what is apache kafka data collection

What is Apache Kafka data collection?
Apache Kafka - Introduction
Apache Kafka originated at LinkedIn and later became an open source Apache project in 2011 and then became an Apache first-class project in 2012. Kafka is written in Scala and Java. Apache Kafka is a fault-tolerant messaging system based on publish and subscribe. It is fast, scalable and distributed by design.
This tutorial will explore the principles, installation, and operation of Kafka, and then introduce the deployment of Kafka clusters. Finally, we will conclude with real-time applications and integration with Big Data Technologies.
Before proceeding with this tutorial, you must have a good understanding of Java, Scala, distributed messaging systems, and Linux environments.
In big data, a large amount of data is used. Regarding data, we have two main challenges. The first challenge is how to collect large amounts of data, and the second challenge is analyzing the collected data. To overcome these challenges, you need a messaging system.
Kafka is designed for distributed high-throughput systems. Kafka tends to work well as an alternative to more traditional mail brokers. Compared to other messaging systems, Kafka has better throughput, built-in partitioning, replication, and inherent fault tolerance, making it ideal for large-scale message processing applications.
What is a mail system?
The messaging system is responsible for transferring data from one application to another, so applications can focus on the data but not worry about how to share it. Distributed messaging is based on the concept of reliable message queues. Messages are queued asynchronously between the client application and the messaging system. Two types of messaging patterns are available - one is point-to-point and the other is a publish-subscribe (pub-sub) messaging system. Most messaging patterns follow pub-sub.
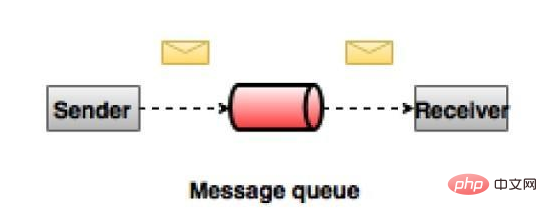
Point-to-point messaging system
In a point-to-point system, messages will remain in queues. One or more consumers can consume messages from the queue, but a specific message can be consumed by at most only one consumer. Once a consumer reads a message from a queue, it disappears from the queue. A typical example of this system is an order processing system, where each order will be processed by one order processor, but multiple order processors can work simultaneously. The diagram below depicts the structure.
Publish-Subscribe Messaging System
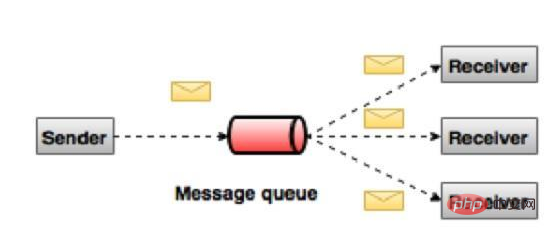
In a publish-subscribe system, messages will remain in topics. Unlike peer-to-peer systems, a consumer can subscribe to one or more topics and consume all messages in that topic. In the Publish-Subscribe system, the message generator is called the publisher, and the message consumer is called the subscriber. A real-life example is Dish TV, which publishes different channels like sports, movies, music, etc. Anyone can subscribe to their own channels and get their subscription channels.
#What is Kafka?
Apache Kafka is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system and powerful queue that can handle large amounts of data and enables you to deliver messages from one endpoint to another. Kafka is suitable for offline and online message consumption. Kafka messages are persisted on disk and replicated within the cluster to prevent data loss. Kafka is built on the ZooKeeper synchronization service. It integrates perfectly with Apache Storm and Spark to stream data analysis in real time.
Advantages The following are several benefits of Kafka -
Reliability - Kafka is distributed, partitioned, replicated and fault-tolerant.
Scalability - The Kafka messaging system scales easily with no downtime.
Durability - Kafka uses a distributed commit log, which means messages remain on disk as quickly as possible, so it is durable.
Performance - Kafka has high throughput for both publish and subscribe messages. It maintains stable performance even when many terabytes of messages are stored.
Kafka is very fast, guaranteeing zero downtime and zero data loss.
Use Cases
Kafka can be used for many use cases. Some of them are listed below -
Metrics - Kafka is often used to run monitoring data. This involves aggregating statistics from distributed applications to produce a centralized feed of operational data.
Log aggregation solution - Kafka can be used across an organization to collect logs from multiple services and serve them to multiple servers in a standard format.
Stream Processing - Popular frameworks like Storm and Spark
Streaming reads data from a topic, processes it, and writes the processed data to a new topic that is available to users and applications . Kafka's strong durability is also very useful in stream processing.
Kafka requires
Kafka is a unified platform for processing all real-time data sources. Kafka supports low-latency messaging and guarantees fault tolerance in the presence of machine failures. It has the ability to handle a large number of different consumers. Kafka is very fast, performing 2 million writes/second. Kafka persists all data to disk, which essentially means that all writes go to the operating system's (RAM) page cache. This transfers data from the page cache to the web socket very efficiently.
For more Apache related knowledge, please visit the Apache usage tutorial column!
The above is the detailed content of what is apache kafka data collection. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 PHP Framework Performance Comparison: The Ultimate Showdown of Speed vs. Efficiency
Apr 30, 2024 pm 12:27 PM
PHP Framework Performance Comparison: The Ultimate Showdown of Speed vs. Efficiency
Apr 30, 2024 pm 12:27 PM
According to benchmarks, Laravel excels in page loading speed and database queries, while CodeIgniter excels in data processing. When choosing a PHP framework, you should consider application size, traffic patterns, and development team skills.
 How to conduct concurrency testing and debugging in Java concurrent programming?
May 09, 2024 am 09:33 AM
How to conduct concurrency testing and debugging in Java concurrent programming?
May 09, 2024 am 09:33 AM
Concurrency testing and debugging Concurrency testing and debugging in Java concurrent programming are crucial and the following techniques are available: Concurrency testing: Unit testing: Isolate and test a single concurrent task. Integration testing: testing the interaction between multiple concurrent tasks. Load testing: Evaluate an application's performance and scalability under heavy load. Concurrency Debugging: Breakpoints: Pause thread execution and inspect variables or execute code. Logging: Record thread events and status. Stack trace: Identify the source of the exception. Visualization tools: Monitor thread activity and resource usage.
 Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
Application of algorithms in the construction of 58 portrait platform
May 09, 2024 am 09:01 AM
1. Background of the Construction of 58 Portraits Platform First of all, I would like to share with you the background of the construction of the 58 Portrait Platform. 1. The traditional thinking of the traditional profiling platform is no longer enough. Building a user profiling platform relies on data warehouse modeling capabilities to integrate data from multiple business lines to build accurate user portraits; it also requires data mining to understand user behavior, interests and needs, and provide algorithms. side capabilities; finally, it also needs to have data platform capabilities to efficiently store, query and share user profile data and provide profile services. The main difference between a self-built business profiling platform and a middle-office profiling platform is that the self-built profiling platform serves a single business line and can be customized on demand; the mid-office platform serves multiple business lines, has complex modeling, and provides more general capabilities. 2.58 User portraits of the background of Zhongtai portrait construction
 How to add a server in eclipse
May 05, 2024 pm 07:27 PM
How to add a server in eclipse
May 05, 2024 pm 07:27 PM
To add a server to Eclipse, follow these steps: Create a server runtime environment Configure the server Create a server instance Select the server runtime environment Configure the server instance Start the server deployment project
 The evasive module protects your website from application layer DOS attacks
Apr 30, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
The evasive module protects your website from application layer DOS attacks
Apr 30, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
There are a variety of attack methods that can take a website offline, and the more complex methods involve technical knowledge of databases and programming. A simpler method is called a "DenialOfService" (DOS) attack. The name of this attack method comes from its intention: to cause normal service requests from ordinary customers or website visitors to be denied. Generally speaking, there are two forms of DOS attacks: the third and fourth layers of the OSI model, that is, the network layer attack. The seventh layer of the OSI model, that is, the application layer attack. The first type of DOS attack - the network layer, occurs when a large number of of junk traffic flows to the web server. When spam traffic exceeds the network's ability to handle it, the website goes down. The second type of DOS attack is at the application layer and uses combined
 How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
To successfully deploy and maintain a PHP website, you need to perform the following steps: Select a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) Install PHP Create a database and connect PHP Upload code to the server Set up domain name and DNS Monitoring website maintenance steps include updating PHP and web servers, and backing up the website , monitor error logs and update content.
 How to leverage Kubernetes Operator simplifiy PHP cloud deployment?
May 06, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
How to leverage Kubernetes Operator simplifiy PHP cloud deployment?
May 06, 2024 pm 04:51 PM
KubernetesOperator simplifies PHP cloud deployment by following these steps: Install PHPOperator to interact with the Kubernetes cluster. Deploy the PHP application, declare the image and port. Manage the application using commands such as getting, describing, and viewing logs.
 How to implement PHP security best practices
May 05, 2024 am 10:51 AM
How to implement PHP security best practices
May 05, 2024 am 10:51 AM
How to Implement PHP Security Best Practices PHP is one of the most popular backend web programming languages used for creating dynamic and interactive websites. However, PHP code can be vulnerable to various security vulnerabilities. Implementing security best practices is critical to protecting your web applications from these threats. Input validation Input validation is a critical first step in validating user input and preventing malicious input such as SQL injection. PHP provides a variety of input validation functions, such as filter_var() and preg_match(). Example: $username=filter_var($_POST['username'],FILTER_SANIT




