Java collection class graphic tutorial

java集合类详解:(推荐:java视频教程)
1、java集合类图
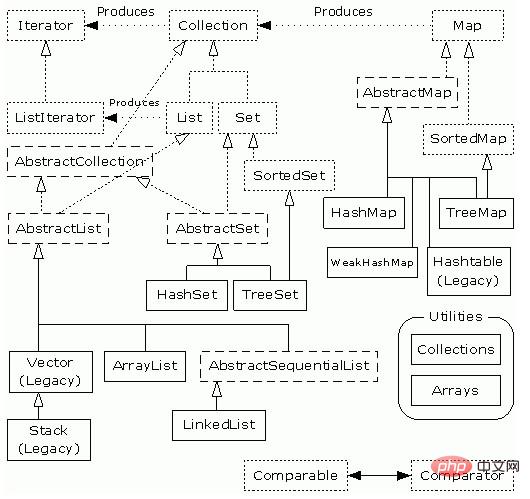
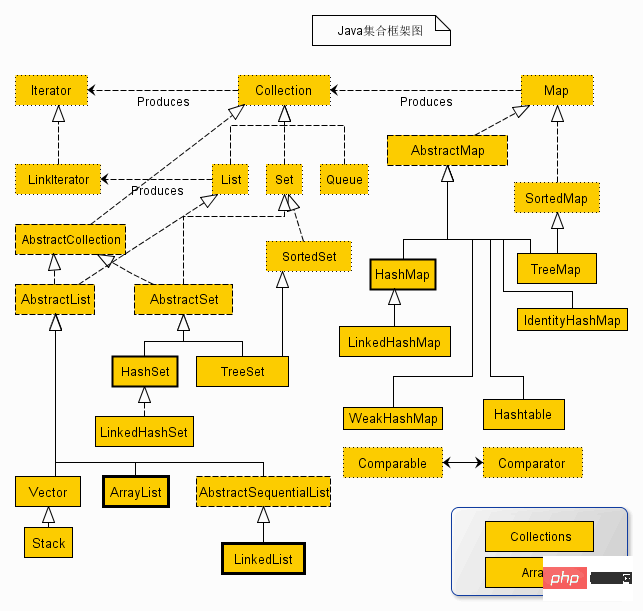
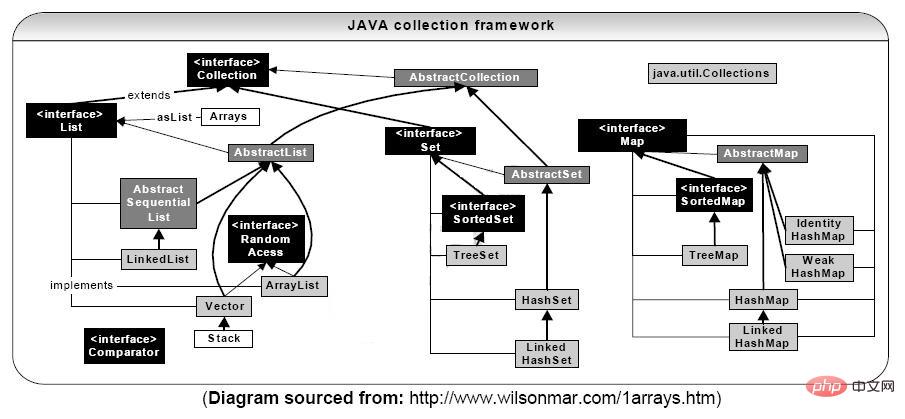
上述类图中,实线边框的是实现类,比如ArrayList,LinkedList,HashMap等,折线边框的是抽象类,比如AbstractCollection,AbstractList,AbstractMap等,而点线边框的是接口,比如Collection,Iterator,List等。
发现一个特点,上述所有的集合类,都实现了Iterator接口,这是一个用于遍历集合中元素的接口,主要包含hashNext(),next(),remove()三种方法。
它的一个子接口LinkedIterator在它的基础上又添加了三种方法,分别是add(),previous(),hasPrevious()。也就是说如果是先Iterator接口,那么在遍历集合中元素的时候,只能往后遍历,被遍历后的元素不会在遍历到,通常无序集合实现的都是这个接口。
比如HashSet,HashMap;而那些元素有序的集合,实现的一般都是LinkedIterator接口,实现这个接口的集合可以双向遍历,既可以通过next()访问下一个元素,又可以通过previous()访问前一个元素,比如ArrayList。
还有一个特点就是抽象类的使用。如果要自己实现一个集合类,去实现那些抽象的接口会非常麻烦,工作量很大。这个时候就可以使用抽象类,这些抽象类中给我们提供了许多现成的实现,我们只需要根据自己的需求重写一些方法或者添加一些方法就可以实现自己需要的集合类,工作流大大降低。
2、详解
2.1HashSet
HashSet是Set接口的一个子类,主要的特点是:里面不能存放重复元素,而且采用散列的存储方法,所以没有顺序。这里所说的没有顺序是指:元素插入的顺序与输出的顺序不一致。
代码实例:HashSetDemo
package edu.sjtu.erplab.collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<string> set=new HashSet<string>();
set.add("a");
set.add("b");
set.add("c");
set.add("c");
set.add("d");
//使用Iterator输出集合
Iterator<string> iter=set.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext())
{
System.out.print(iter.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用For Each输出结合
for(String e:set)
{
System.out.print(e+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用toString输出集合
System.out.println(set);
}
}</string></string></string>代码实例:SetTest
package edu.sjtu.erplab.collection;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class SetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
Set<string> words=new HashSet<string>();
//通过输入流代开文献
//方法1:这个方法不需要抛出异常
InputStream inStream=SetTest.class.getResourceAsStream("Alice.txt");
//方法2:这个方法需要抛出异常
//InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\Documents\\workspace\\JAVAStudy\\src\\edu\\sjtu\\erplab\\collection\\Alice.txt");
Scanner in=new Scanner(inStream);
while(in.hasNext())
{
words.add(in.next());
}
Iterator<string> iter=words.iterator();
for(int i=0;i<p>2.2ArrayList</p>
<p>ArrayList是List的子类,它和HashSet想法,允许存放重复元素,因此有序。集合中元素被访问的顺序取决于集合的类型。如果对ArrayList进行访问,迭代器将从索引0开始,每迭代一次,索引值加1。然而,如果访问HashSet中的元素,每个元素将会按照某种随机的次序出现。虽然可以确定在迭代过程中能够遍历到集合中的所有元素,但却无法预知元素被访问的次序。</p>
<p>代码实例:ArrayListDemo</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">package edu.sjtu.erplab.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<string> arrList=new ArrayList<string>();
arrList.add("a");
arrList.add("b");
arrList.add("c");
arrList.add("c");
arrList.add("d");
//使用Iterator输出集合
Iterator<string> iter=arrList.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext())
{
System.out.print(iter.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用For Each输出结合
for(String e:arrList)
{
System.out.print(e+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用toString输出集合
System.out.println(arrList);
}
}</string></string></string>2.3 ListIterator
ListIterator是一种可以在任何位置进行高效地插入和删除操作的有序序列。
代码实例:LinkedListTest
package edu.sjtu.erplab.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class LinkedListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<string> a=new ArrayList<string>();
a.add("a");
a.add("b");
a.add("c");
System.out.println(a);
List<string> b=new ArrayList<string>();
b.add("d");
b.add("e");
b.add("f");
b.add("g");
System.out.println(b);
//ListIterator在Iterator基础上添加了add(),previous()和hasPrevious()方法
ListIterator<string> aIter=a.listIterator();
//普通的Iterator只有三个方法,hasNext(),next()和remove()
Iterator<string> bIter=b.iterator();
//b归并入a当中,间隔交叉得插入b中的元素
while(bIter.hasNext())
{
if(aIter.hasNext())
aIter.next();
aIter.add(bIter.next());
}
System.out.println(a);
//在b中每隔两个元素删除一个
bIter=b.iterator();
while(bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next();
if(bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next();//remove跟next是成对出现的,remove总是删除前序
bIter.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(b);
//删除a中所有的b中的元素
a.removeAll(b);
System.out.println(a);
}
}</string></string></string></string></string></string>2.4HashMap
HashMap的存取实现
//存储时: int hash = key.hashCode();// 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值 int index = hash % Entry[].length; Entry[index] = value; //取值时: int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = hash % Entry[].length; return Entry[index];
2.5WeekHashMapDemo
package edu.sjtu.erplab.collection;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
public class WeekHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 100;
if (args.length > 0) {
size = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
}
Key[] keys = new Key[size];
WeakHashMap<key> whm = new WeakHashMap<key>();
for (int i = 0; i <p>比较</p>
<p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/image/490/242/862/1574755726970514.jpg" class="lazy" title="1574755726970514.jpg" alt="Java collection class graphic tutorial"></p>
<p>更多java相关文章请关注<a href="https://www.php.cn/java/base/" target="_blank">Java基础教程</a>栏目。</p></key></key>The above is the detailed content of Java collection class graphic tutorial. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo




