redis sentinel cluster graphic tutorial

Sentinel is a high-availability solution for Redis: a Sentinel system composed of one or more Sentinel instances can monitor any number of master servers and the servers under these master servers. All slave servers, and when the monitored master server goes offline, automatically upgrade a slave server under the offline master server to the new master server. Recommended: redis video tutorial
For example:

After Server1 goes offline:

Upgrade Server2 to the new main server:

2. Redis master-slave separation
Before explaining the Sentinel cluster, let's first build a simple master-slave separation (read-write separation).
First of all, we default that everyone has installed redis, then we will copy multiple copies of redis.conf and create multiple directories to distinguish multiple redis services:

Here, each directory has its own redis.conf configuration file. Next, we first set the configuration file of the main server.
1. Configure Master
1. Modify the port
# Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344). # If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket. port 6380
The default port of redis is 6379. Here we set the port of the main server to 6380
2. Modify pidfile
# If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup # and removes it at exit. # # When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is # specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file # is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid". # # Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it # nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally. pidfile /var/run/redis_6380.pid
pidfile is a pid process number assigned to us by Linux when we start redis. If no modification is made here, it will affect the subsequent startup of the redis service
3. Start redis

Start redis, we can see that redis has occupied port 6380
Enter the client
redis-cli -p 6380 127.0.0.1:6380> info ... # Replication role:master connected_slaves:0 master_repl_offset:0 repl_backlog_active:0 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0 repl_backlog_histlen:0 ...
us As you can see, the current role of redis is a service started by the master.
2. Configure Slave
Same as configuring master above, we need to modify the port number and pid file. After modification, we have two methods to configure the slave service
1. Configure the slave service in the configuration file
################################# REPLICATION ################################# # Master-Slave replication. Use slaveof to make a Redis instance a copy of # another Redis server. A few things to understand ASAP about Redis replication. # # 1) Redis replication is asynchronous, but you can configure a master to # stop accepting writes if it appears to be not connected with at least # a given number of slaves. # 2) Redis slaves are able to perform a partial resynchronization with the # master if the replication link is lost for a relatively small amount of # time. You may want to configure the replication backlog size (see the next # sections of this file) with a sensible value depending on your needs. # 3) Replication is automatic and does not need user intervention. After a # network partition slaves automatically try to reconnect to masters # and resynchronize with them. # # slaveof <masterip> <masterport> slaveof 127.0.0.1 6380
We can directly modify the slaveof attribute in the configuration file. We directly configure the IP address and port number of the main server. If the main server here has a configuration password
You can set the link password by configuring masterauth
# If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration # directive below) it is possible to tell the slave to authenticate before # starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will # refuse the slave request. # # masterauth <master-password>
Start the redis service:

We can see that there are two running now, We enter the client of 6381 and take a look at its status.
# Replication role:slave master_host:127.0.0.1 master_port:6380 master_link_status:up master_last_io_seconds_ago:1 master_sync_in_progress:0 slave_repl_offset:71 slave_priority:100 slave_read_only:1 connected_slaves:0 master_repl_offset:0 repl_backlog_active:0 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0 repl_backlog_histlen:0
We can see that the current redis is a slave service, connected to the service of 6380.
2. Set after the service starts
After we modify the server configuration file of port 6382, start the service
Enter the client, Check the status of the current server:
# Replication role:master connected_slaves:0 master_repl_offset:0 repl_backlog_active:0 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0 repl_backlog_histlen:0
We can see that the status of the current server is running as a main service. Let’s modify its status next:
127.0.0.1:6382> slaveof 127.0.0.1 6380 //修改后状态 # Replication role:slave master_host:127.0.0.1 master_port:6380 master_link_status:up master_last_io_seconds_ago:1 master_sync_in_progress:0 slave_repl_offset:617 slave_priority:100 slave_read_only:1 connected_slaves:0 master_repl_offset:0 repl_backlog_active:0 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0 repl_backlog_histlen:0
3. Summary
Let’s first take a look at the current status of the master:
# Replication role:master connected_slaves:2 slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6381,state=online,offset=785,lag=0 slave1:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6382,state=online,offset=785,lag=0 master_repl_offset:785 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:2 repl_backlog_histlen:784
We can see that the two slave services are already connected to the master server. The difference between the above two configurations is that when the salve is disconnected After the line is reconnected,
If we modify the class configuration file, we will connect to the master by ourselves after reconnection, and synchronize the data on the master.
If we manually connect to the main server , after reconnection, the slave server will read its own local rdb reply data and will not automatically connect to the main service
If we need to set up read-write separation, we only need to set it in the main server:
# Note: read only slaves are not designed to be exposed to untrusted clients # on the internet. It's just a protection layer against misuse of the instance. # Still a read only slave exports by default all the administrative commands # such as CONFIG, DEBUG, and so forth. To a limited extent you can improve # security of read only slaves using 'rename-command' to shadow all the # administrative / dangerous commands. slave-read-only yes
3. Sentinel
1. Configuration port
In the sentinel.conf configuration file, we can find port attribute, here is used to set the port of sentinel. Under normal circumstances, at least three sentinels are needed to monitor redis. We can start multiple sentinel services by modifying the port.
# port <sentinel-port># The port that this sentinel instance will run on port 26379
2. Configure the IP and port of the main server
We change the listening port to 6380, and add a weight of 2. The weight here is used to calculate what we need Which server should be upgraded to the main server
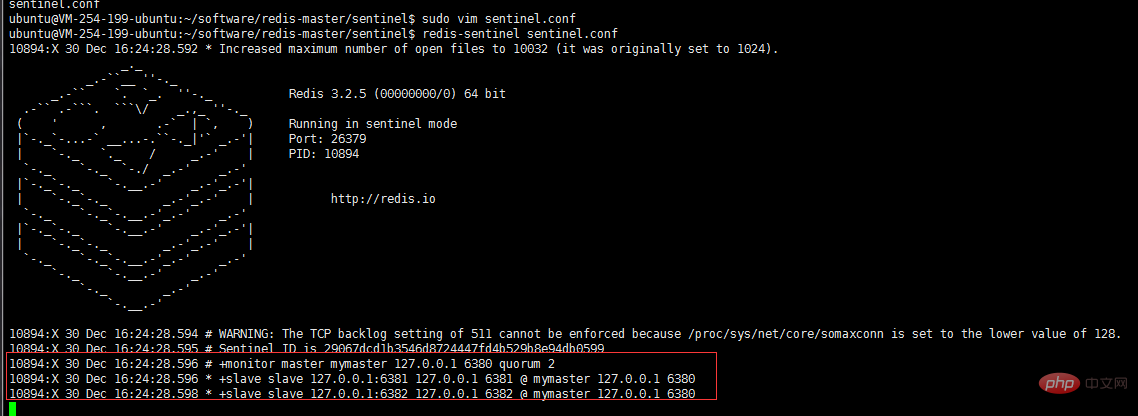
# sentinel monitor <master-name> <ip> <redis-port> <quorum> # # Tells Sentinel to monitor this master, and to consider it in O_DOWN # (Objectively Down) state only if at least <quorum> sentinels agree. # # Note that whatever is the ODOWN quorum, a Sentinel will require to # be elected by the majority of the known Sentinels in order to # start a failover, so no failover can be performed in minority. # # Slaves are auto-discovered, so you don't need to specify slaves in # any way. Sentinel itself will rewrite this configuration file adding # the slaves using additional configuration options. # Also note that the configuration file is rewritten when a # slave is promoted to master. # # Note: master name should not include special characters or spaces. # The valid charset is A-z 0-9 and the three characters ".-_". sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6380 2
3. Start Sentinel
/sentinel$ redis-sentinel sentinel.conf

After Sentinel starts, it will monitor that there is now a main server. Two slave servers
当我们把其中一个从服务器器关闭之后,我们可以看到日志:
10894:X 30 Dec 16:27:03.670 # +sdown slave 127.0.0.1:6381 127.0.0.1 6381 @ mymaster 127.0.0.1 6380
日志表示,6381这个从服务器已经从主服务器中脱离了出来,我们重新把6381 接回去。
10894:X 30 Dec 16:28:43.288 * +reboot slave 127.0.0.1:6381 127.0.0.1 6381 @ mymaster 127.0.0.1 638010894:X 30 Dec 16:28:43.365 # -sdown slave 127.0.0.1:6381 127.0.0.1 6381 @ mymaster 127.0.0.1 6380
4、关闭Master
我们手动关闭Master 之后,sentinel 在监听master 确实是断线了之后,将会开始计算权值,然后重新分配主服务器
我们可以看到,6380主服务器断了之后,sentinel 帮我们选了6382作为新的主服务器
我们进到6382的客户端,查看他的状态:
# Replication role:master connected_slaves:1 slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6381,state=online,offset=13751,lag=0 master_repl_offset:13751 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:2 repl_backlog_histlen:13750
我们可以看到 6382,重slave 荣升为master
127.0.0.1:6382> set name jaycekon OK
原本的没有权限写,也得到了相应的权限
5、重连Master
大家可能会好奇,如果master 重连之后,会不会抢回属于他的位置,答案是否定的,就比如你被一个小弟抢了你老大的位置,他肯给回你这个位置吗。因此当master 回来之后,他也只能当个小弟
4、Sentinel 总结
一、Sentinel的作用:
A、Master 状态监测
B、如果Master 异常,则会进行Master-slave 转换,将其中一个Slave作为Master,将之前的Master作为Slave
C、Master-Slave切换后,master_redis.conf、slave_redis.conf和sentinel.conf的内容都会发生改变,即master_redis.conf中会多一行slaveof的配置,sentinel.conf的监控目标会随之调换
二、Sentinel的工作方式:
1):每个Sentinel以每秒钟一次的频率向它所知的Master,Slave以及其他 Sentinel 实例发送一个 PING 命令
2):如果一个实例(instance)距离最后一次有效回复 PING 命令的时间超过 down-after-milliseconds 选项所指定的值, 则这个实例会被 Sentinel 标记为主观下线。
3):如果一个Master被标记为主观下线,则正在监视这个Master的所有 Sentinel 要以每秒一次的频率确认Master的确进入了主观下线状态。
4):当有足够数量的 Sentinel(大于等于配置文件指定的值)在指定的时间范围内确认Master的确进入了主观下线状态, 则Master会被标记为客观下线
5):在一般情况下, 每个 Sentinel 会以每 10 秒一次的频率向它已知的所有Master,Slave发送 INFO 命令
6):当Master被 Sentinel 标记为客观下线时,Sentinel 向下线的 Master 的所有 Slave 发送 INFO 命令的频率会从 10 秒一次改为每秒一次
7):若没有足够数量的 Sentinel 同意 Master 已经下线, Master 的客观下线状态就会被移除。
若 Master 重新向 Sentinel 的 PING 命令返回有效回复, Master 的主观下线状态就会被移除。
更多redis相关文章请关注redis数据库教程栏目。
The above is the detailed content of redis sentinel cluster graphic tutorial. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.






