 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 PHP+Redis ordered collection to achieve real-time update of 24-hour rankings
PHP+Redis ordered collection to achieve real-time update of 24-hour rankings
PHP+Redis ordered collection to achieve real-time update of 24-hour rankings
Basic introduction
Redis ordered set, like a set, is also a collection of string type elements, and duplicate members are not allowed.
The difference is that each element is associated with a double type score. Redis uses scores to sort the members of the collection from small to large.
The members of an ordered set are unique, but the scores can be repeated.
Sets are implemented through hash tables, so the complexity of adding, deleting, and searching is O (1). The maximum number of members in a collection is 2^32 - 1^ (4294967295, each collection can store more than 4 billion members).
An ordered set is first of all a set, and its members are unique. Secondly, each member is associated with a score, so that the members can be sorted according to the score.
Description of requirements
Imagine that there are millions of player data in a game. If you now need to compile a top 10 ranking based on the player’s experience value Bang, what would you do? The general approach is to write a SQL statement similar to the following to obtain:
select * from game_socre order by score desc limit 0,20
This method is feasible when the amount of data is small, but the query speed will be slower when the amount of data is large. , especially when joint table query is required, the speed decrease will be even more obvious.
Implementation
At this time you can consider using redis to implement this function.
The redis data type mainly used to implement this function is the redis ordered set zset. zset is an extension of the set type, which has one more sequence attribute than the original type. This attribute will automatically adjust the order value each time data is inserted to ensure that the value values are continuously arranged in a certain order.
The main implementation ideas are:
1. When a new player participates in the game, add a new record to the zset in redis (the content of the record depends on the specific requirements) score is 0
2. When the player's experience value changes, modify the player's score value
3. Use the ZREVRANGE method of redis to obtain the rankings
Return in order In the set key, the members in the specified range. The positions of the members are arranged in descending order of score value (from large to small). Members with the same score value are sorted in reverse lexicographic order. The ZREVRANGE command is identical to the ZRANGE command except that the members are arranged in order of decreasing score value.
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> ZADD KEY_NAME SCORE1 VALUE1.. SCOREN VALUEN
1. Data preparation
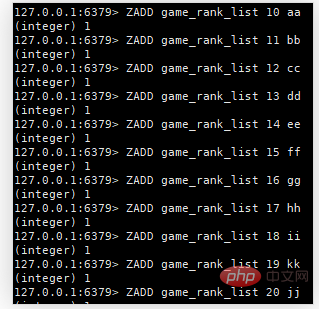
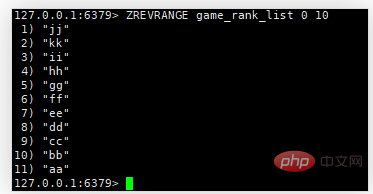
2. Get the score top10 ranking (ZREVRANGE is in descending order, ZRANGE is in ascending order)
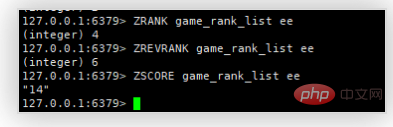
3. View the actual ranking of user ee (ZREVRANK is in descending order, ZRANK is in ascending order), real-time score
Further requirements
Need to implement the latest 24-hour user points rankings and count the top 10 players and points
Implementation
Main implementation ideas Yes:
Use ZADD to add the user's points information by hour, and then use ZUNIONSTORE union to achieve the total game points for 24 hours to achieve the "24-hour ranking"; (If you have a better idea, you can It would be better if you leave a message below and give me some advice)
ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...]
The Redis Zunionstore command calculates the union of one or more given ordered sets, in which the number of given keys must be specified with the numkeys parameter, and the The union (result set) is stored in destination.
By default, the score of a member in the result set is the sum of the scores of that member in all given sets.
Problems you may encounter
1. Problem with the same score
When Redis encounters the same score, it follows the dictionary order of the set members themselves. Sorting, here is sorting according to the two strings "user2" and "user3". If sorted in reverse order, user3 will naturally be ranked first. To solve this problem, we can consider adding a timestamp to the score. The calculation formula is:
Score with timestamp = actual score*10000000000 (9999999999 – timestamp)
timestamp We use the system The time() function provided, that is, the number of seconds since January 1, 1970, we use a 32-bit timestamp (this can last until 2038), since a 32-bit timestamp is a 10-digit decimal integer (the maximum value is 4294967295 ), so we let the timestamp occupy the lower 10 bits (decimal integer), the actual score is expanded by 10^10 times, and then the result of adding the two parts is used as the score of zset. Considering that we are sorting in reverse chronological order, the timestamp part needs to be reversed, which is why we subtract the timestamp from 9999999999. When we want to read the player's actual score, we simply remove the last 10 digits.
Initially, this plan seems good, but there are two problems in it.
The first problem is a minor one. Using seconds as the timestamp may not be sufficiently differentiated. If two timestamps with the same score appear in the same second, the previous problem will still occur. Of course, we can choose a timestamp with higher precision, but In actual scenarios, it doesn’t matter who is in front at the same second.
The second problem is a big one, because the fraction type of Redis uses double, and the 64-bit double-precision floating point number has only 52 significant digits. The integer range it can accurately express is - 2^53 to 2 ^53, which can only represent up to 16 decimal integers (the maximum value is 9007199254740992, in fact, even 16 digits cannot be fully represented). This means that if the previous timestamp takes up 10 digits, the score will only have 6 digits, which is not enough for some leaderboard scores. We could consider reducing the number of timestamp digits, say starting on January 1, 2015, but that would still not add a few digits. Or reduce the distinction and use minutes and hours as timestamp units.
If the score type of Redis is int64, we will not have the above troubles. Speaking of which, in fact, Redis should really provide an additional int64 type ZSet, but currently it can only be a fantasy unless you change its source code.
For more PHP related knowledge, please visit PHP Chinese website!
The above is the detailed content of PHP+Redis ordered collection to achieve real-time update of 24-hour rankings. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Future of PHP: Adaptations and Innovations
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, containerization and microservice architectures, supporting Docker and Kubernetes; 2) introducing JIT compilers and enumeration types to improve performance and data processing efficiency; 3) Continuously optimize performance and promote best practices.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.



