How to use redis in projects
Redis, as an in-memory database with excellent performance, has a variety of application scenarios in Internet companies. This article introduces the scenarios in which the author uses Redis in projects.

Mainly introduced from the following aspects:
Distributed locks (Recommended learning: Redis video Tutorial)
Interface current limiter
Order cache
Redis and DB data consistency processing
Prevent cache penetration and avalanche
Distributed session sharing
Order cache
The storage structure of the entire order is as follows:
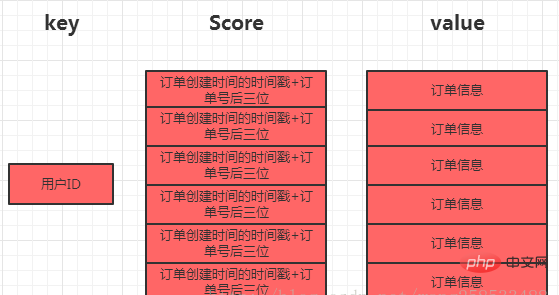
Use Redis's zset data structure to store each user's orders, arranged in reverse order by order time, with the user's unique identifier as the key, the user's order collection as the value, and the last three digits of the order number as the timestamp of the order creation time as the score
Why not just use the timestamp of the order time as the score? Because the order time is only accurate to the second, multiple orders may appear in the same second, so the same score will appear. Adding the last three digits of the order number can basically avoid this situation.
Only put the user’s first N orders, because few users will view orders from long ago, so this will save a lot of space. If a user needs to check the orders after the first N orders, they can query them from the database. Of course, the probability of this is relatively small.
The above is the detailed content of How to use redis in projects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Solution to 0x80242008 error when installing Windows 11 10.0.22000.100
May 08, 2024 pm 03:50 PM
Solution to 0x80242008 error when installing Windows 11 10.0.22000.100
May 08, 2024 pm 03:50 PM
1. Start the [Start] menu, enter [cmd], right-click [Command Prompt], and select Run as [Administrator]. 2. Enter the following commands in sequence (copy and paste carefully): SCconfigwuauservstart=auto, press Enter SCconfigbitsstart=auto, press Enter SCconfigcryptsvcstart=auto, press Enter SCconfigtrustedinstallerstart=auto, press Enter SCconfigwuauservtype=share, press Enter netstopwuauserv , press enter netstopcryptS
 Golang API caching strategy and optimization
May 07, 2024 pm 02:12 PM
Golang API caching strategy and optimization
May 07, 2024 pm 02:12 PM
The caching strategy in GolangAPI can improve performance and reduce server load. Commonly used strategies are: LRU, LFU, FIFO and TTL. Optimization techniques include selecting appropriate cache storage, hierarchical caching, invalidation management, and monitoring and tuning. In the practical case, the LRU cache is used to optimize the API for obtaining user information from the database. The data can be quickly retrieved from the cache. Otherwise, the cache can be updated after obtaining it from the database.
 Caching mechanism and application practice in PHP development
May 09, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
Caching mechanism and application practice in PHP development
May 09, 2024 pm 01:30 PM
In PHP development, the caching mechanism improves performance by temporarily storing frequently accessed data in memory or disk, thereby reducing the number of database accesses. Cache types mainly include memory, file and database cache. Caching can be implemented in PHP using built-in functions or third-party libraries, such as cache_get() and Memcache. Common practical applications include caching database query results to optimize query performance and caching page output to speed up rendering. The caching mechanism effectively improves website response speed, enhances user experience and reduces server load.
 How to upgrade Win11 English 21996 to Simplified Chinese 22000_How to upgrade Win11 English 21996 to Simplified Chinese 22000
May 08, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
How to upgrade Win11 English 21996 to Simplified Chinese 22000_How to upgrade Win11 English 21996 to Simplified Chinese 22000
May 08, 2024 pm 05:10 PM
First you need to set the system language to Simplified Chinese display and restart. Of course, if you have changed the display language to Simplified Chinese before, you can just skip this step. Next, start operating the registry, regedit.exe, directly navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlNlsLanguage in the left navigation bar or the upper address bar, and then modify the InstallLanguage key value and Default key value to 0804 (if you want to change it to English en-us, you need First set the system display language to en-us, restart the system and then change everything to 0409) You must restart the system at this point.
 How to use Redis cache in PHP array pagination?
May 01, 2024 am 10:48 AM
How to use Redis cache in PHP array pagination?
May 01, 2024 am 10:48 AM
Using Redis cache can greatly optimize the performance of PHP array paging. This can be achieved through the following steps: Install the Redis client. Connect to the Redis server. Create cache data and store each page of data into a Redis hash with the key "page:{page_number}". Get data from cache and avoid expensive operations on large arrays.
 Can navicat connect to redis?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:12 PM
Can navicat connect to redis?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 05:12 PM
Yes, Navicat can connect to Redis, which allows users to manage keys, view values, execute commands, monitor activity, and diagnose problems. To connect to Redis, select the "Redis" connection type in Navicat and enter the server details.
 How to find the update file downloaded by Win11_Share the location of the update file downloaded by Win11
May 08, 2024 am 10:34 AM
How to find the update file downloaded by Win11_Share the location of the update file downloaded by Win11
May 08, 2024 am 10:34 AM
1. First, double-click the [This PC] icon on the desktop to open it. 2. Then double-click the left mouse button to enter [C drive]. System files will generally be automatically stored in C drive. 3. Then find the [windows] folder in the C drive and double-click to enter. 4. After entering the [windows] folder, find the [SoftwareDistribution] folder. 5. After entering, find the [download] folder, which contains all win11 download and update files. 6. If we want to delete these files, just delete them directly in this folder.
 PHP Redis caching applications and best practices
May 04, 2024 am 08:33 AM
PHP Redis caching applications and best practices
May 04, 2024 am 08:33 AM
Redis is a high-performance key-value cache. The PHPRedis extension provides an API to interact with the Redis server. Use the following steps to connect to Redis, store and retrieve data: Connect: Use the Redis classes to connect to the server. Storage: Use the set method to set key-value pairs. Retrieval: Use the get method to obtain the value of the key.






