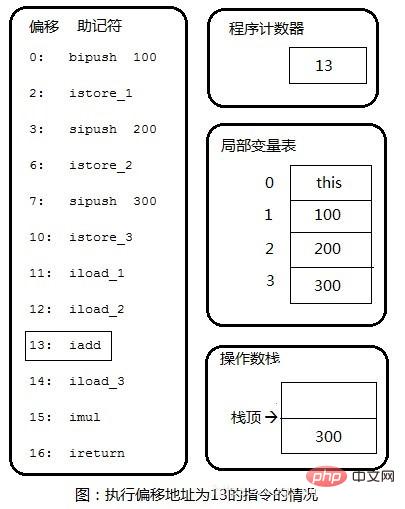
Step 6: Copy the third number 300 from the local variable table to the top of the stack. The next step is to pop the two 300s off the stack, perform integer multiplication, and push the final result 90000 onto the stack.
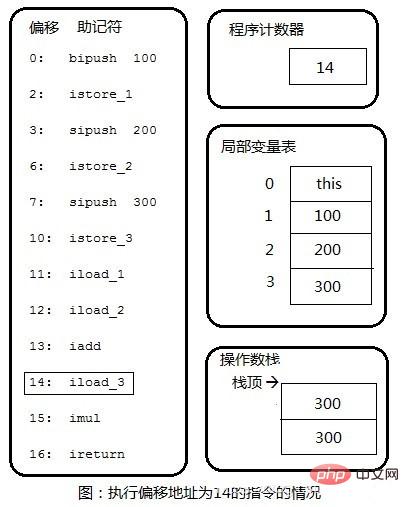
Step 7: The method ends and the integer value at the top of the operand stack is returned to the caller of this method.
The above is a complete introduction to the JAVA virtual machine-bytecode execution engine. For more related questions, please visit the PHP Chinese website: JAVA Video Tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to JAVA Virtual Machine (JVM) (6) - bytecode execution engine. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 A distributed JVM monitoring tool, very practical!
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:15 PM
A distributed JVM monitoring tool, very practical!
Aug 15, 2023 pm 05:15 PM
This project is designed to facilitate developers to monitor multiple remote host JVMs faster. If your project is Spring boot, it is very easy to integrate. Just introduce the jar package. If it is not Spring boot, don’t be discouraged. You can quickly initialize a Spring boot program and introduce it yourself. Jar package is enough
 Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
JVM command line parameters allow you to adjust JVM behavior at a fine-grained level. The common parameters include: Set the Java heap size (-Xms, -Xmx) Set the new generation size (-Xmn) Enable the parallel garbage collector (-XX:+UseParallelGC) Reduce the memory usage of the Survivor area (-XX:-ReduceSurvivorSetInMemory) Eliminate redundancy Eliminate garbage collection (-XX:-EliminateRedundantGCs) Print garbage collection information (-XX:+PrintGC) Use the G1 garbage collector (-XX:-UseG1GC) Set the maximum garbage collection pause time (-XX:MaxGCPau
 JVM memory management key points and precautions
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:26 AM
JVM memory management key points and precautions
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:26 AM
Key points and precautions for mastering JVM memory usage JVM (JavaVirtualMachine) is the environment in which Java applications run, and the most important one is the memory management of the JVM. Properly managing JVM memory can not only improve application performance, but also avoid problems such as memory leaks and memory overflows. This article will introduce the key points and considerations of JVM memory usage and provide some specific code examples. JVM memory partitions JVM memory is mainly divided into the following areas: Heap (He
 Analysis of the functions and principles of JVM virtual machine
Feb 22, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
Analysis of the functions and principles of JVM virtual machine
Feb 22, 2024 pm 01:54 PM
An introduction to the analysis of the functions and principles of the JVM virtual machine: The JVM (JavaVirtualMachine) virtual machine is one of the core components of the Java programming language, and it is one of the biggest selling points of Java. The role of the JVM is to compile Java source code into bytecodes and be responsible for executing these bytecodes. This article will introduce the role of JVM and how it works, and provide some code examples to help readers understand better. Function: The main function of JVM is to solve the problem of portability of Java programs on different platforms.
 Java Error: JVM memory overflow error, how to deal with and avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Java Error: JVM memory overflow error, how to deal with and avoid
Jun 24, 2023 pm 02:19 PM
Java is a popular programming language. During the development of Java applications, you may encounter JVM memory overflow errors. This error usually causes the application to crash, affecting the user experience. This article will explore the causes of JVM memory overflow errors and how to deal with and avoid such errors. What is JVM memory overflow error? The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is the running environment for Java applications. In the JVM, memory is divided into multiple areas, including heap, method area, stack, etc. The heap is used to store created objects
 How to adjust JVM heap memory size efficiently?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
How to adjust JVM heap memory size efficiently?
Feb 18, 2024 pm 01:39 PM
JVM memory parameter settings: How to reasonably adjust the heap memory size? In Java applications, the JVM is the key component responsible for managing memory. Among them, heap memory is used to store object instances. The size setting of heap memory has an important impact on the performance and stability of the application. This article will introduce how to reasonably adjust the heap memory size, with specific code examples. First, we need to understand some basic knowledge about JVM memory. The JVM's memory is divided into several areas, including heap memory, stack memory, method area, etc. in
 Java program to check if JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit
Sep 05, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Java program to check if JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit
Sep 05, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
Before writing a java program to check whether the JVM is 32-bit or 64-bit, let us first discuss about the JVM. JVM is a java virtual machine, responsible for executing bytecode. It is part of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE). We all know that java is platform independent, but JVM is platform dependent. We need separate JVM for each operating system. If we have the bytecode of any java source code, we can easily run it on any platform due to JVM. The entire process of java file execution is as follows - First, we save the java source code with .java extension and the compiler converts it into bytecode with .class extension. This happens at compile time. Now, at runtime, J
 Demystifying the working principle of JVM: In-depth exploration of the principles of Java virtual machine
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:28 PM
Demystifying the working principle of JVM: In-depth exploration of the principles of Java virtual machine
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:28 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM principles: In-depth exploration of the working principle of the Java virtual machine requires specific code examples 1. Introduction With the rapid development and widespread application of the Java programming language, the Java Virtual Machine (JavaVirtualMachine, referred to as JVM) has also become indispensable in software development. a part of. As the running environment for Java programs, JVM can provide cross-platform features, allowing Java programs to run on different operating systems. In this article, we will delve into how the JVM works



