Servlet JSP ServletConfig object
The ServletConfig object has four methods.

##getInitParameter, getInitParameterNames, getServletName
(1) getInitParameter, getInitParameterNames are used to obtain the parameters in Web.xml Name, parameter value. (2)getServletName Gets the Servlet-name in Web.xml. ExampleThe following is the file content of Web.xml:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>TestServletConfig</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.djun.serveleMapping.TestServletConfig</servlet-class>
<!--配置Servlet的初始化参数-->
<!-- 如何获取初始化的参数?
1、getInitParameter(String name)
Returns a String containing the value of the named initialization parameter,
or null if the parameter does not exist.
2、 getInitParameterNames()
Returns the names of the servlet's initialization parameters as an Enumeration of String objects,
or an empty Enumeration if the servlet has no initialization parameters.
-->
<init-param>
<param-name>username</param-name>
<param-value>admin</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>passworld</param-name>
<param-value>admin</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--
指定Servlet JSP被创建的时机
若数值 a<0,则仅在第一次的时候被创建。
若 a>=0 , 则在当前应用被Servlet容器加载时创建实例
数值越小越早被创建
-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>TestServletConfig</servlet-name>
<!--只要后缀为html的文件都由该类处理-->
<url-pattern>/servletConfig</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Copy after login
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
public class TestServletConfig implements Servlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("Init TestServletConfig...");
System.out.println("-----------执行getInitParameter--------");
String username = servletConfig.getInitParameter("username");
String passworld = servletConfig.getInitParameter("passworld");
System.out.println("username: " + username+"\n"+"password : "+passworld);
System.out.println("----------执行getInitParameterNames------");
Enumeration<String> names = servletConfig.getInitParameterNames();
while(names.hasMoreElements()){
String name = names.nextElement();
String value = servletConfig.getInitParameter(name);
System.out.println("username: " + name+"\n"+"password : "+value);
}
String servletName = servletConfig.getServletName();
System.out.println(servletName);
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("TestServletConfig....");
}
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}Copy after login
getServletContext
(1) Servlet for each Web The application creates a corresponding ServletContext object. The ServletContext object is included in the ServletConfig object. A reference to the ServletContext object can be returned by calling the ServletContext.getServletContext() method.(2) getContextPath()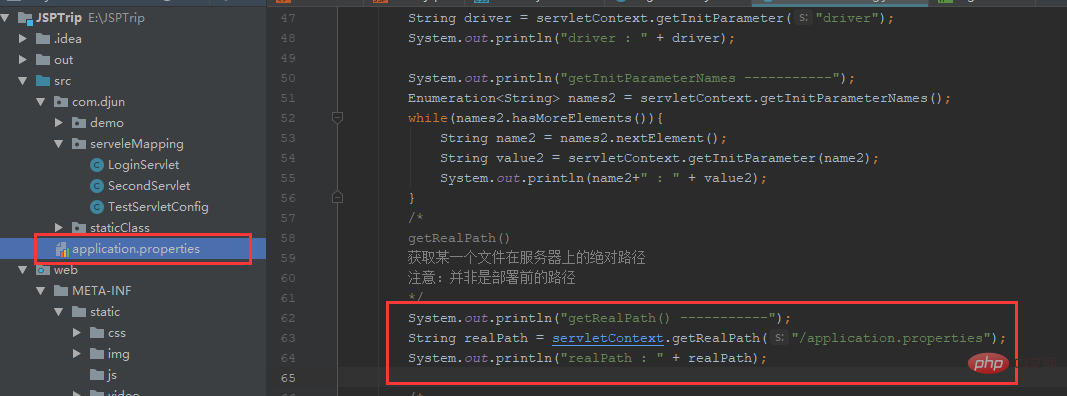
System.out.println("getContextPath() -----------");
String contextPath = servletContext.getContextPath();
System.out.println(contextPath);
String fileName = "application.properties";
try {
File file = new File(realPath+ "/" + fileName);
ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(realPath + "/" + fileName);
System.out.println(realPath+ "/" + fileName);
System.out.println("1. "+ is);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}Copy after login
The above is the detailed content of Servlet JSP ServletConfig object. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement of this Website
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article
R.E.P.O. Energy Crystals Explained and What They Do (Yellow Crystal)
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
R.E.P.O. Best Graphic Settings
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
Assassin's Creed Shadows: Seashell Riddle Solution
3 weeks ago
By DDD
What's New in Windows 11 KB5054979 & How to Fix Update Issues
2 weeks ago
By DDD
Will R.E.P.O. Have Crossplay?
1 months ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
CakePHP Tutorial
 1382
1382
 52
52
 1382
1382
 52
52


