 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Problem
PHP Problem
 Detailed introduction to the underlying operating principle of PHP
Detailed introduction to the underlying operating principle of PHP
Detailed introduction to the underlying operating principle of PHP

PHP is a dynamic language suitable for web development. To be more specific, it is a software framework that uses C language to implement a large number of component modules. It is a powerful UI framework.
In short; PHP dynamic language execution process: after getting a piece of code, after lexical analysis, syntax analysis and other stages, the source program will be translated into instructions (opcodes), and then the ZEND virtual machine will Execute these instructions once to complete the operation. PHP itself is implemented in C, so the functions ultimately called are also C functions. In fact, we can regard PHP as a software developed in C.
1. The design concept and characteristics of PHP
1. Multi-process model: Since PHP is a multi-process model, different requests do not interfere with each other, so It is guaranteed that the failure of a request will not affect the entire service. Currently, PHP has already supported the multi-threading model.
2. Weakly typed language: Unlike C/C, JAVA, C# and other languages, PHP is a weakly typed language. The type of a variable is not determined at the beginning. It is determined during operation and implicit or explicit type conversion may occur. The flexibility of this mechanism is very convenient and efficient in web development. The details will be discussed in PHP later. Variables are detailed in.
3. The engine (Zend) component (ext) mode reduces internal coupling.
4. The middle layer (sapi). The full name of Sapi is Server Application Programming Interface, which isolates the web server and PHP.
5. The syntax is simple and flexible, without too many specifications. Disadvantages lead to a mixture of styles.
2. The four-layer system of PHP
The core architecture of PHP is as follows:
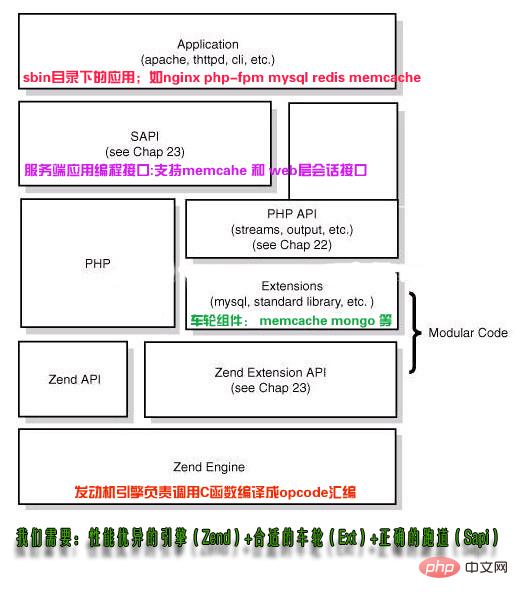
PHP is a 4-layer system from bottom to top System:
1. Zend engine: Zend is implemented entirely in pure C and is the core part of PHP. It translates PHP code (lexical, syntax analysis and other compilation processes) into executable opcode processing and implementation Corresponding processing methods, implementing basic data structures (such as hashtable, OO), memory allocation mechanism and management, and providing corresponding api methods for external calls are the core of everything. All peripheral functions are implemented around Zend.
2. Extensions: Around the Zend engine, extensions provide various basic services in a component-based manner. Our common various built-in functions (array series), standard libraries, etc. are all implemented through extensions. Users You can also implement typical applications of your own extension as needed).
3. Sapi: The full name of Sapi is Server Application Programming Interface, which is the server application programming interface. Sapi enables PHP to interact with peripheral data through a series of hook functions. This is a very elegant and successful design of PHP. Through sapi, PHP itself is successfully decoupled and isolated from the upper-layer application. PHP can no longer consider how to be compatible with different applications, and the application itself can also implement different processing methods according to its own characteristics.
4. Upper-layer application: This is the PHP program we usually write. We can obtain various application modes through different spai methods. How to implement web applications through webserver, run them in script mode on the command line, etc. wait.
We need: A high-performance engine (Zend) The right wheels (Ext) The right track (Sapi).
3. Sapi
Sapi allows external applications to exchange data with PHP through a series of interfaces and implement specific processing methods according to different application characteristics. Some of our common sapis are:
1. apache2handler: This is the processing method when using apache as the webserver and running in mod_PHP mode. It is also the most widely used one now.
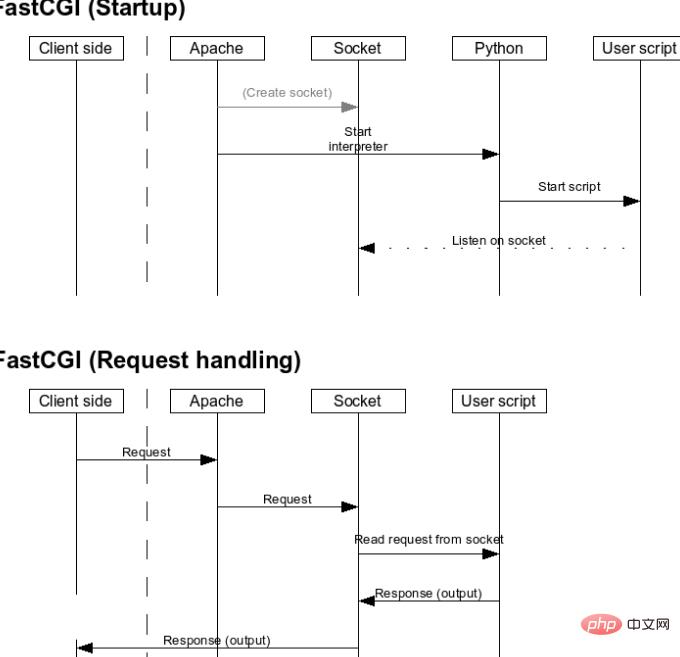
2. cgi: This is another direct interaction method between webserver and PHP, which is the famous fastcgi protocol. Recently, fastcgi PHP has been used more and more, and it is also the only method supported by asynchronous webserver. ; Typical application nginx server; fastcgi is simply an extension of PHP.
The FastCGI process manager (IIS ISAPI or Apache Module) is loaded when the Web Server starts.
The FastCGI process manager initializes itself and starts multiple CGI interpreter processes (visible multiple php-cgi ) and wait for the connection from the Web Server.
When a client request reaches the Web Server, the FastCGI process manager selects and connects to a CGI interpreter. The web server sends CGI environment variables and standard input to the FastCGI subprocess php-cgi.
After the FastCGI sub-process completes processing, it returns standard output and error information to the Web Server from the same connection. When the FastCGI child process closes the connection, the request is processed. The FastCGI child process then waits for and handles the next connection from the FastCGI process manager (running in the Web Server). In CGI mode, php-cgi exits at this point.
In the above situation, you can imagine how slow CGI usually is. Every web request to PHP must reparse php.ini, reload all extensions and reinitialize all data structures. With FastCGI, all of this happens only once, when the process starts. An added bonus is that persistent database connections work.
3. cli: application mode called by command line
Command-line interface (English: command-line interface, abbreviation: CLI) is the most widely used user interface before the popularity of graphical user interfaces. It usually does not support the mouse. The user inputs instructions through the keyboard, and the computer executes the instructions after receiving them. Some people also call it Character User Interface (CUI).
It is generally believed that the command line interface (CLI) is not as convenient for users to operate as the graphical user interface (GUI). Because command line interface software usually requires the user to memorize the operating commands, however, due to its own characteristics, the command line interface saves computer system resources compared to the graphical user interface. Under the premise of memorizing the commands, using the command line interface is often faster than using the graphical user interface. Therefore, operating systems with graphical user interfaces retain optional command line interfaces.
4. PHP execution process
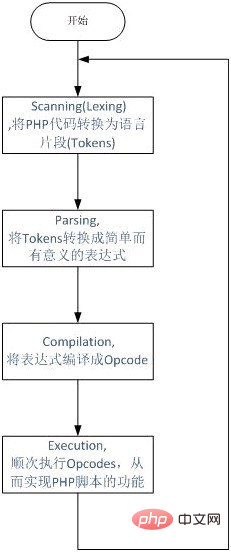
PHP dynamic language execution process: After getting a piece of code, after lexical analysis, grammar After the parsing and other stages, the source program will be translated into instructions (opcodes), and then the ZEND virtual machine will execute these instructions in sequence to complete the operation. PHP itself is implemented in C, so the functions ultimately called are also C functions. In fact, we can regard PHP as a software developed in C.
The core of PHP execution is the translated instructions, which are also opcodes.
Opcode is the most basic unit of PHP program execution.
In the field of computer science, operation code (Operation Code, OPCode) is used to describe machine language instructions, specifying the part of the machine code to perform a certain operation. The instruction format and specifications that constitute OPCode are processed by specified by the instruction specification of the device.
An opcode consists of two parameters (op1, op2), return value and processing function. The PHP program is ultimately translated into the sequential execution of a set of opcode processing functions.
Several common processing functions:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
5. HashTable-core data structure
HashTable is the core data structure of Zend. In PHP, it is used to implement almost all common functions. The PHP array we know is its typical application. In addition, within zend, such as function symbol table, global variables, etc. are also based on hash table and have the following characteristics:
1. Supports typical key->value query
2. Can be used as an array
3. Adding and deleting nodes is O(1) complexity
4. Key supports mixed types: there are associated number combination index arrays at the same time
5. Value supports mixed types: array("string",2332)
6. Supports linear traversal: such as foreach
Zend hash table implements the typical hash table hash structure, and at the same time provides the function of forward and reverse traversal of the array by attaching a doubly linked list. Its structure is as shown below:
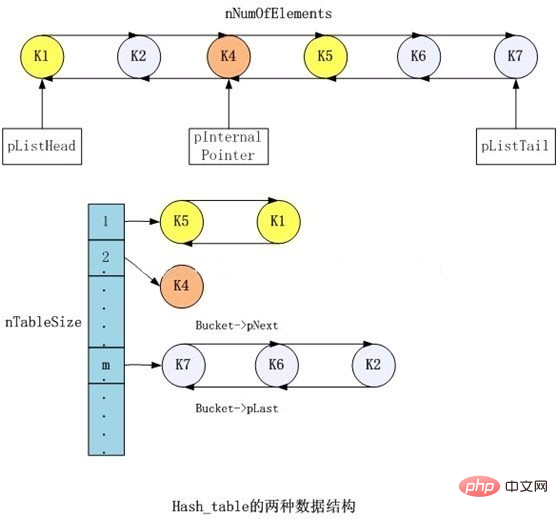
It can be seen that in the hash table, there is both a hash structure in the form of key->value and a doubly linked list mode, making it very Conveniently supports fast search and linear traversal.
1. Hash structure: Zend’s hash structure is a typical hash table model, which resolves conflicts through a linked list. It should be noted that zend's hash table is a self-growing data structure. When the hash table is full, it will dynamically expand by 2 times and reposition elements. The initial size is 8. In addition, when performing key->value fast search, zend itself has also made some optimizations to speed up the process by exchanging space for time. For example, a variable nKeyLength is used in each element to identify the length of the key for quick determination.
2. Doubly linked list: Zend hash table implements linear traversal of elements through a linked list structure. In theory, it is enough to use a one-way linked list for traversal. The main purpose of using a two-way linked list is to quickly delete and avoid traversal. Zend hash table is a composite structure. When used as an array, it supports common associative arrays and can also be used as sequential index numbers, and even allows a mixture of the two. PHP associative array: Associative array is a typical hash_table application. A query process goes through the following steps (as can be seen from the code, this is a common hash query process and some quick judgments are added to speed up the search.):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
4、PHP索引数组:索引数组就是我们常见的数组,通过下标访问。例如 $arr[0],Zend HashTable内部进行了归一化处理,对于index类型key同样分配了hash值和nKeyLength(为0)。内部成员变量 nNextFreeElement就是当前分配到的最大id,每次push后自动加一。正是这种归一化处理,PHP才能够实现关联和非关联的混合。由于 push操作的特殊性,索引key在PHP数组中先后顺序并不是通过下标大小来决定,而是由push的先后决定。例如 $arr[1] = 2; $arr[2] = 3;对于double类型的key,Zend HashTable会将他当做索引key处理。
六、Hash Table变量
PHP是一门弱类型语言,本身不严格区分变量的类型。PHP在变量申明的时候不需要指定类型。
PHP在程序运行期间可能进行变量类型的隐示转换。 和其他强类型语言一样,程序中也可以进行显示的类型转换。
PHP变量可以分为简单类型(int、string、bool)、集合类型(array resource object)和常量(const)。以上所有的变量在底层都是同一种结构 zval。
Zval主要由三部分组成:
type:指定了变量所述的类型(整数、字符串、数组等)
refcount&is_ref:用来实现引用计数(后面具体介绍)
value:核心部分,存储了变量的实际数据
Zvalue是用来保存一个变量的实际数据。因为要存储多种类型,所以zvalue是一个union,也由此实现了弱类型。
引用计数在内存回收、字符串操作等地方使用非常广泛。PHP中的变量就是引用计数的典型应用。Zval的引用计数通过成员变量is_ref和ref_count实现,通过引用计数,多个变量可以共享同一份数据。避免频繁拷贝带来的大量消耗。在进行赋值操作时,zend将变量指向相同的zval同时ref_count++,在unset操作时,对应的ref_count-1。只有ref_count减为0时才会真正执行销毁操作。如果是引用赋值,则zend会修改is_ref为1。
PHP变量通过引用计数实现变量共享数据,那如果改变其中一个变量值呢?当试图写入一个变量时,Zend若发现该变量指向的zval被多个变量共 享,则为其复制一份ref_count为1的zval,并递减原zval的refcount,这个过程称为“zval分离”。可见,只有在有写操作发生时 zend才进行拷贝操作,因此也叫copy-on-write(写时拷贝)对于引用型变量,其要求和非引用型相反,引用赋值的变量间必须是捆绑的,修改一个变量就修改了所有捆绑变量。整数、浮点数是PHP中的基础类型之一,也是一个简单型变量。对于整数和浮点数,在zvalue中直接存储对应的值。其类型分别是long和double。
从zvalue结构中可以看出,对于整数类型,和c等强类型语言不同,PHP是不区分int、unsigned int、long、long long等类型的,对它来说,整数只有一种类型也就是long。由此,可以看出,在PHP里面,整数的取值范围是由编译器位数来决定而不是固定不变的。
对于浮点数,类似整数,它也不区分float和double而是统一只有double一种类型。在PHP中,如果整数范围越界了怎么办?这种情况下会自动转换为double类型,这个一定要小心,很多trick都是由此产生。
和整数一样,字符变量也是PHP中的基础类型和简单型变量。通过zvalue结构可以看出,在PHP中,字符串是由由指向实际数据的指针和长度结 构体组成,这点和c++中的string比较类似。由于通过一个实际变量表示长度,和c不同,它的字符串可以是2进制数据(包含\0),同时在PHP中, 求字符串长度strlen是O(1)操作。在新增、修改、追加字符串操作时,PHP都会重新分配内存生成新的字符串。最后,出于安全考虑,PHP在生成一个字符串时末尾仍然会添加\0。
常见的字符串拼接方式及速度比较:假设有如下4个变量:$strA=‘123’; $strB = ‘456’; $intA=123; intB=456;
现在对如下的几种字符串拼接方式做一个比较和说明:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
也是malloc内存。不过sprintf的方式最具可读性,实际中可以根据具体情况灵活选择。
PHP的数组通过Zend HashTable来天然实现。foreach操作如何实现?对一个数组的foreach就是通过遍历hashtable中的双向链表完成。对于索引数组,通过foreach遍 历效率比for高很多,省去了key->value的查找。count操作直接调用 HashTable->NumOfElements,O(1)操作。对于’123’这样的字符串,zend会转换为其整数形 式。$arr[‘123’]和$arr[123]是等价的
Resource type variables are the most complex variables in PHP and are also a composite structure. PHP's zval can represent a wide range of data types, but it is difficult to fully describe custom data types. Since there is no efficient way to represent these composite structures, there is no way to use traditional operators on them. To solve this problem, you only need to refer to the pointer through an essentially arbitrary identifier (label), which is called a resource.
In zval, for resource, lval is used as a pointer, directly pointing to the address of the resource. Resource can be any composite structure. The familiar mysqli, fsock, memcached, etc. are all resources.
How to use resources:
Registration: For a custom data type, you want to use it as a resource. First, you need to register it, and zend will assign it a globally unique identifier.
Get a resource variable: For resources, zend maintains an id->hash_tale of actual data. For a resource, only its id is recorded in zval. When fetching, find the specific value in the hash_table through the id and return it.
Resource destruction: The data types of resources are diverse. Zend itself has no way to destroy it. Therefore, users need to provide a destruction function when registering resources.
When unset resources, zend calls the corresponding function to complete the destruction. Also delete it from the global resource table.
Resources can persist for a long time, not only after all variables referencing it go out of scope, but even after a request ends and a new request is generated. These resources are called persistent resources because they persist throughout the life cycle of the SAPI unless specifically destroyed. In many cases, persistent resources can improve performance to a certain extent. For example, in our common mysql_pconnect, persistent resources allocate memory through pemalloc so that they will not be released when the request ends. For zend, there is no distinction between the two per se.
How are local variables and global variables implemented in PHP? For a request, PHP can see two symbol tables (symbol_table and active_symbol_table) at any time, with the former used to maintain global variables. The latter is a pointer pointing to the currently active variable symbol table. When the program enters a function, zend will allocate a symbol table x to it and point active_symbol_table to a. In this way, the distinction between global and local variables is achieved.
Get variable values: PHP's symbol table is implemented through hash_table. Each variable is assigned a unique identifier. When obtaining, the corresponding zval is found from the table according to the identifier and returned.
Using global variables in functions: In functions, we can use global variables by explicitly declaring global. Create a reference to the variable with the same name in symbol_table in active_symbol_table. If there is no variable with the same name in symbol_table, it will be created first.
Recommended php Chinese website video tutorial: PHP video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to the underlying operating principle of PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Project Configuration
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we will understand the Environment Variables, General Configuration, Database Configuration and Email Configuration in CakePHP.
 PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 Installation and Upgrade guide for Ubuntu and Debian
Dec 24, 2024 pm 04:42 PM
PHP 8.4 brings several new features, security improvements, and performance improvements with healthy amounts of feature deprecations and removals. This guide explains how to install PHP 8.4 or upgrade to PHP 8.4 on Ubuntu, Debian, or their derivati
 CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP Date and Time
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work with date and time in cakephp4, we are going to make use of the available FrozenTime class.
 CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Working with Database
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Working with database in CakePHP is very easy. We will understand the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations in this chapter.
 CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
CakePHP File upload
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:27 PM
To work on file upload we are going to use the form helper. Here, is an example for file upload.
 Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
Discuss CakePHP
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:28 PM
CakePHP is an open-source framework for PHP. It is intended to make developing, deploying and maintaining applications much easier. CakePHP is based on a MVC-like architecture that is both powerful and easy to grasp. Models, Views, and Controllers gu
 CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
CakePHP Routing
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
In this chapter, we are going to learn the following topics related to routing ?
 CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
CakePHP Creating Validators
Sep 10, 2024 pm 05:26 PM
Validator can be created by adding the following two lines in the controller.



