 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Golang
Golang
 Introduction to the overall architecture of go microservice framework go-micro
Introduction to the overall architecture of go microservice framework go-micro
Introduction to the overall architecture of go microservice framework go-micro
A small project in the product mouth, from project establishment to development and launch, will become more and more complex as time and demand continue to surge, turning into a large project. If the early project If the architecture is not designed well, the code will become more and more bloated and difficult to maintain. Each subsequent product iteration will affect the whole system.
Microservice-based projects and loosely coupled relationships between modules are a good choice. Although it increases maintenance costs, it is still worth it.

In addition to the stability of microservice projects, I am also personally concerned about several issues:
1: The efficiency and security of data transmission between services.
2: Dynamic expansion of services, that is, service registration and discovery, and service clustering.
3: Microservice functions can be customized, because not all functions will meet your needs. It is inevitable that you need to develop some functions according to your own needs.
go-micro is a good rpc microservice framework under go language. It has perfect functions and has also solved several problems that I am concerned about:
1: The transmission format between services is protobuf, which is extremely efficient, very fast and safe.
2: go-micro's service registration and discovery are diverse. I personally prefer etcdv3's service discovery and registration.
3: The main functions have corresponding interfaces. As long as the corresponding interfaces are implemented, you can customize the plug-in according to your own needs.
In my spare time, I systematically read the source code of go-micro. The more I read, the more I felt that this framework was well written, and I learned a lot from it. I just want to compile a series of posts and share my experience of learning go-micro with everyone.
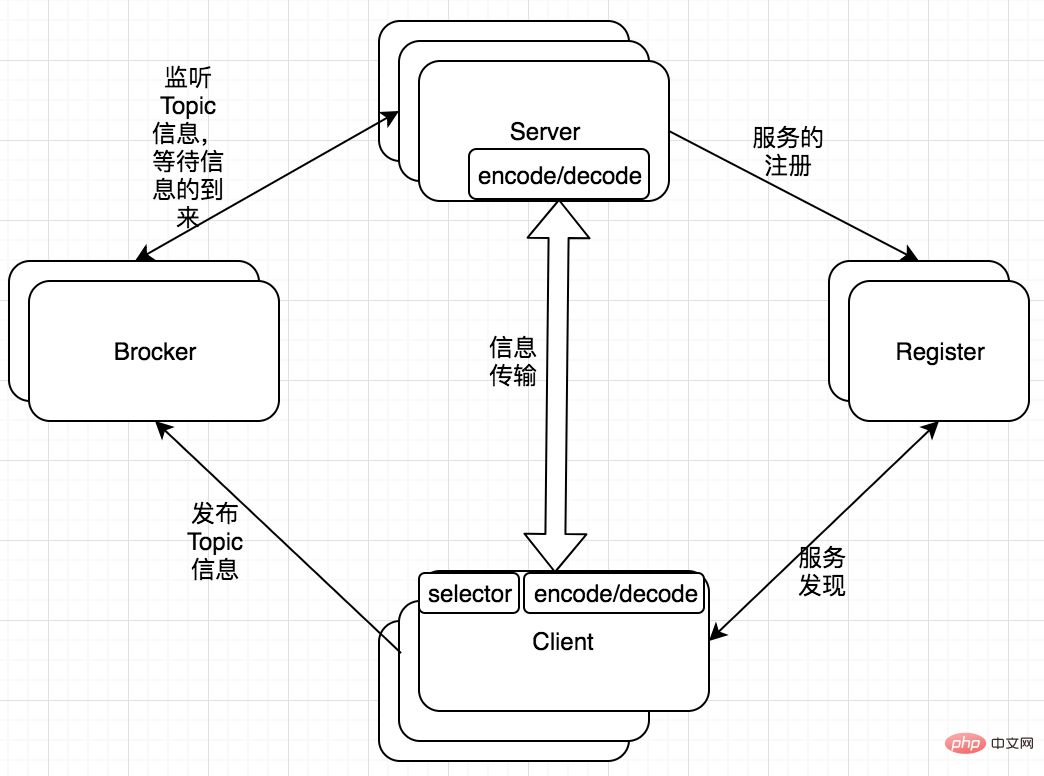
The communication process of go-micro is as follows

Server monitors the client’s calls and processes the information pushed by Brocker. And the server needs to register its existence or death with the Register so that the client can know its status.
Register service registration discovery.
The client gets the Server information from the Register, and then selects a Server for communication based on the algorithm for each call. Of course, communication requires a series of processes such as encoding/decoding and selecting a transmission protocol.
If you need to notify all servers, you can use Brocker to push information.
Brocker information queue receives and publishes information.
The reason why go-micro can be highly customized is inseparable from its framework structure. go-micro consists of 8 key interfaces. Each interface can be re-implemented according to its own needs. This The eight main intefaces also constitute the framework structure of go-micro.
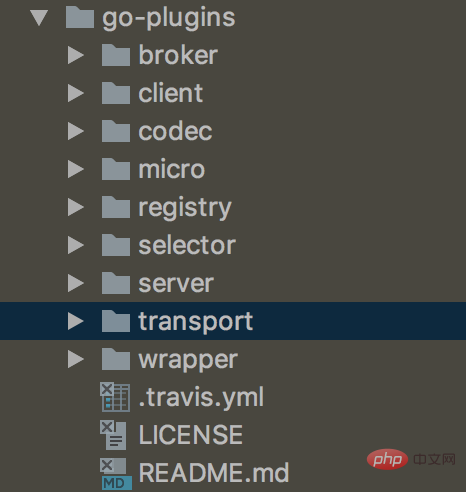
These interfaces go-micir has its own default implementation, and there is also a go-plugins that is an alternative to the implementation of these interfaces. You can also implement your own plug-ins according to your needs.

This post is mainly to introduce you to the main structure of go-micro and the functions of these interfaces. We will talk about the specific details in future articles:
Transort
Interface for communication between services. That is, the final implementation of service sending and receiving is customized by these interfaces.
Source code:
type Socket interface {
Recv(*Message) error
Send(*Message) error
Close() error
}
type Client interface {
Socket
}
type Listener interface {
Addr() string
Close() error
Accept(func(Socket)) error
}
type Transport interface {
Dial(addr string, opts ...DialOption) (Client, error)
Listen(addr string, opts ...ListenOption) (Listener, error)
String() string
}Transport's Listen method is generally called by the server. It listens to a port and waits for the client to call.
Transport's Dial is the method used by the client to connect to the service. It returns a Client interface, which returns a Client interface. This Client is embedded in the Socket interface. The methods of this interface are to specifically send and receive communication information.
http transmission is the default synchronous communication mechanism of go-micro. Of course, there are many other plug-ins: grpc, nats, tcp, udp, rabbitmq, nats, all of which have been implemented so far. You can find it in go-plugins.
Codec
With the transmission method, the next thing to solve is the transmission encoding and decoding problem. go-micro has many encoding and decoding methods. The default implementation is protobuf, of course, there are other implementation methods, such as json, protobuf, jsonrpc, mercury, etc.
Source code
type Codec interface {
ReadHeader(*Message, MessageType) error
ReadBody(interface{}) error
Write(*Message, interface{}) error
Close() error
String() string
}
type Message struct {
Id uint64
Type MessageType
Target string
Method string
Error string
Header map[string]string
}The Write method of the Codec interface is the encoding process, and the two Reads are the decoding process.
Registry
Service registration and discovery, currently implemented consul, mdns, etcd, etcdv3, zookeeper, kubernetes., etc.,
type Registry interface {
Register(*Service, ...RegisterOption) error
Deregister(*Service) error
GetService(string) ([]*Service, error)
ListServices() ([]*Service, error)
Watch(...WatchOption) (Watcher, error)
String() string
Options() Options
}To put it simply, the Service registers and the Client uses the watch method for monitoring. When a service is added or deleted, this method will be triggered to remind the client to update the Service information.
The default service registration and discovery is consul, but I personally do not recommend it because you cannot use consul cluster directly
我个人比较喜欢etcdv3集群。大家可以根据自己的喜好选择。
Selector
以Registry为基础,Selector 是客户端级别的负载均衡,当有客户端向服务发送请求时, selector根据不同的算法从Registery中的主机列表,得到可用的Service节点,进行通信。目前实现的有循环算法和随机算法,默认的是随机算法。
源码:
type Selector interface {
Init(opts ...Option) error
Options() Options
// Select returns a function which should return the next node
Select(service string, opts ...SelectOption) (Next, error)
// Mark sets the success/error against a node
Mark(service string, node *registry.Node, err error)
// Reset returns state back to zero for a service
Reset(service string)
// Close renders the selector unusable
Close() error
// Name of the selector
String() string
}默认的是实现是本地缓存,当前实现的有blacklist,label,named等方式。
Broker
Broker是消息发布和订阅的接口。很简单的一个例子,因为服务的节点是不固定的,如果有需要修改所有服务行为的需求,可以使服务订阅某个主题,当有信息发布时,所有的监听服务都会收到信息,根据你的需要做相应的行为。
源码
type Broker interface {
Options() Options
Address() string
Connect() error
Disconnect() error
Init(...Option) error
Publish(string, *Message, ...PublishOption) error
Subscribe(string, Handler, ...SubscribeOption) (Subscriber, error)
String() string
}Broker默认的实现方式是http方式,但是这种方式不要在生产环境用。go-plugins里有很多成熟的消息队列实现方式,有kafka、nsq、rabbitmq、redis,等等。
Client
Client是请求服务的接口,他封装Transport和Codec进行rpc调用,也封装了Brocker进行信息的发布。
源码
type Client interface {
Init(...Option) error
Options() Options
NewMessage(topic string, msg interface{}, opts ...MessageOption) Message
NewRequest(service, method string, req interface{}, reqOpts ...RequestOption) Request
Call(ctx context.Context, req Request, rsp interface{}, opts ...CallOption) error
Stream(ctx context.Context, req Request, opts ...CallOption) (Stream, error)
Publish(ctx context.Context, msg Message, opts ...PublishOption) error
String() string
}当然他也支持双工通信 Stream 这些具体的实现方式和使用方式,以后会详细解说。
默认的是rpc实现方式,他还有grpc和http方式,在go-plugins里可以找到
Server
Server看名字大家也知道是做什么的了。监听等待rpc请求。监听broker的订阅信息,等待信息队列的推送等。
源码
type Server interface {
Options() Options
Init(...Option) error
Handle(Handler) error
NewHandler(interface{}, ...HandlerOption) Handler
NewSubscriber(string, interface{}, ...SubscriberOption) Subscriber
Subscribe(Subscriber) error
Register() error
Deregister() error
Start() error
Stop() error
String() string
}默认的是rpc实现方式,他还有grpc和http方式,在go-plugins里可以找到
Service
Service是Client和Server的封装,他包含了一系列的方法使用初始值去初始化Service和Client,使我们可以很简单的创建一个rpc服务。
源码:
type Service interface {
Init(...Option)
Options() Options
Client() client.Client
Server() server.Server
Run() error
String() string
}The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the overall architecture of go microservice framework go-micro. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Evaluating the cost/performance of commercial support for a Java framework involves the following steps: Determine the required level of assurance and service level agreement (SLA) guarantees. The experience and expertise of the research support team. Consider additional services such as upgrades, troubleshooting, and performance optimization. Weigh business support costs against risk mitigation and increased efficiency.
 How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
The lightweight PHP framework improves application performance through small size and low resource consumption. Its features include: small size, fast startup, low memory usage, improved response speed and throughput, and reduced resource consumption. Practical case: SlimFramework creates REST API, only 500KB, high responsiveness and high throughput
 How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
The learning curve of a PHP framework depends on language proficiency, framework complexity, documentation quality, and community support. The learning curve of PHP frameworks is higher when compared to Python frameworks and lower when compared to Ruby frameworks. Compared to Java frameworks, PHP frameworks have a moderate learning curve but a shorter time to get started.
 How to use gomega for assertions in Golang unit tests?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
How to use gomega for assertions in Golang unit tests?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
How to use Gomega for assertions in Golang unit testing In Golang unit testing, Gomega is a popular and powerful assertion library that provides rich assertion methods so that developers can easily verify test results. Install Gomegagoget-ugithub.com/onsi/gomega Using Gomega for assertions Here are some common examples of using Gomega for assertions: 1. Equality assertion import "github.com/onsi/gomega" funcTest_MyFunction(t*testing.T){
 How does Go WebSocket integrate with databases?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
How does Go WebSocket integrate with databases?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
How to integrate GoWebSocket with a database: Set up a database connection: Use the database/sql package to connect to the database. Store WebSocket messages to the database: Use the INSERT statement to insert the message into the database. Retrieve WebSocket messages from the database: Use the SELECT statement to retrieve messages from the database.
 How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
Choose the best Go framework based on application scenarios: consider application type, language features, performance requirements, and ecosystem. Common Go frameworks: Gin (Web application), Echo (Web service), Fiber (high throughput), gorm (ORM), fasthttp (speed). Practical case: building REST API (Fiber) and interacting with the database (gorm). Choose a framework: choose fasthttp for key performance, Gin/Echo for flexible web applications, and gorm for database interaction.
 Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
In Go framework development, common challenges and their solutions are: Error handling: Use the errors package for management, and use middleware to centrally handle errors. Authentication and authorization: Integrate third-party libraries and create custom middleware to check credentials. Concurrency processing: Use goroutines, mutexes, and channels to control resource access. Unit testing: Use gotest packages, mocks, and stubs for isolation, and code coverage tools to ensure sufficiency. Deployment and monitoring: Use Docker containers to package deployments, set up data backups, and track performance and errors with logging and monitoring tools.
 What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
There are five misunderstandings in Go framework learning: over-reliance on the framework and limited flexibility. If you don’t follow the framework conventions, the code will be difficult to maintain. Using outdated libraries can cause security and compatibility issues. Excessive use of packages obfuscates code structure. Ignoring error handling leads to unexpected behavior and crashes.




